The key points are:
1. A DMS will allow electronic storage, retrieval and sharing of documents like vehicle registration forms to improve efficiency.
2. It will guarantee recovery of documents if disaster strikes, minimize costs, create a paperless environment and improve security and service delivery.
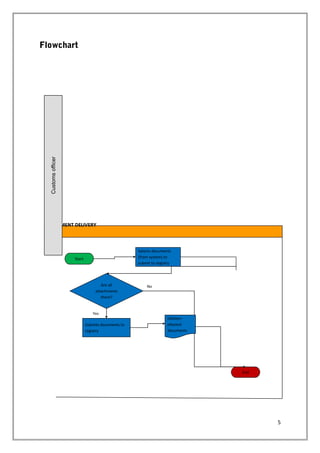
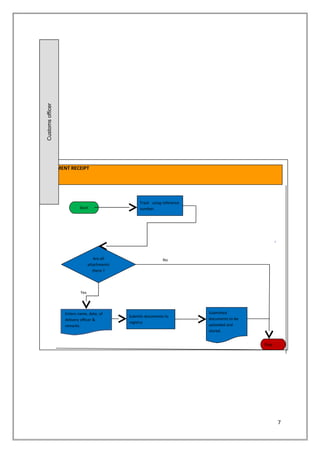
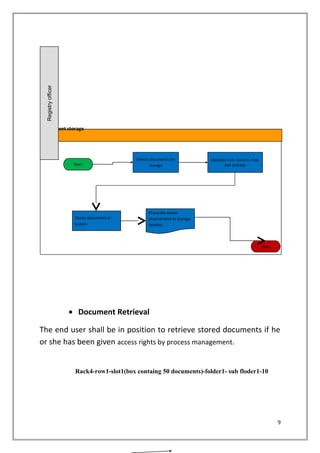
3. The DMS will cover document delivery from customs officers to the registry, document receipt and verification by registry staff, electronic storage of documents and assignment to locations, and retrieval of documents by authorized users.