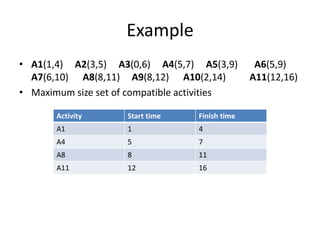
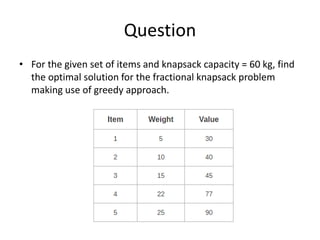
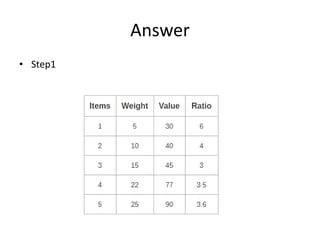
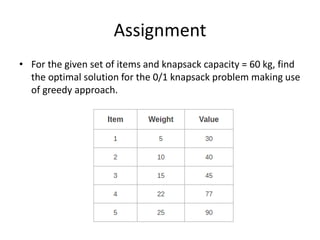
The document discusses various greedy algorithms and optimization problems. It explains that greedy algorithms make locally optimal choices at each step to arrive at a global solution. An example of an activity selection problem is provided where activities are scheduled greedily based on their finish times. The fractional knapsack problem is also summarized, where the greedy approach is to fill items in order of their value to weight ratio until the knapsack is full.