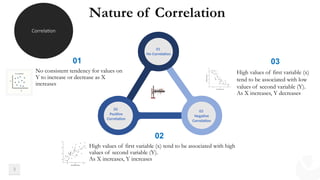
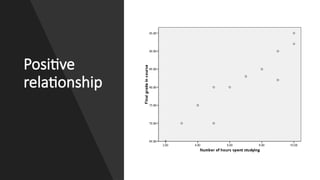
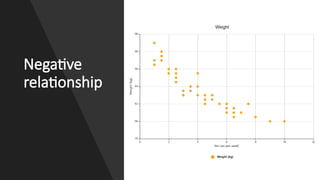
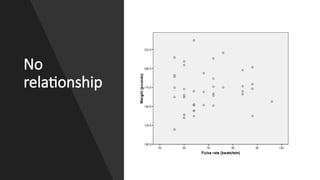
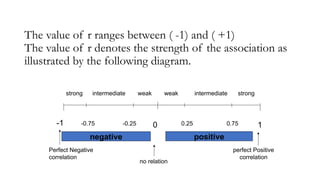
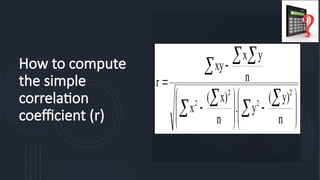
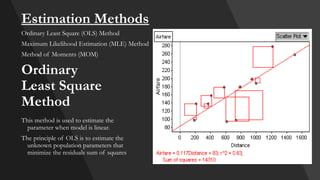
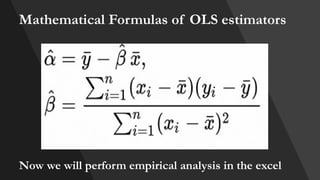
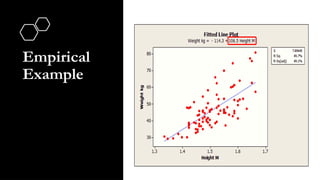
The document explains correlation and regression, highlighting correlation as a method to determine the linear relationship between two variables without inferring causation. It discusses the correlation coefficient, ranging from -1 to +1, which indicates the strength and nature of the relationship. Additionally, regression is introduced as a method to understand how changes in one variable affect another, distinguishing between independent and dependent variables.