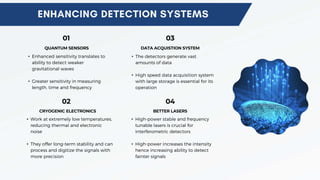
Gravitational waves are produced whenever an object is accelerated relative to another object. The first ever gravitational wave signal was detected by LIGO in 2015, coming from two massive black holes that collided over 13 billion years ago. Pulsar timing arrays can also detect gravitational waves by measuring minute distortions in spacetime through their effects on the arrival times of radio pulses from pulsars. Future detectors like LISA and developments in laser interferometry, cryogenic electronics, data acquisition, and quantum sensors promise to increase gravitational wave detection sensitivity and enable observation of even weaker sources.