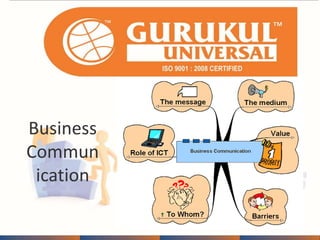
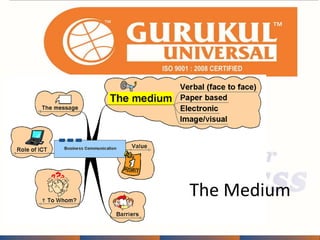
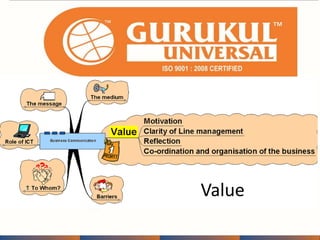
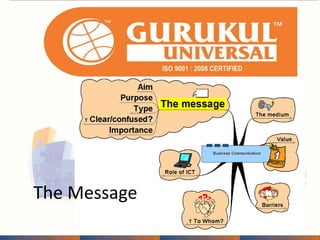
This document provides information about an annual meeting being held by Gurukul Universal, an ISO-certified education company. Gurukul aims to make youth employable and provide quality, affordable education. There is high demand for administrative assistants in India. Gurukul offers job-oriented courses that can allow students to become self-employed or generate jobs for others. The document discusses Gurukul's franchise opportunities, course offerings, quality standards and support provided to franchises.