Embed presentation
Downloaded 65 times
















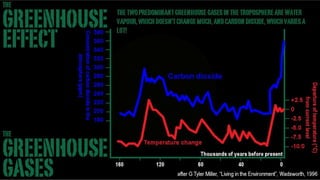
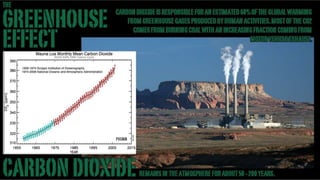
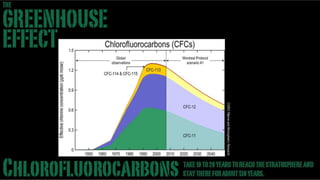


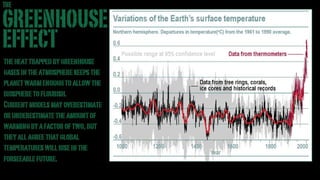


A stand-up version of a presentation on the "Greenhouse Effect" for use in the classroom or with small seminar groups. There are several advantages to doing this in widescreen, in addition to the increased visual impact. One advantage is showing more image area in rooms with low ceiling heights. With the new brighter generation of projectors, the light intensity (measure in lumens) is still quite good even with the longer throw distance this format requires. This is coupled with an increasing availability of projection screens in the 16:9 ratio. There is more room for graphics and photos in the layout options, making the presentation more visually stimulating. Finally, there's a viewer perception that the 16:9 format represents higher production values and a more upscale presentation.






















