The document introduces relational algebra and describes selection and projection operations. It defines relational algebra as a procedural query language that takes relations as input and output. Selection and projection are the fundamental operations that allow querying a relational database. Selection filters tuples based on a predicate, while projection displays only specified attributes rather than the full tuple. Examples demonstrate how to use selection and projection on sample relations.






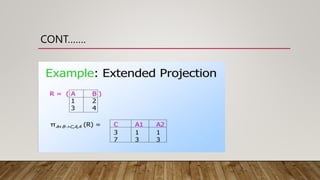
![CONT……..
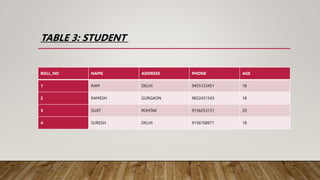
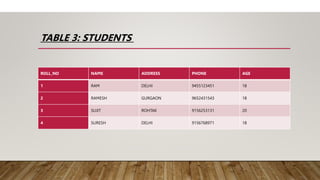
• σ (AGE>18)(STUDENTS)
• SELECT operator does not show any result, the projection operator must
be called before the selection operator to generate or project the result. So,
the correct syntax to generate the result is: ∏(σ (AGE>18)(STUDENT))]
• RESULT:
ROLL_NO NAME ADDRESS PHONE AGE
3 SUJIT ROHTAK 9156253131 20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/group4relationalalgebra-230402155006-8b21a4b0/85/GROUP-4-RELATIONAL-ALGEBRA-pptx-8-320.jpg)