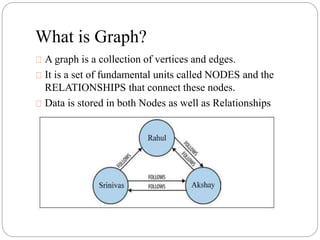
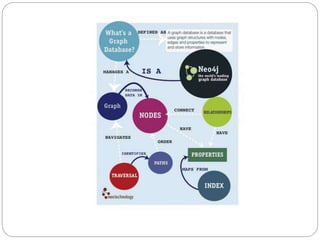
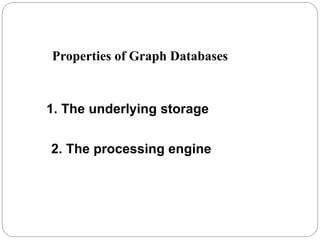
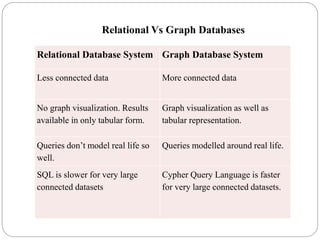
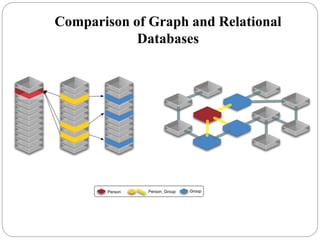
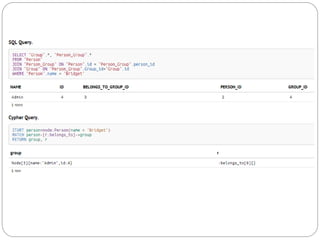
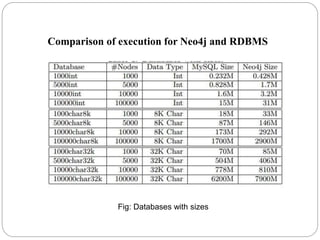
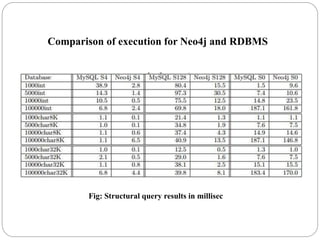
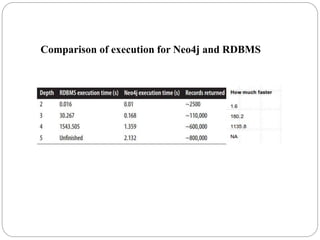
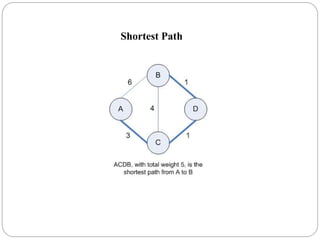
The document discusses a project analyzing social networks using a graph database. It introduces the three project members and defines what a graph is - a collection of nodes and relationships. It then discusses properties of graph databases, why the Neo4j graph database was chosen, its Cypher query language, and compares graph and relational databases. Execution times are faster for graph databases on large connected datasets. Applications discussed include product recommendation and finding shortest paths.