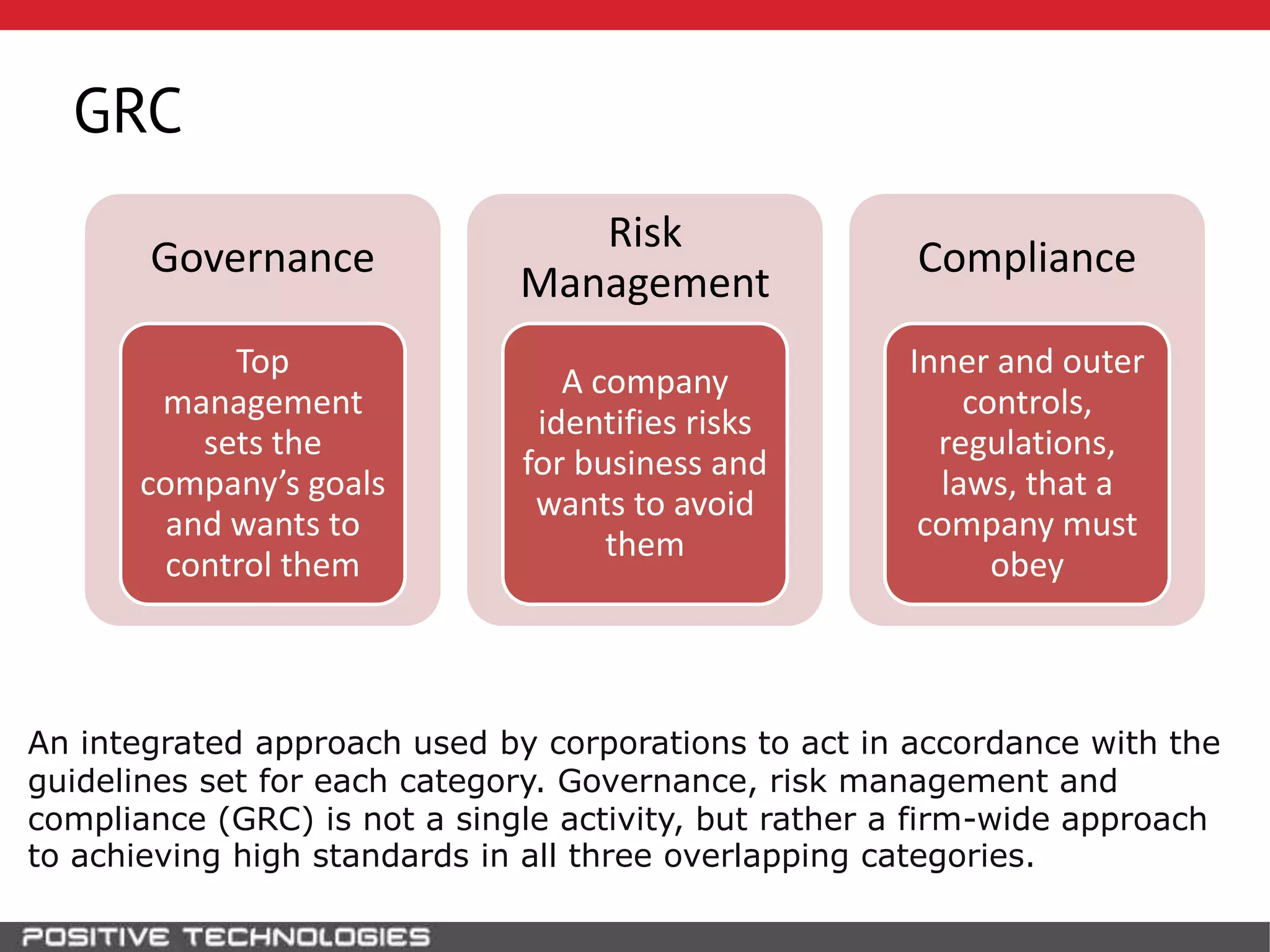
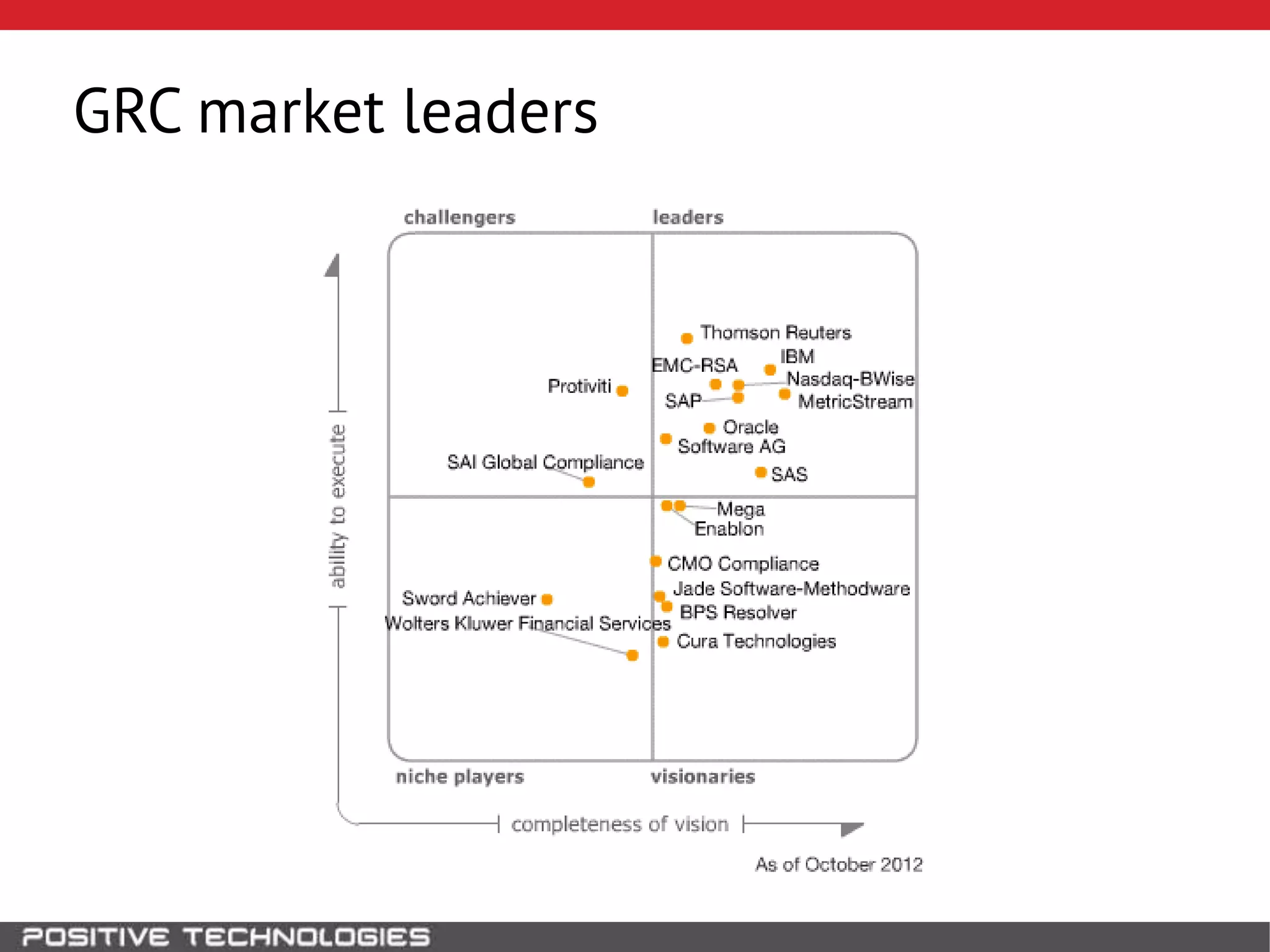
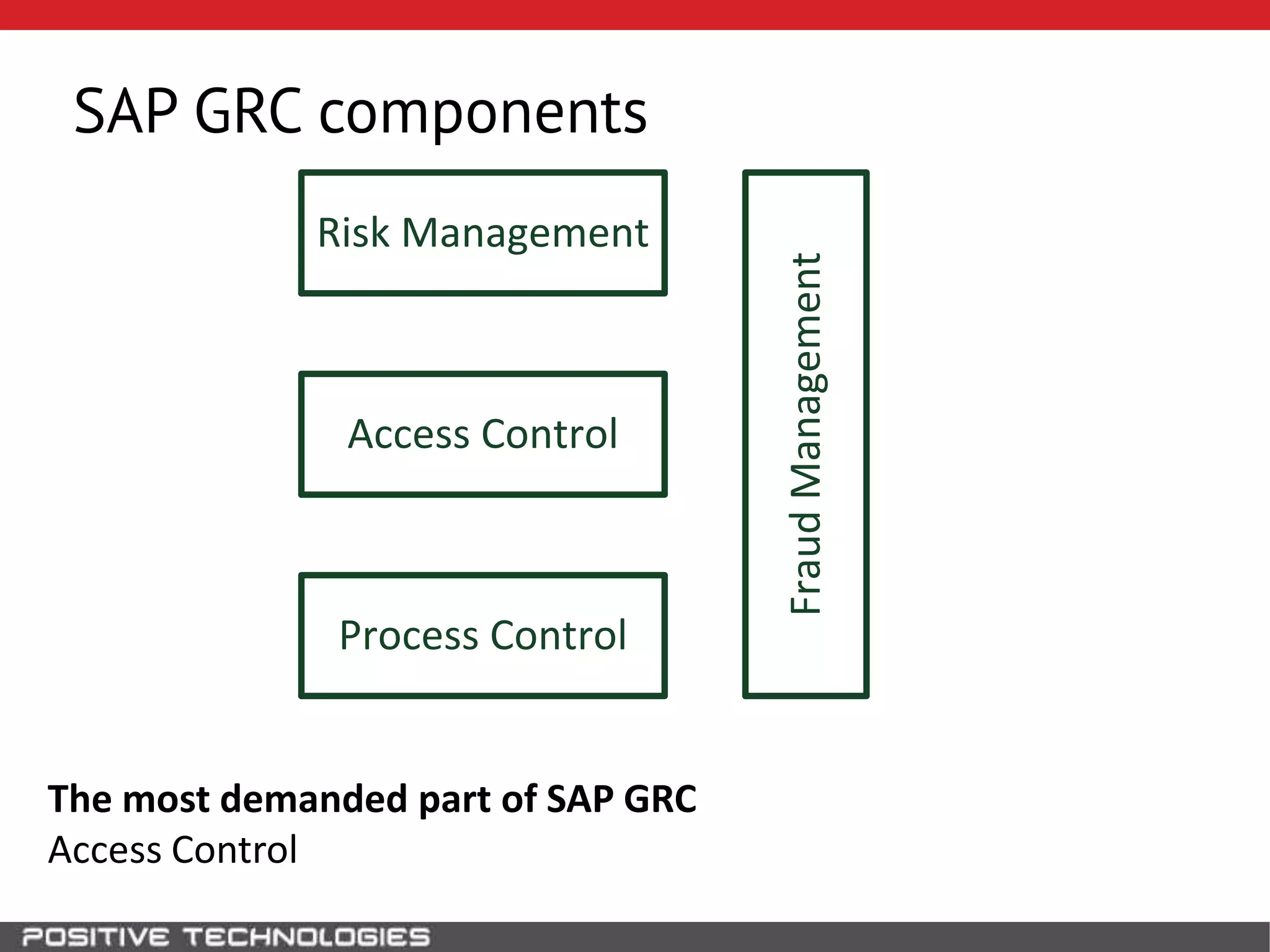
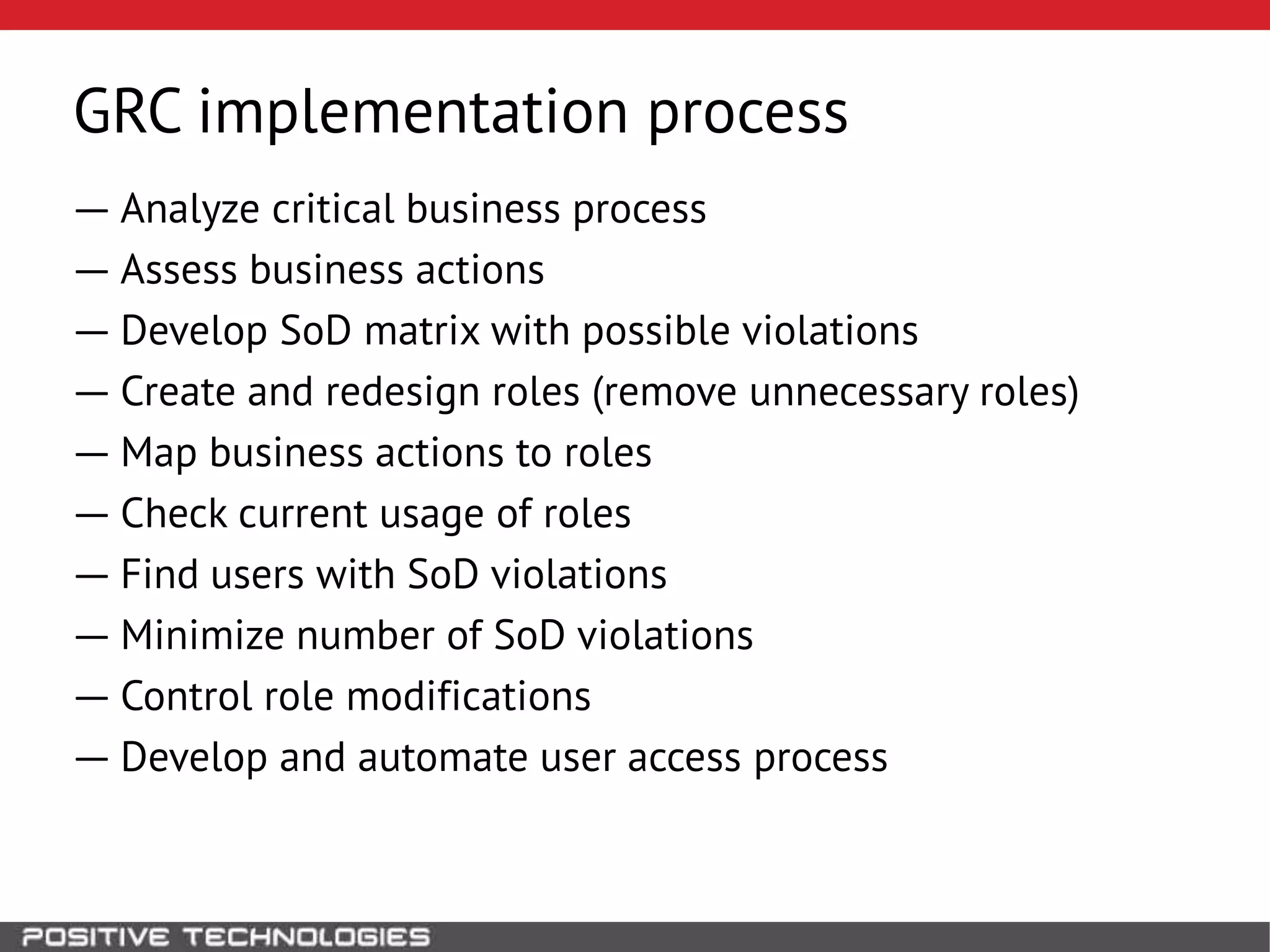
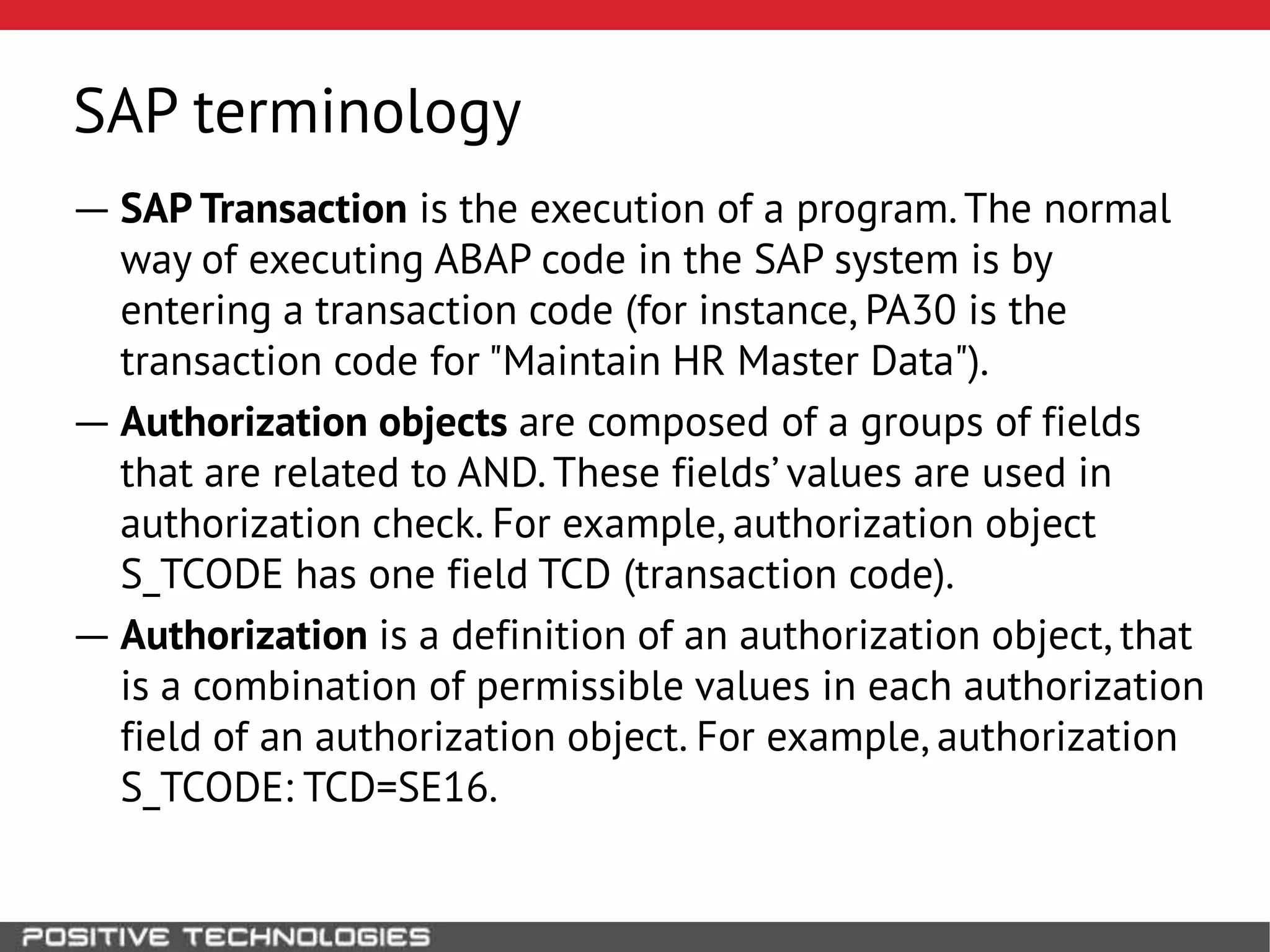
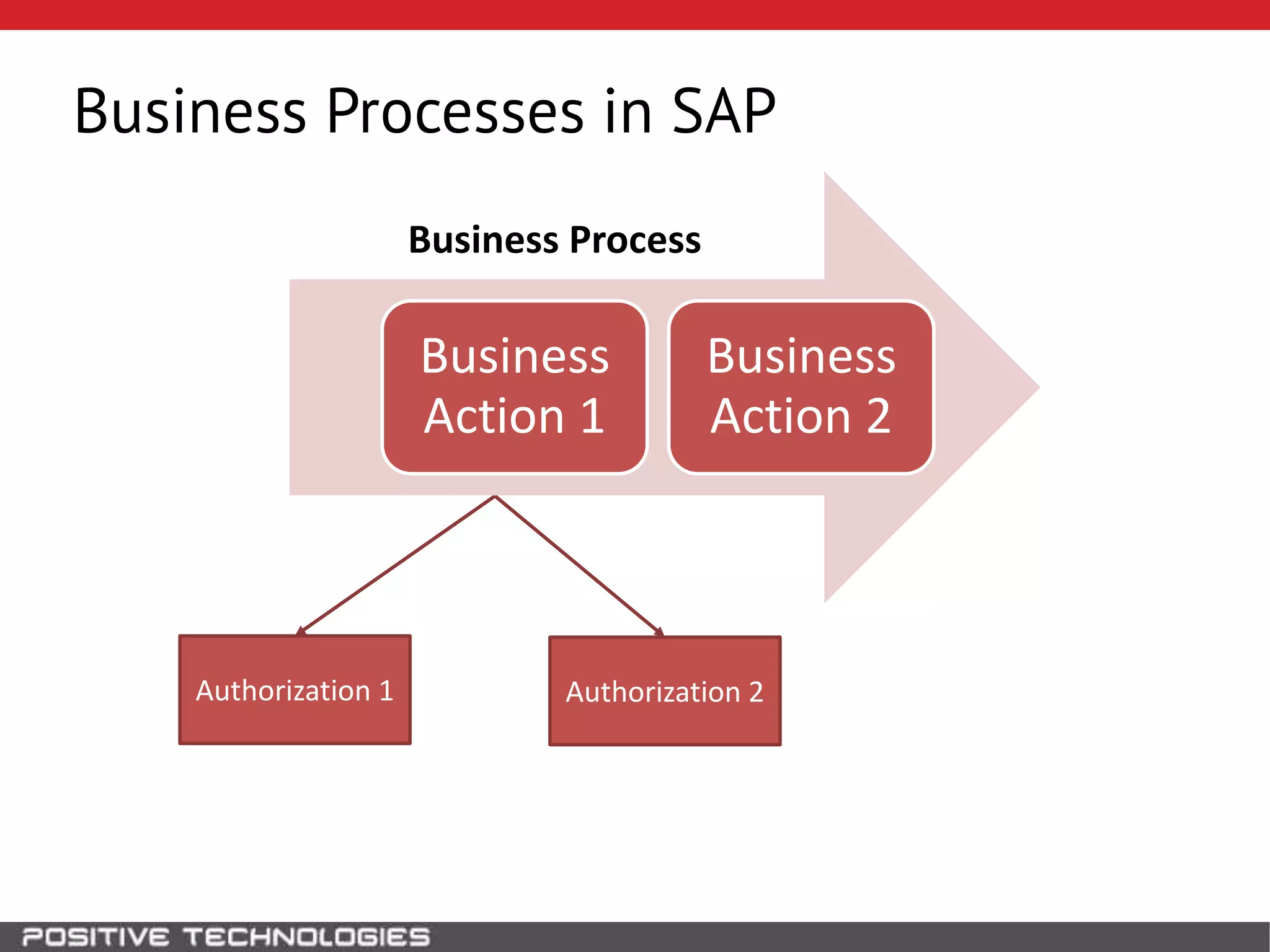
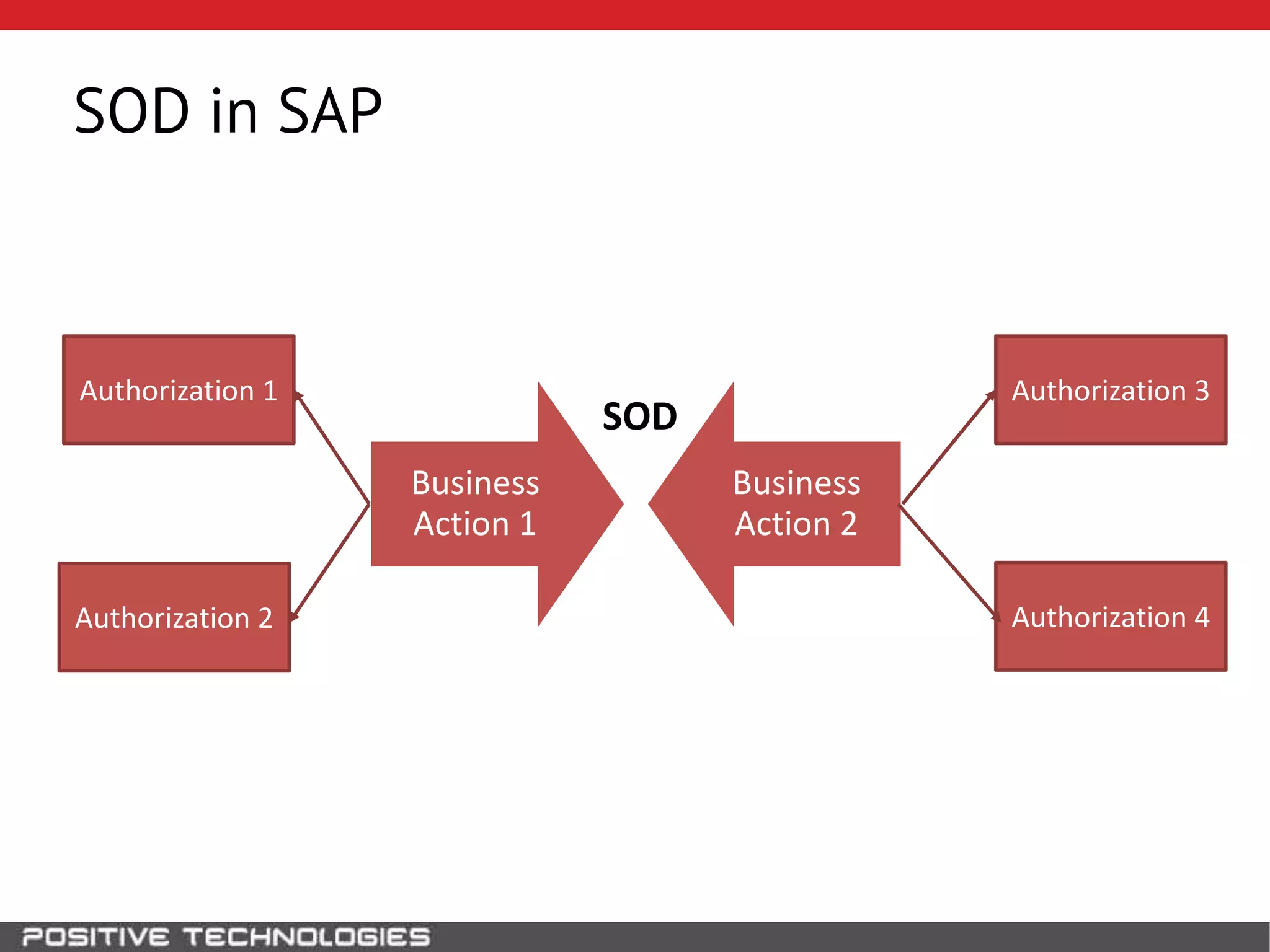
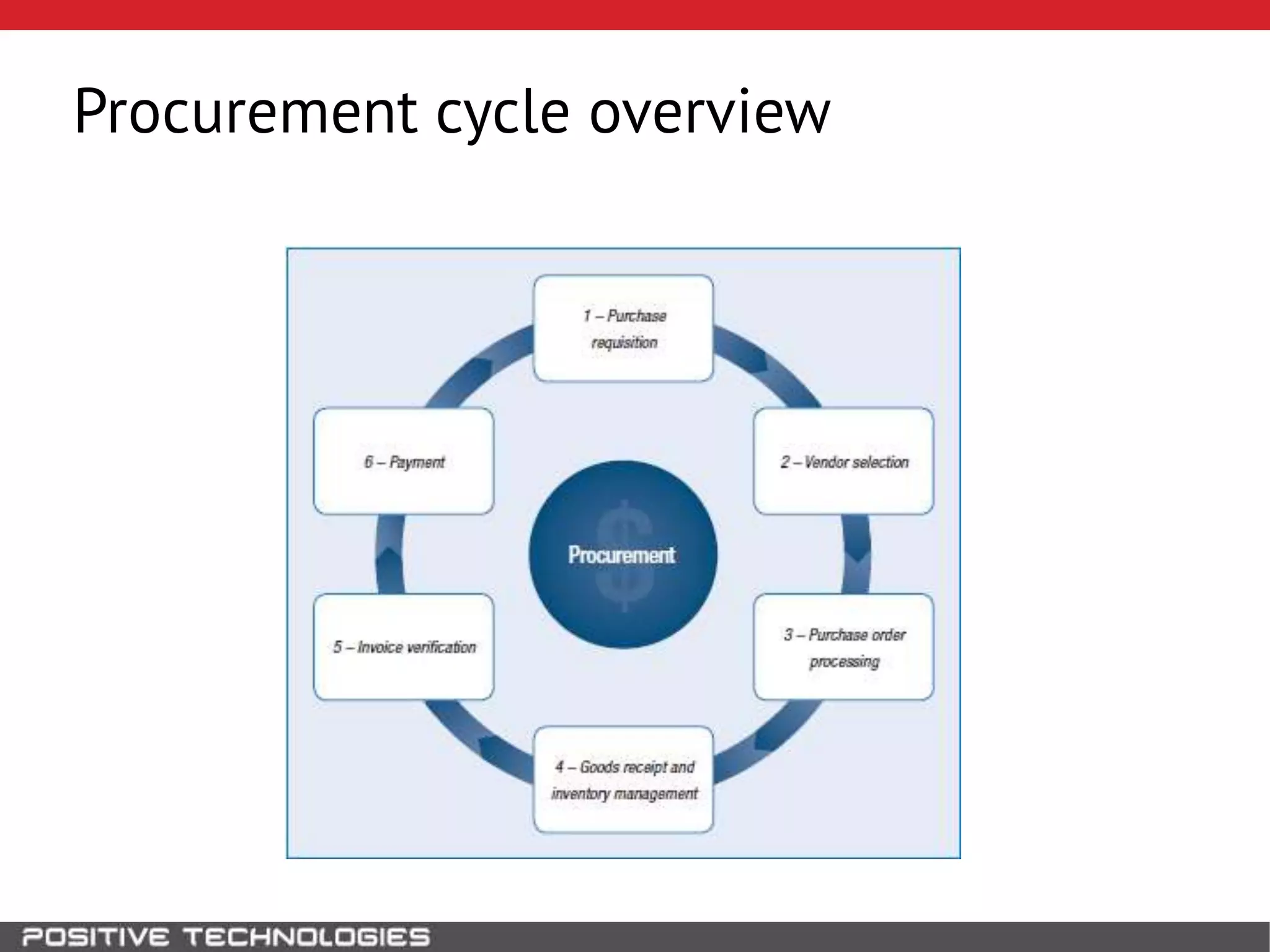
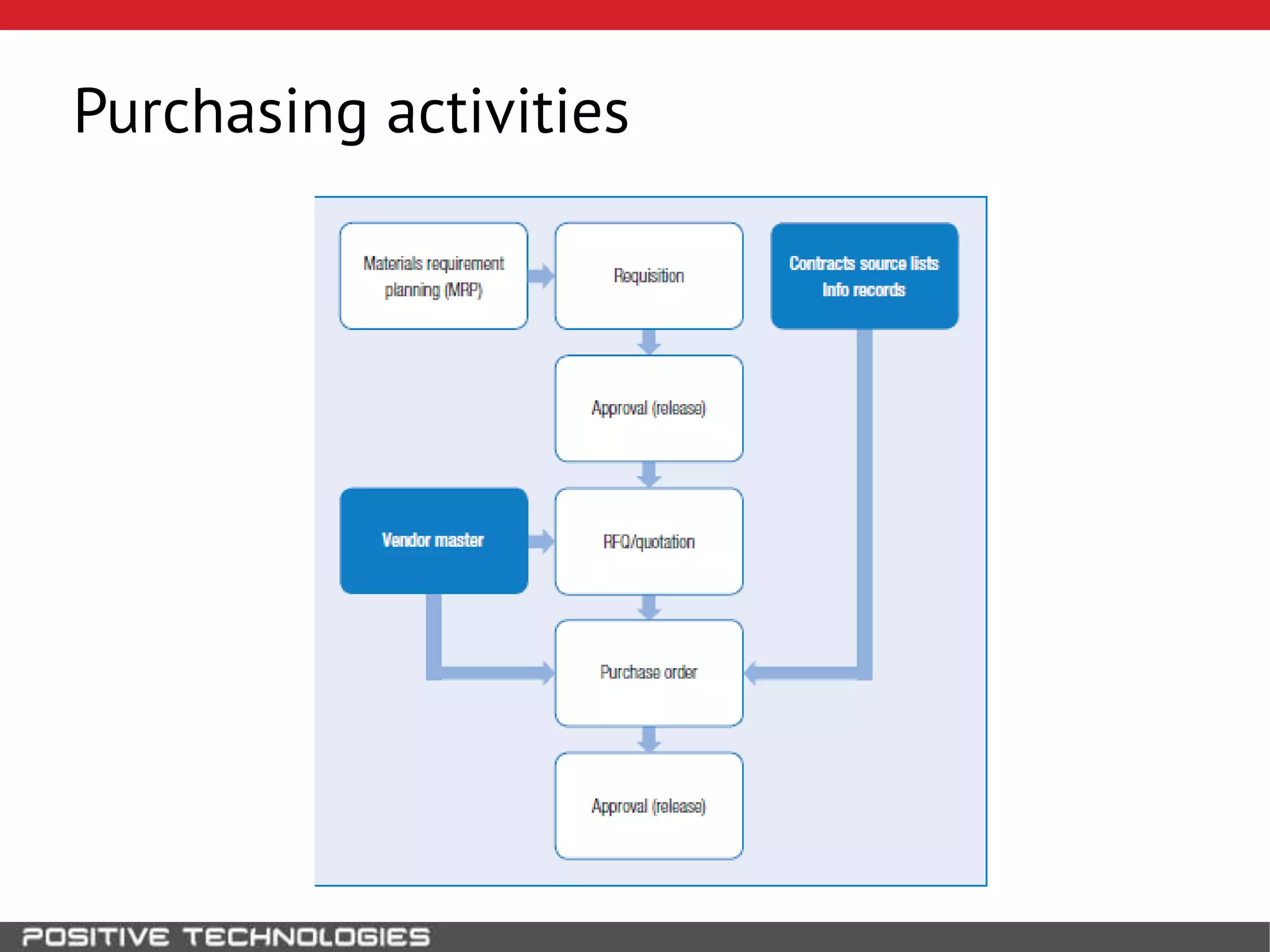
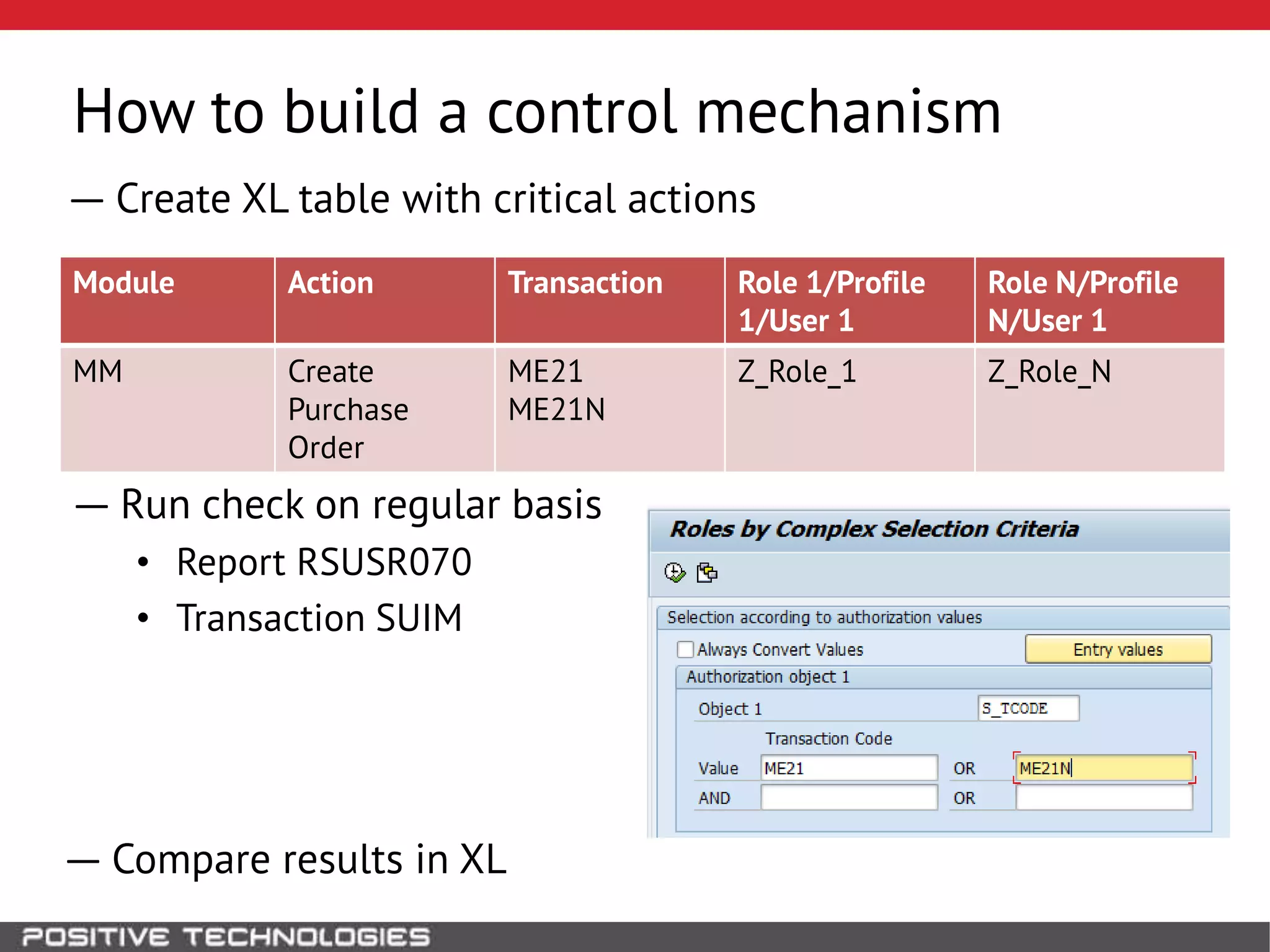
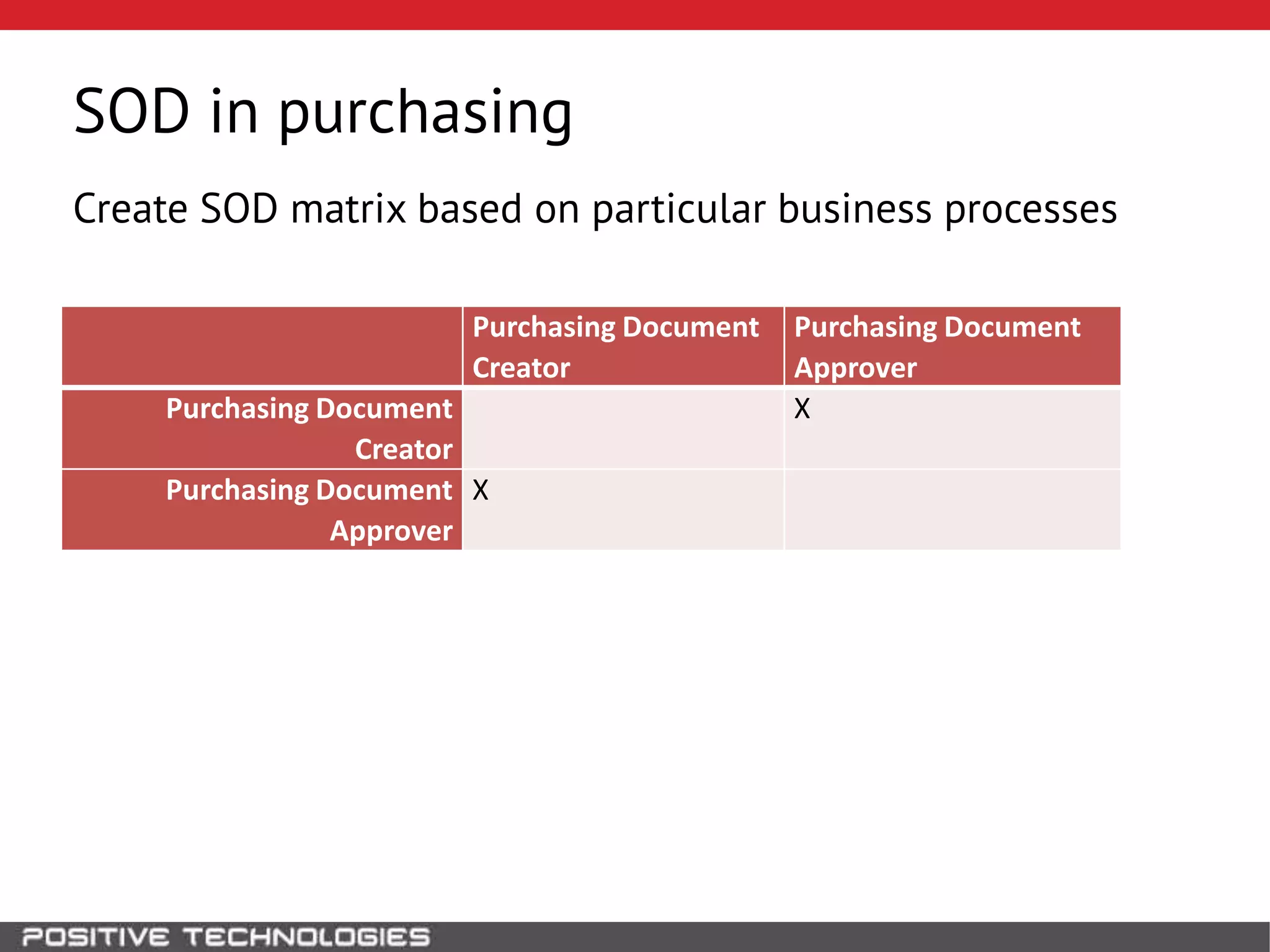
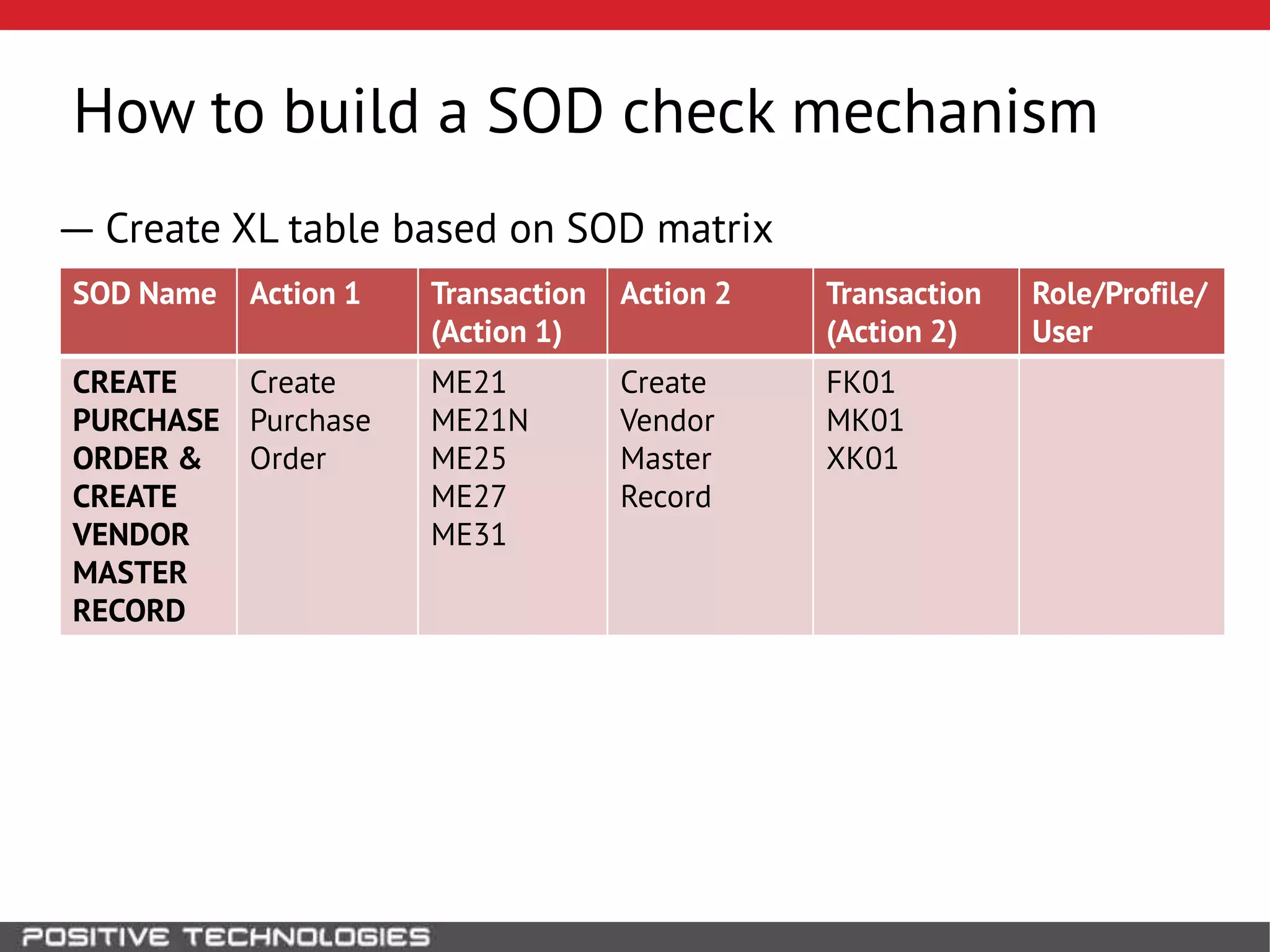
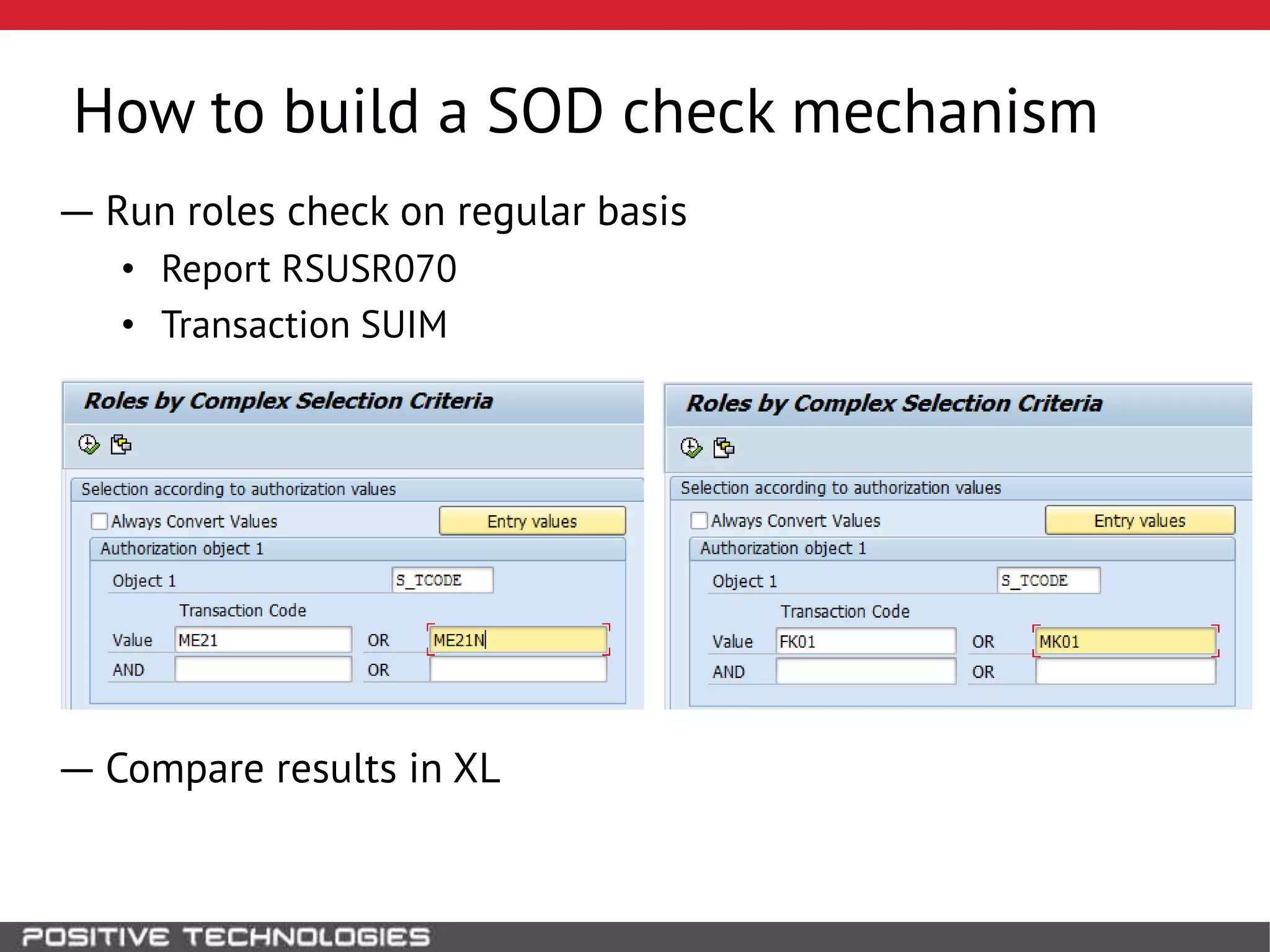
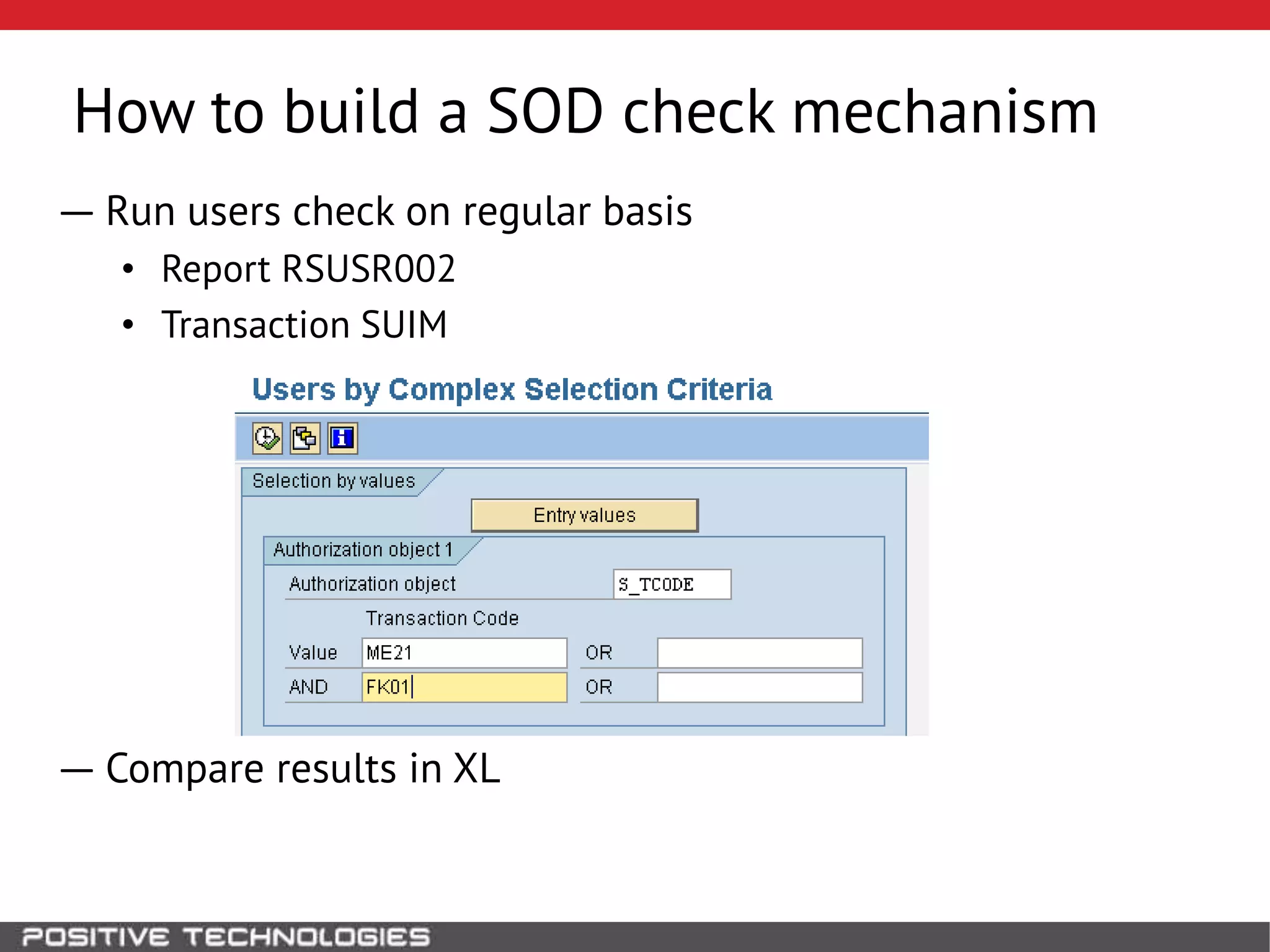
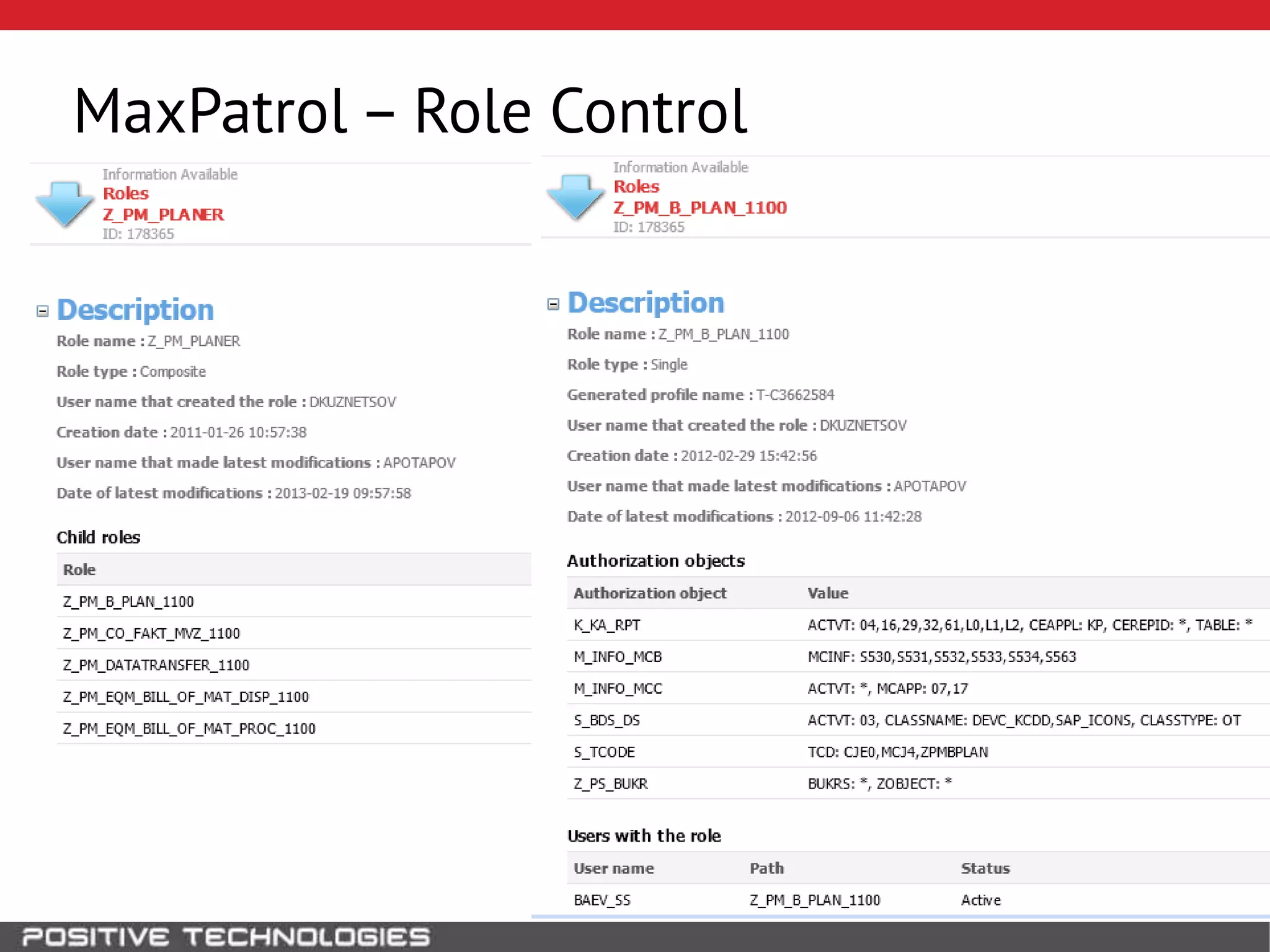
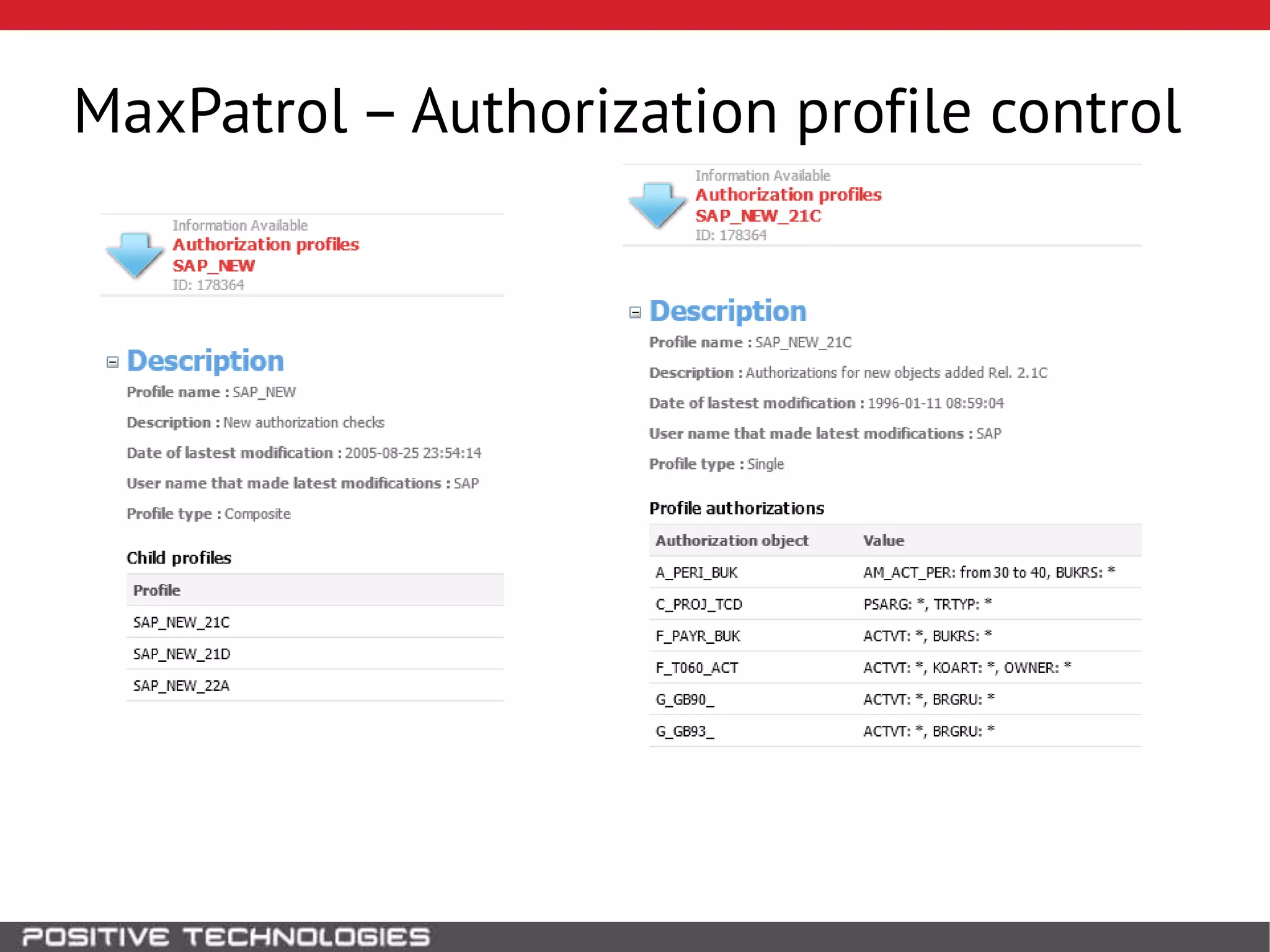
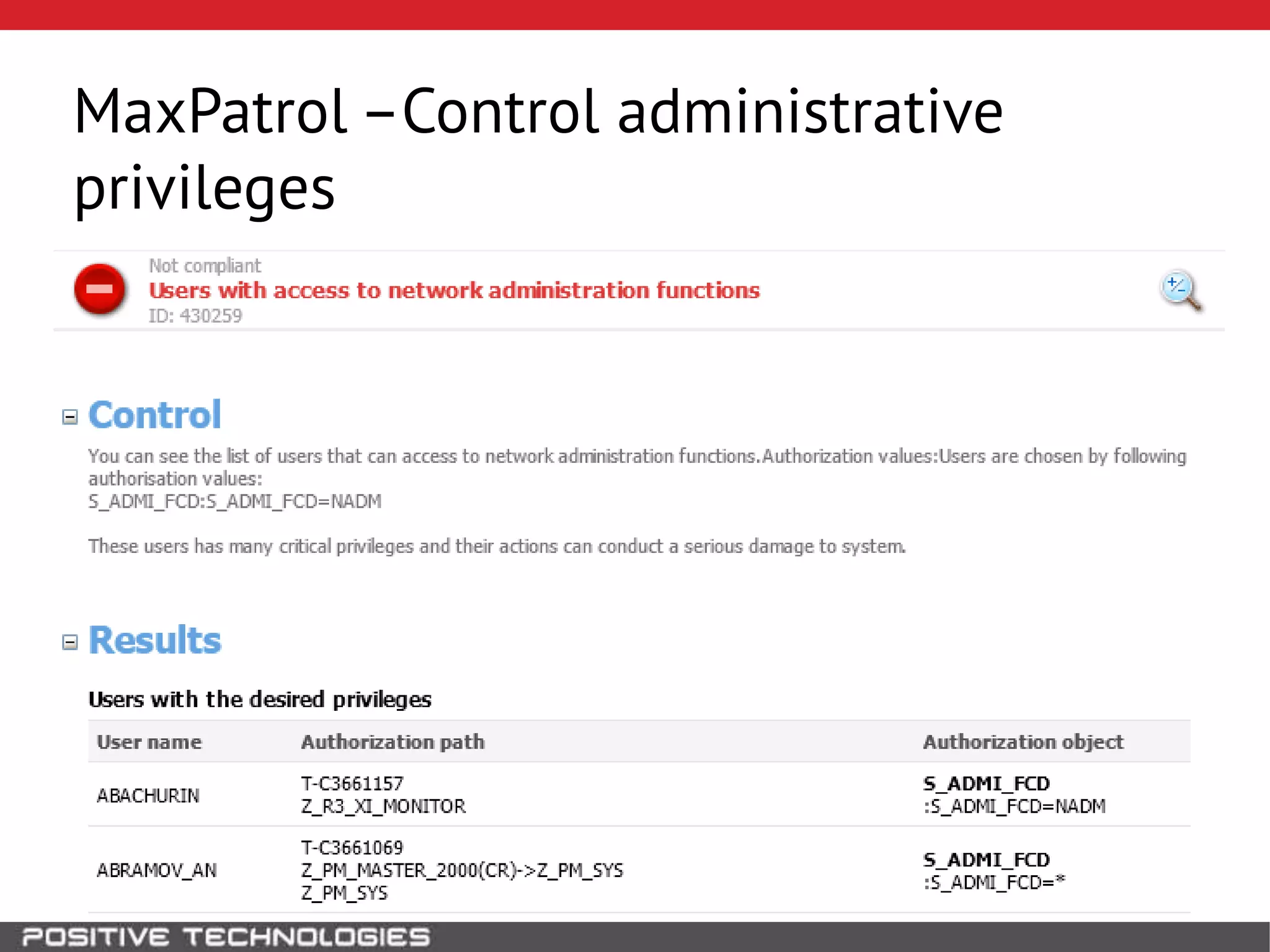
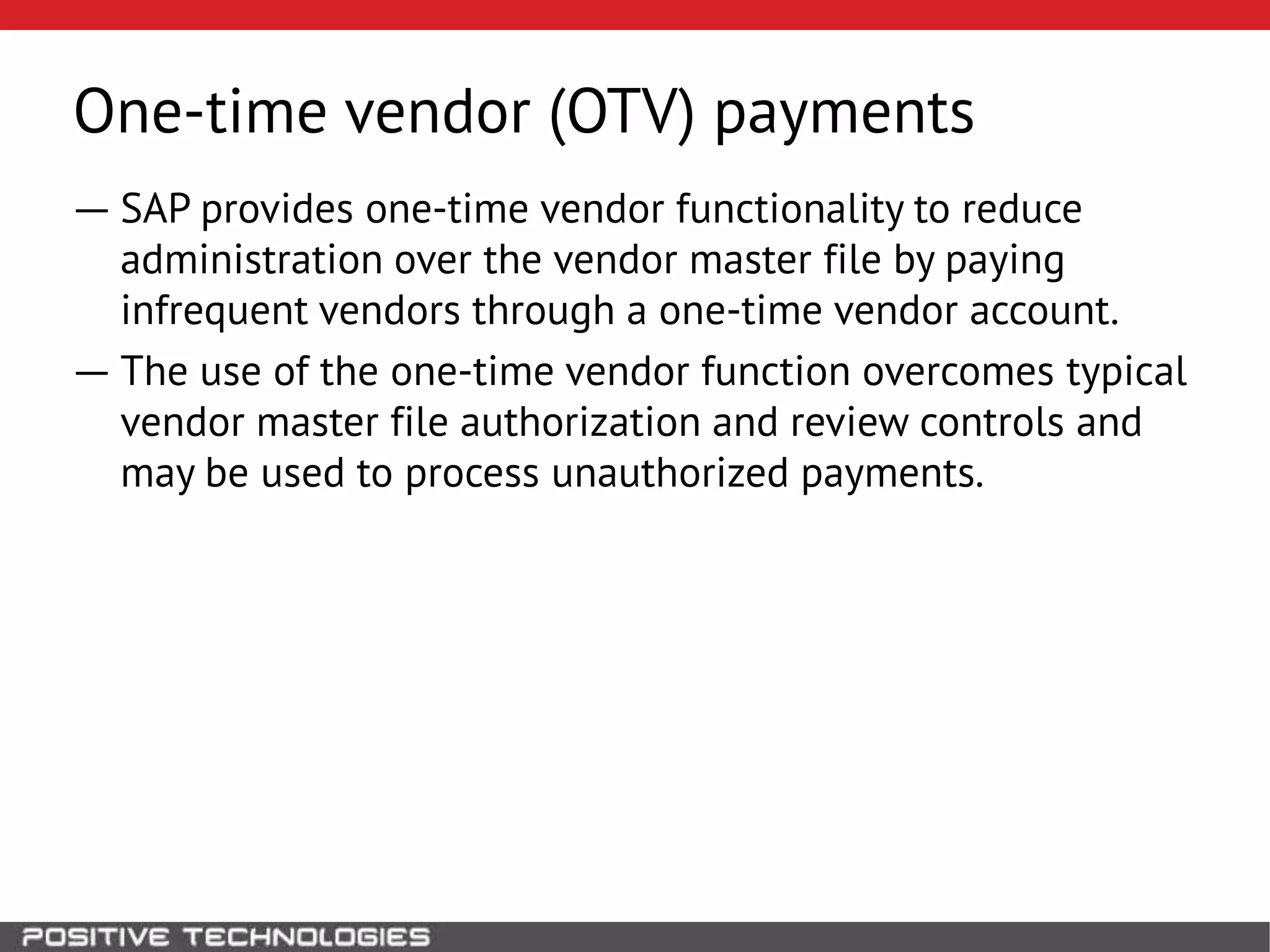
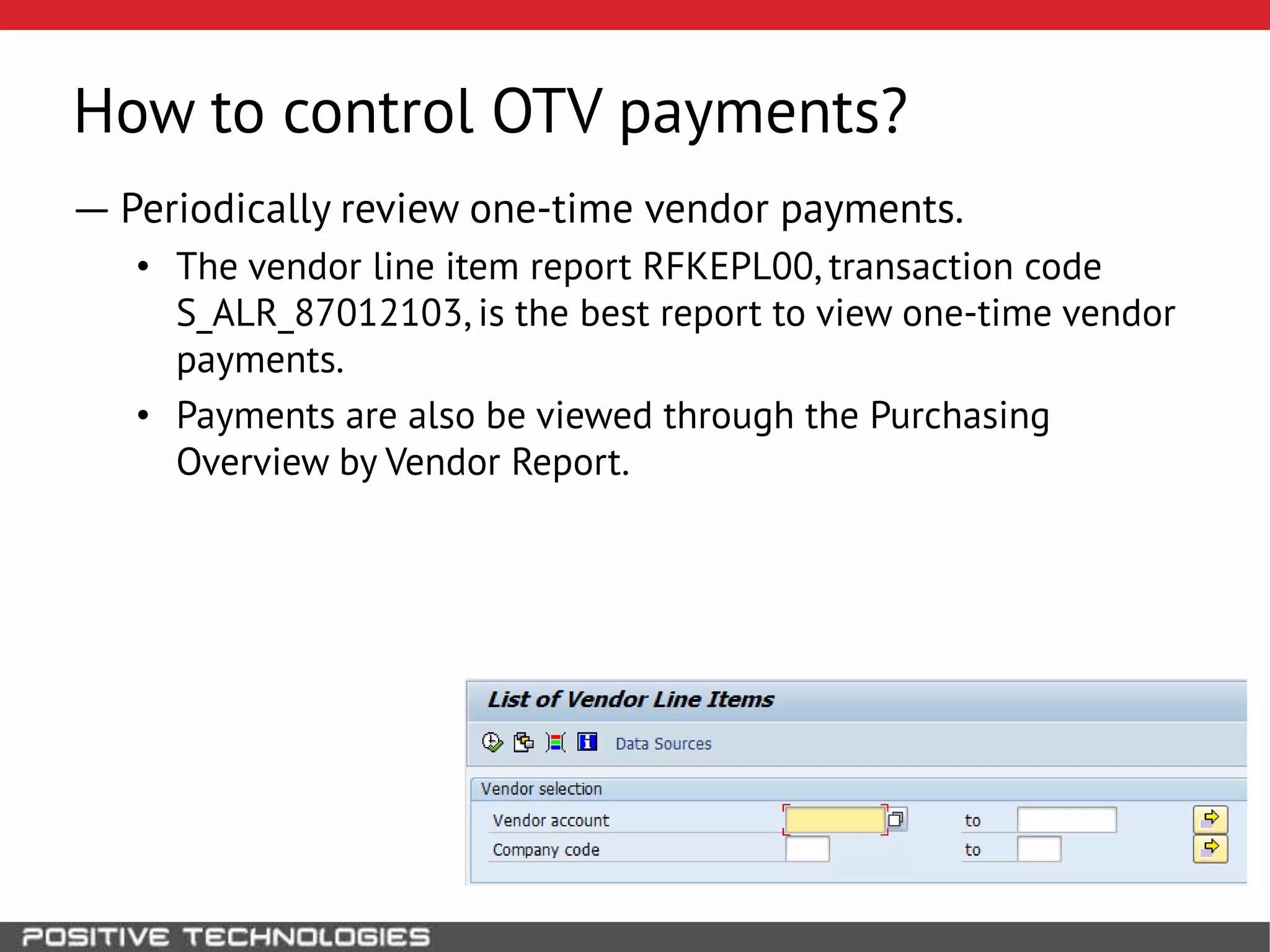
This document discusses building a governance, risk, and compliance (GRC) system for SAP. It outlines how to build mechanisms to control access, detect segregation of duties violations, and detect fraud. It describes analyzing critical business processes and roles in SAP, developing a separation of duties matrix, and using reports to check for violations. It provides examples of how to monitor roles and detect fraudulent purchasing patterns like abuse of one-time vendors. The conclusion recommends automating controls and identifying business actions that produce risks if not properly separated.