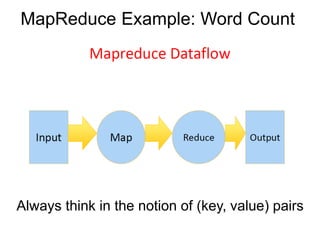
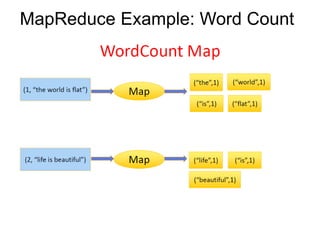
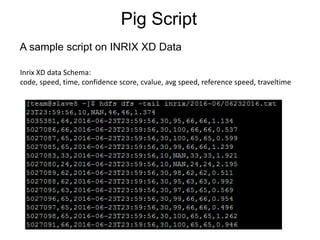
This document provides an overview of Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS), MapReduce, and Apache Pig. It describes how HDFS stores and replicates large files across clusters of machines for high throughput access. MapReduce is introduced as a programming model for processing large datasets in parallel. Word count is used as an example MapReduce job. Apache Pig is presented as a framework for analyzing large datasets with a higher level of abstraction than MapReduce. Finally, common HDFS commands and a sample Pig script are shown.