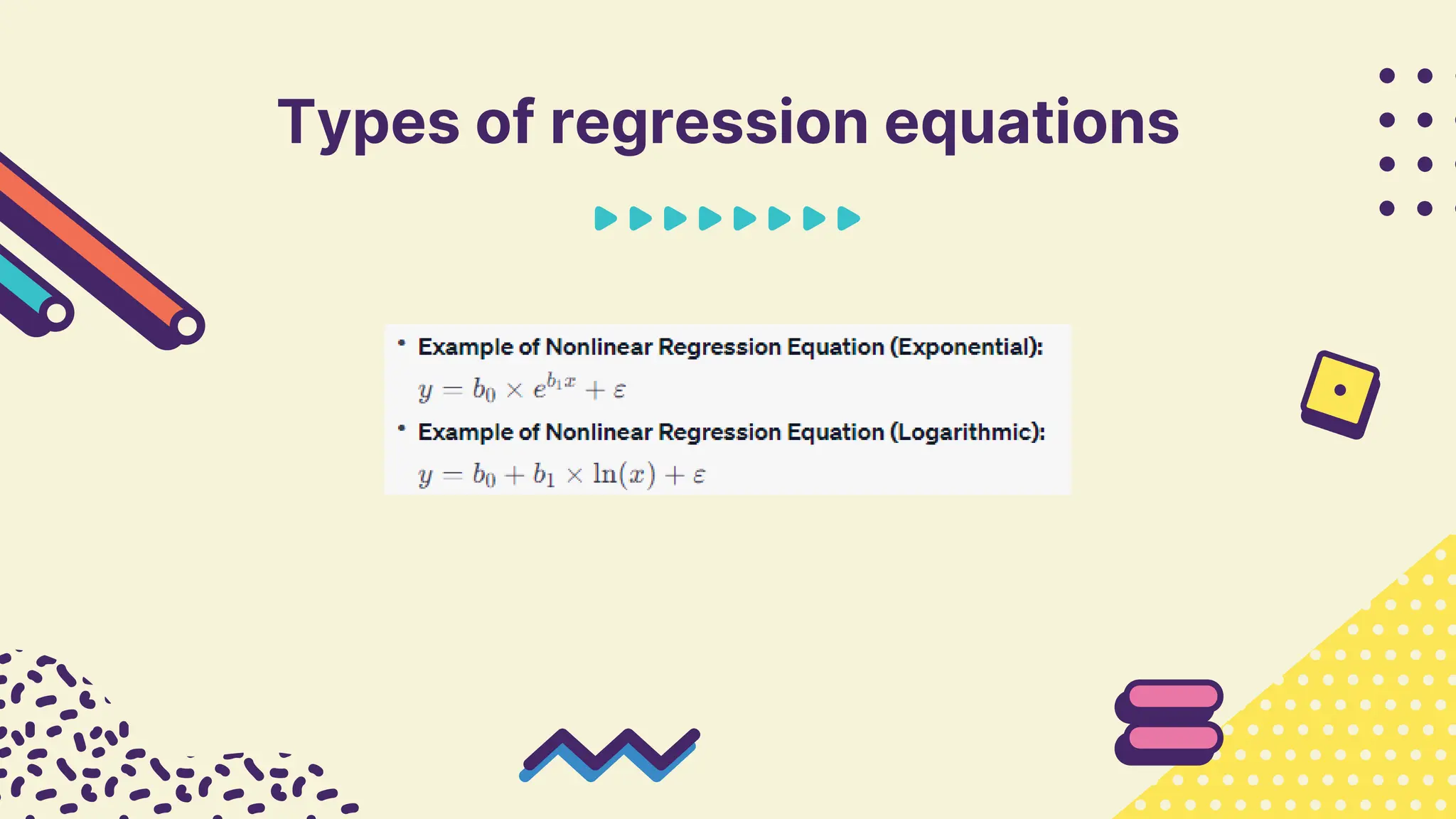
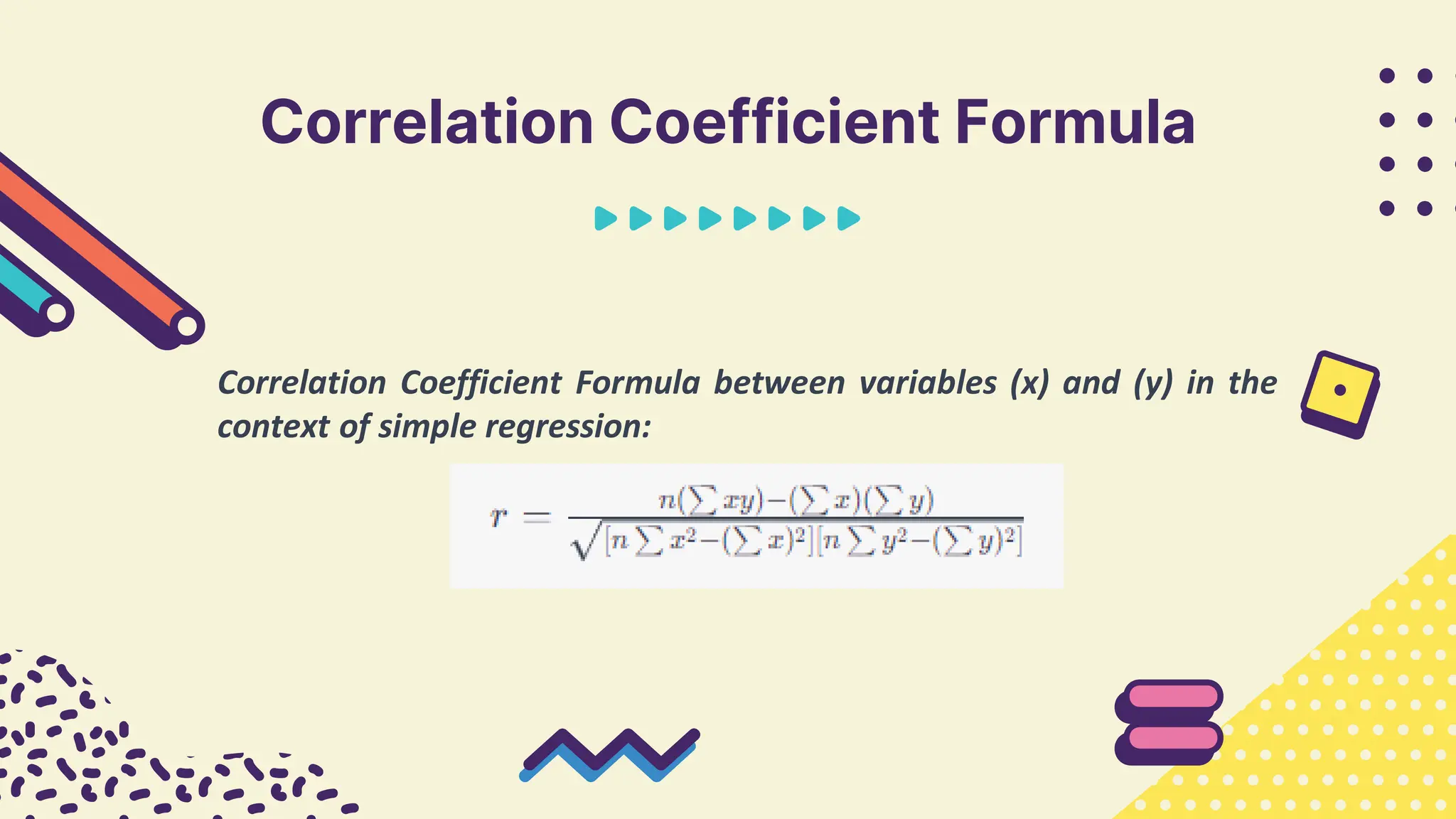
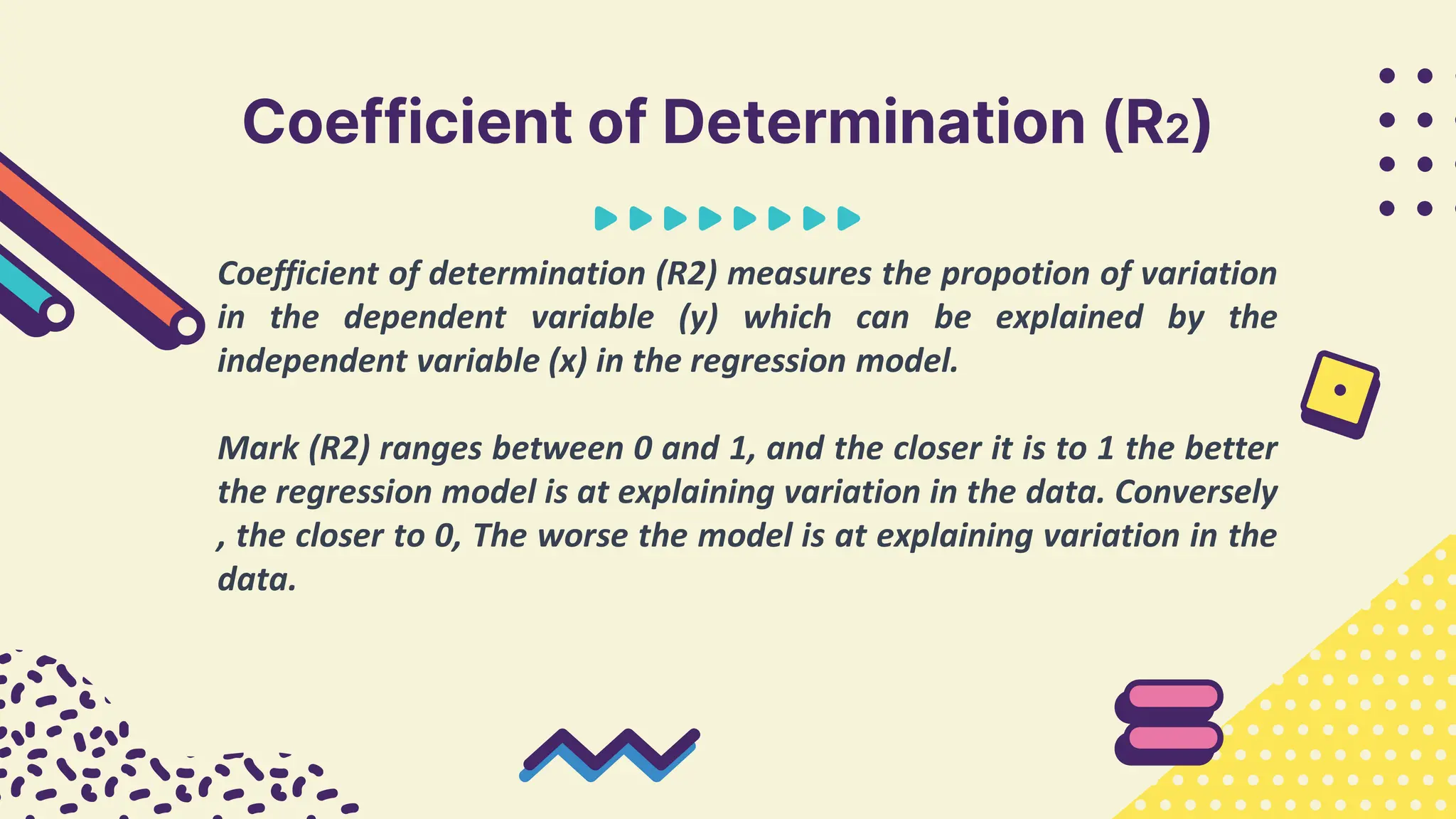
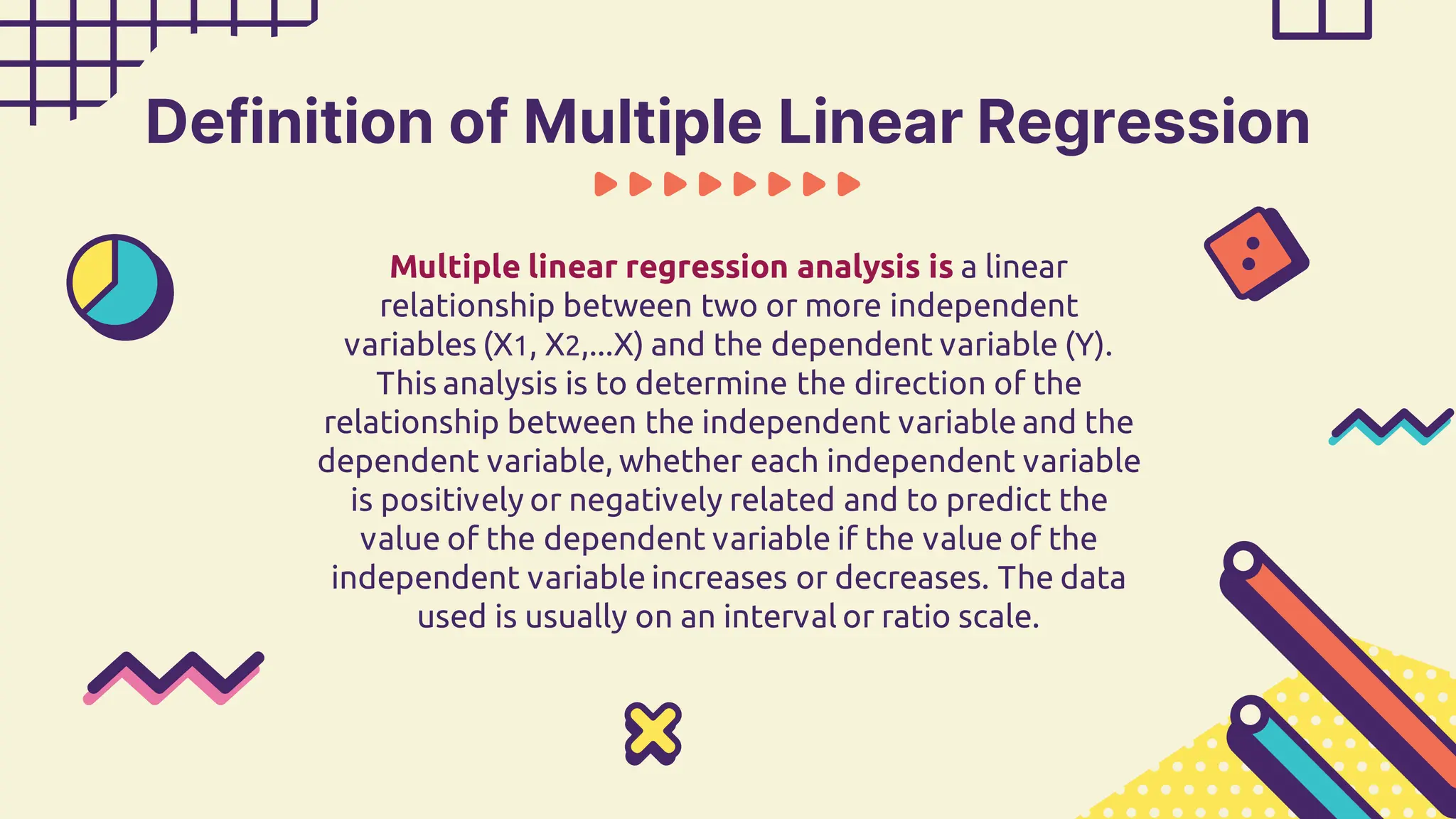
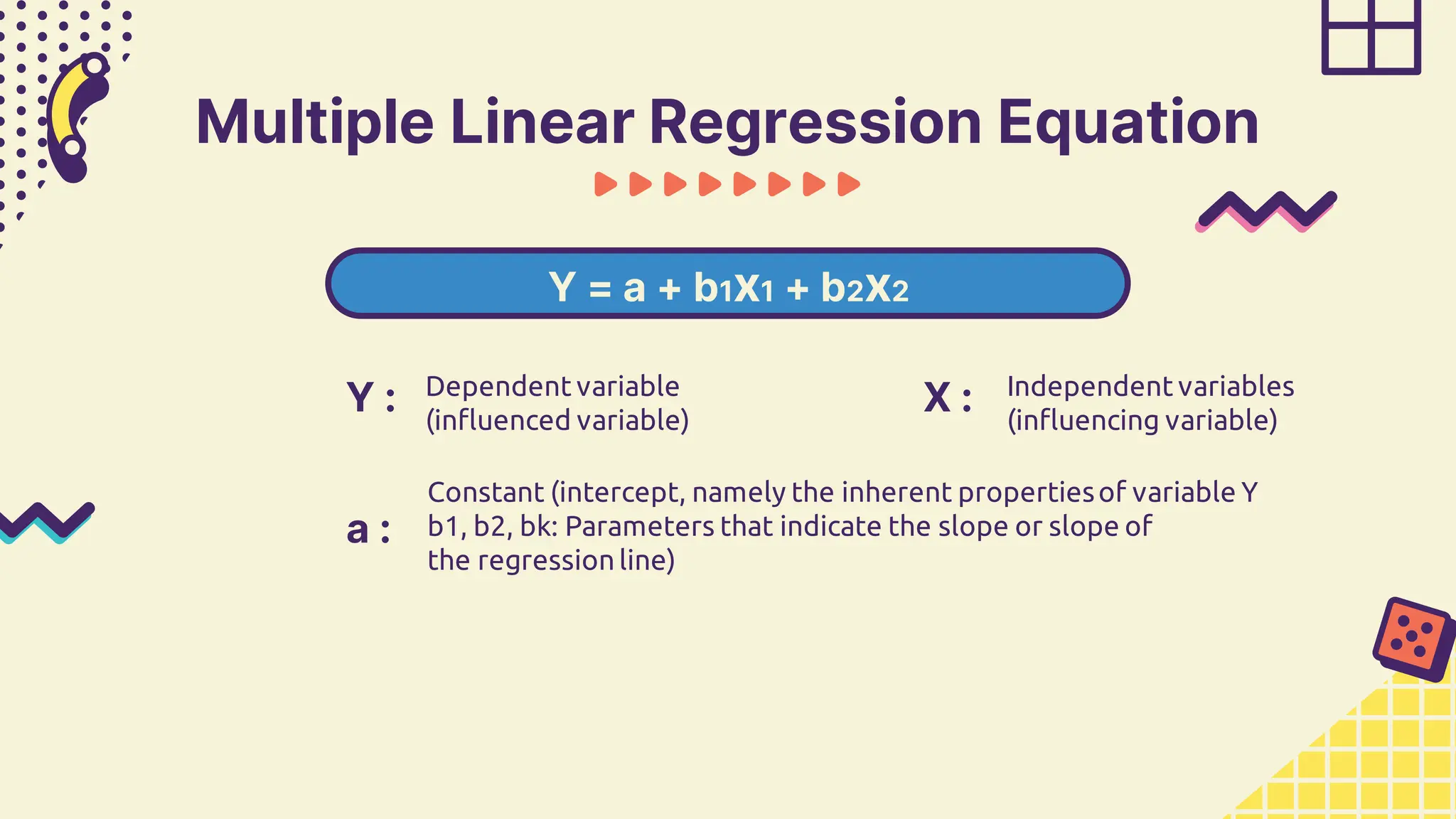
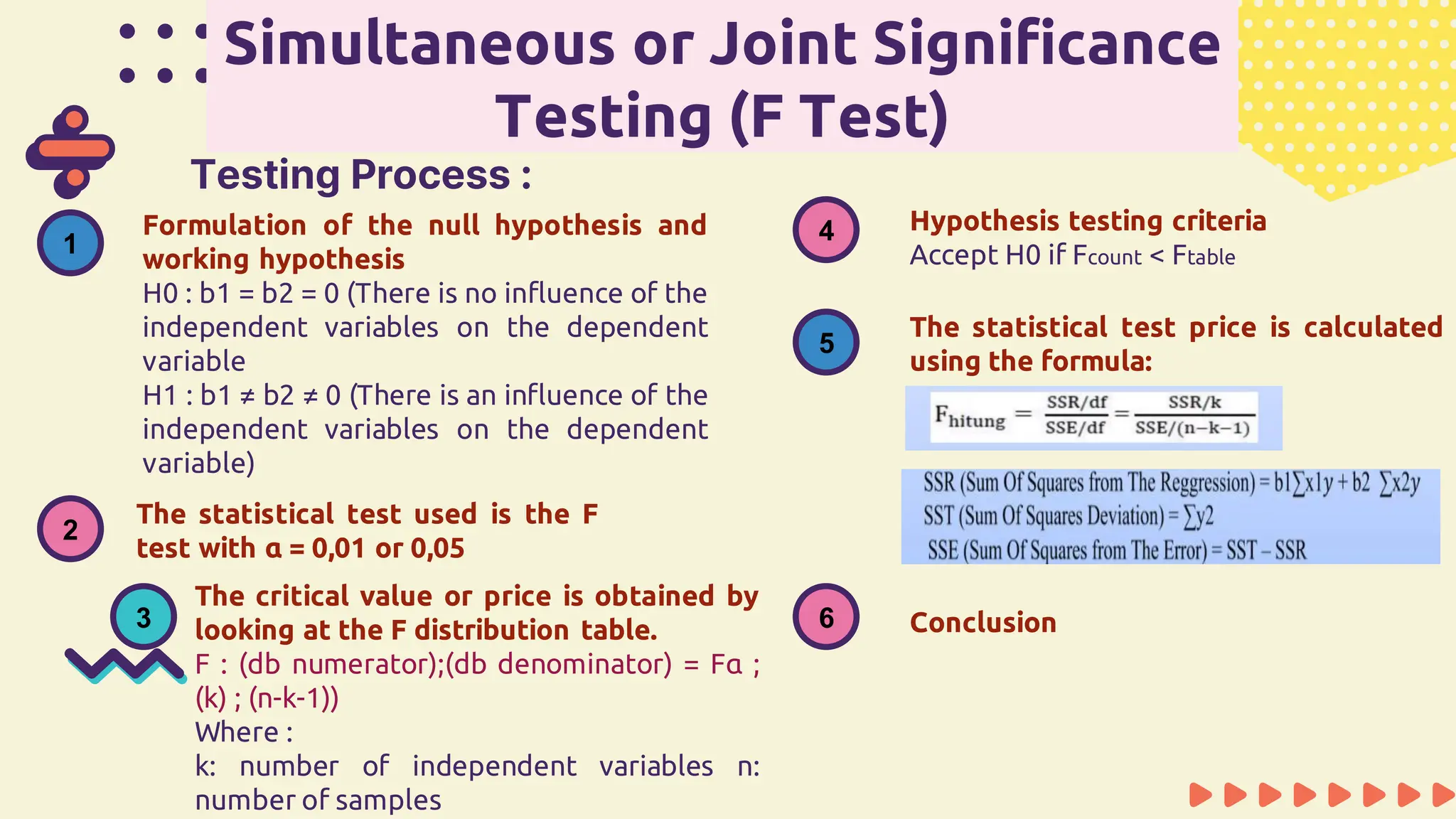
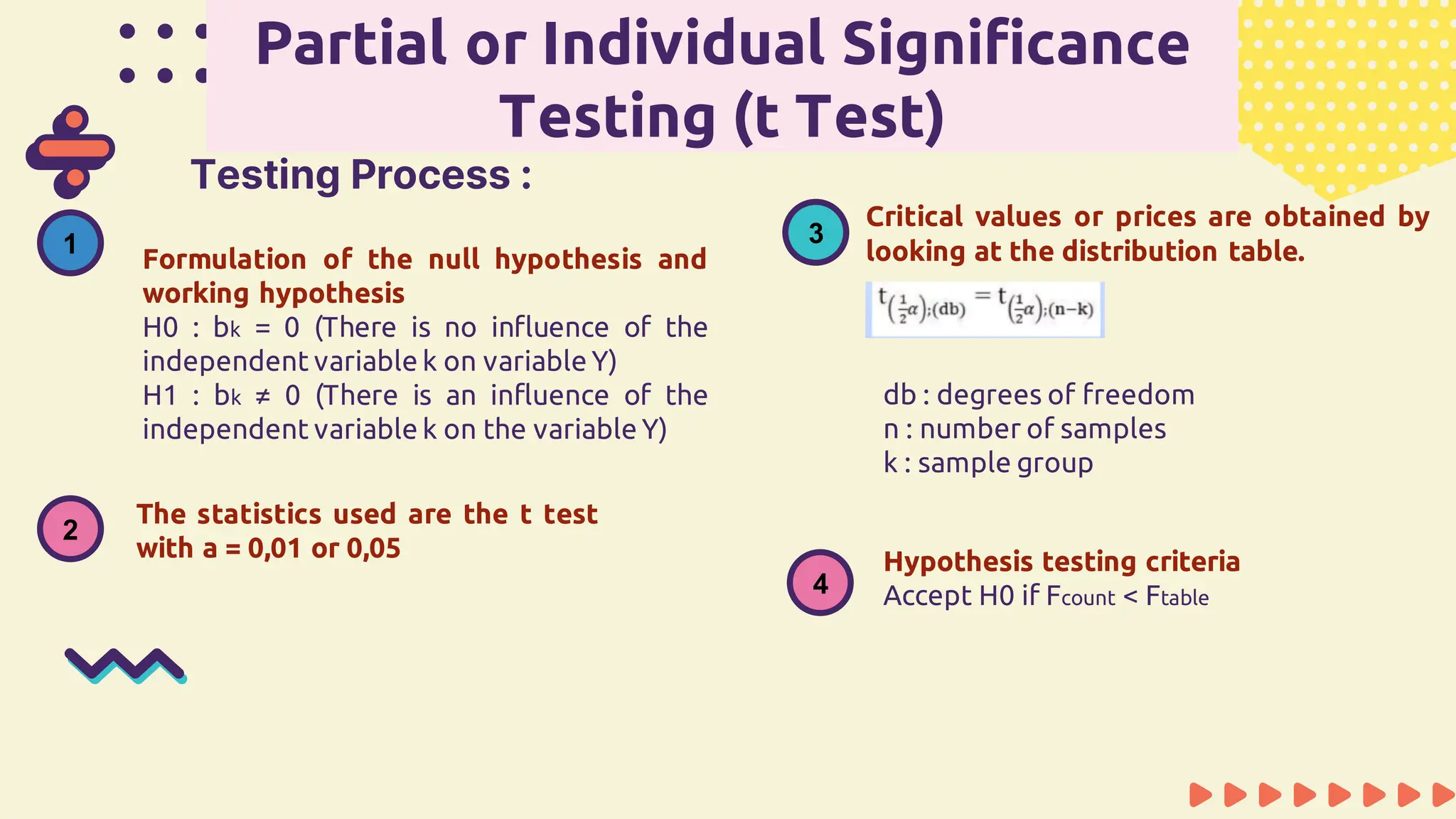
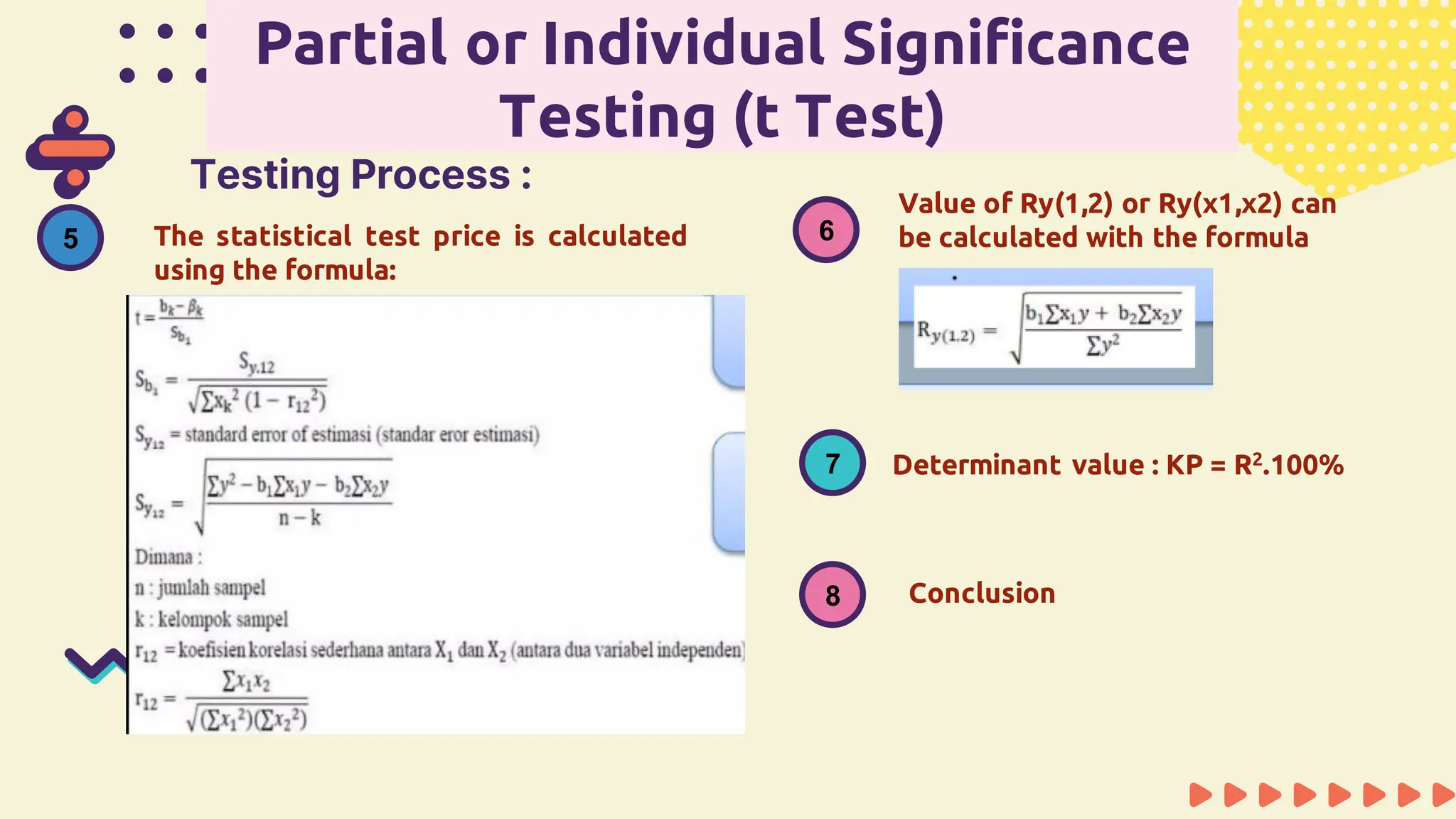
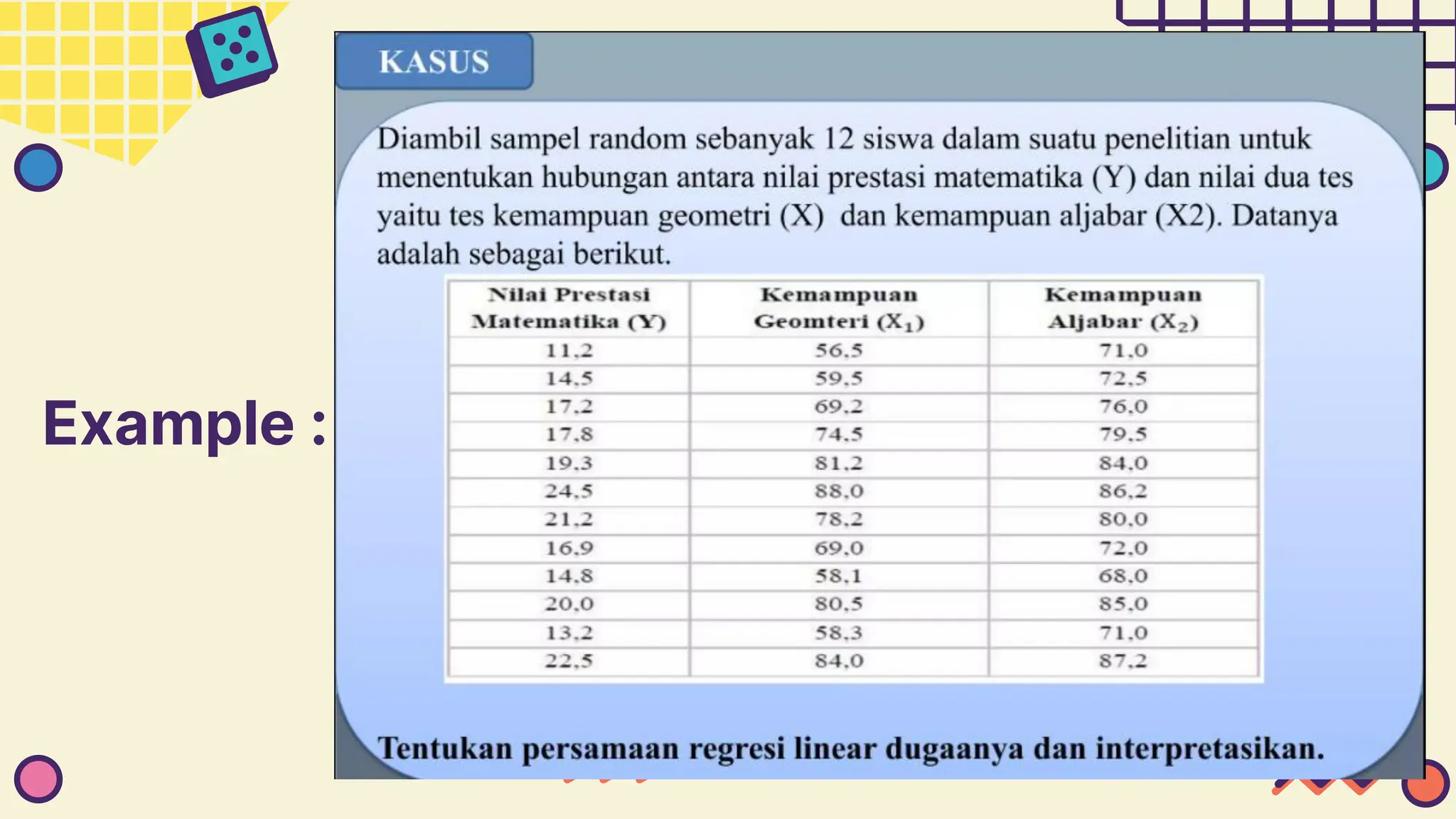
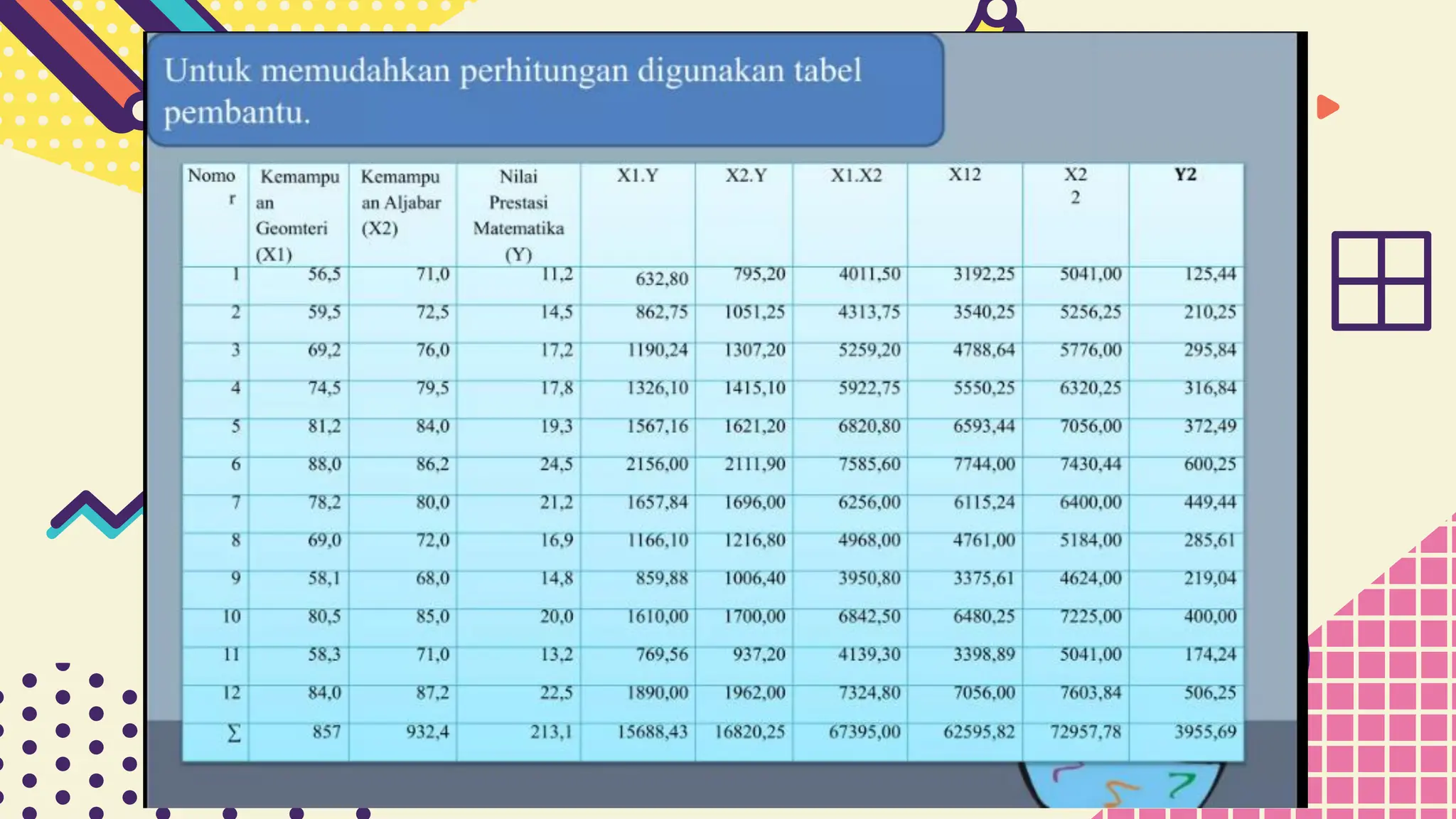
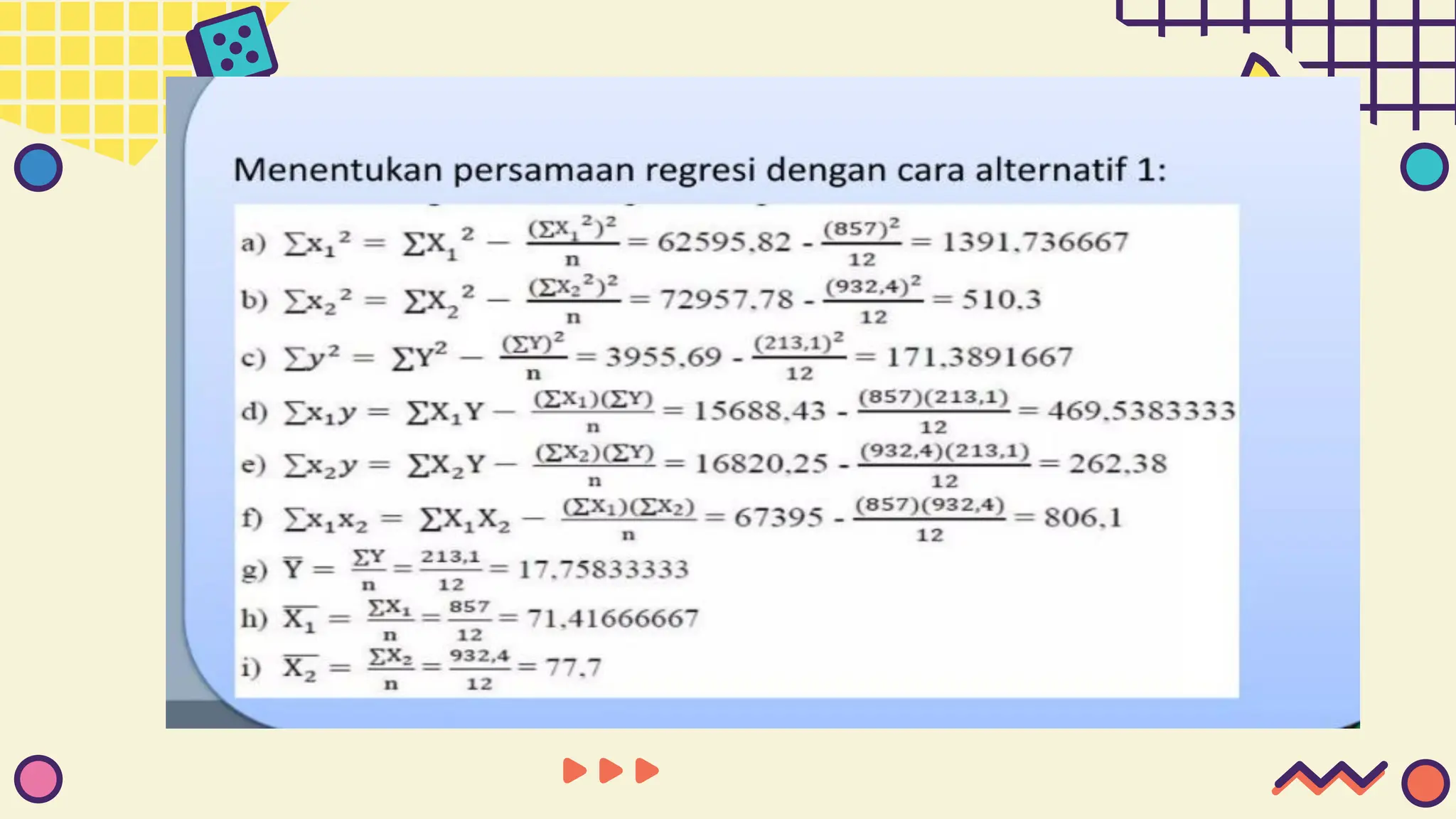
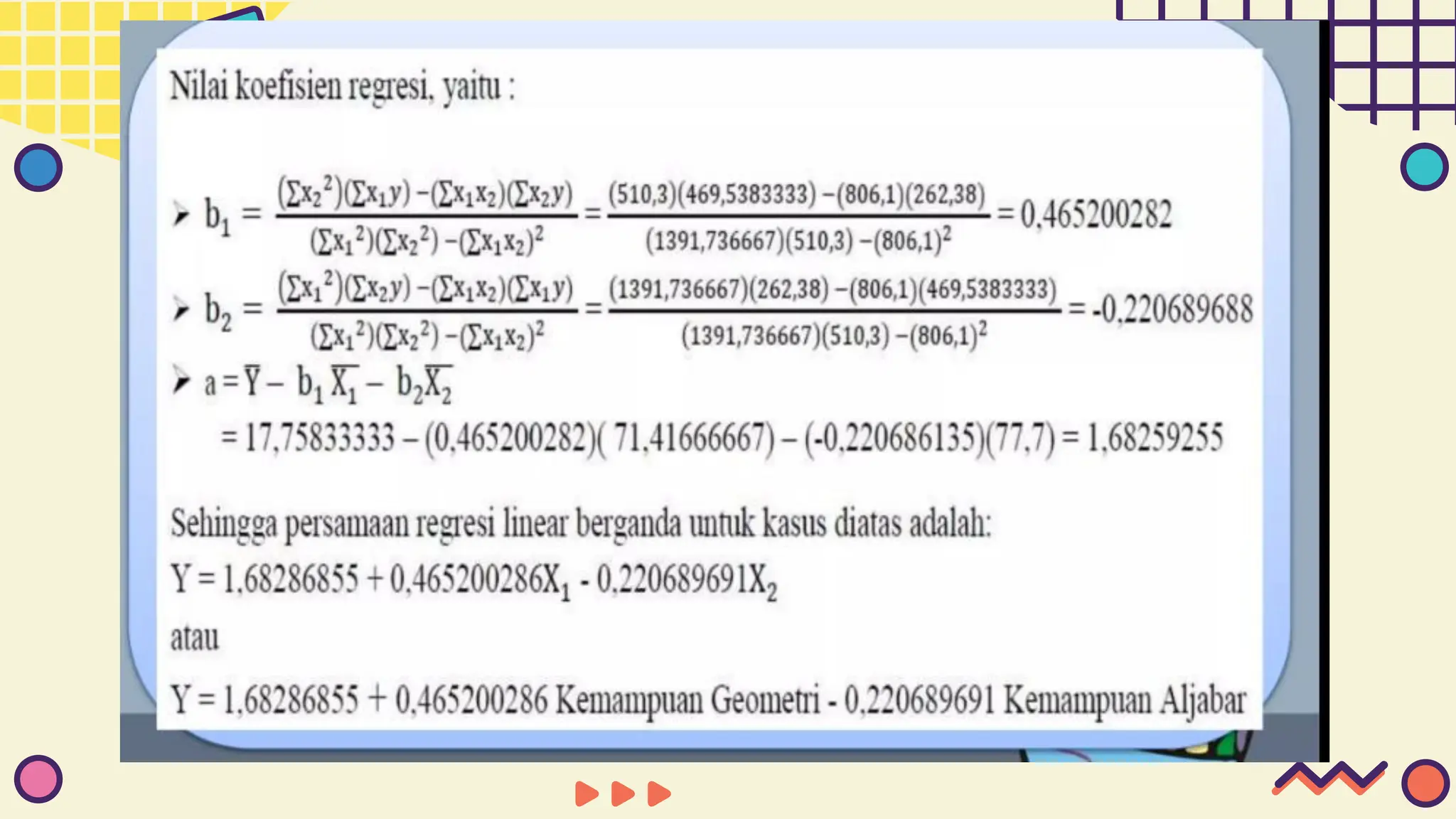
This document provides information about simple and multiple linear regression analysis. It defines simple regression as exploring the relationship between two variables, a dependent and independent variable. Multiple linear regression analyzes the relationship between one dependent variable and two or more independent variables. The document discusses regression equations, correlation coefficients, coefficients of determination, and how to test the significance of regression models using F tests and t tests.