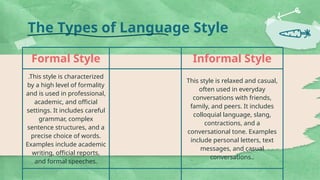
The document outlines the concepts of language style and register in sociolinguistics, defining language style as an individual's consistent tendencies or preferences in communication, while describing types of styles such as formal, informal, colloquial, slang, jargon, vernacular, pidgin, and creole. It further elaborates on language register, emphasizing variations in language use based on context, audience, purpose, and social setting, detailing five main types: frozen, formal, consultative, casual, and intimate. The conclusion highlights the distinction between style and register and their relevance in communication.