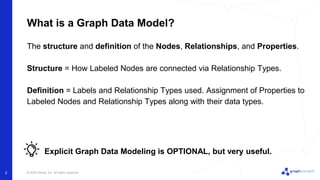
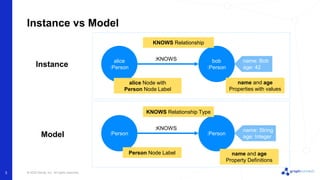
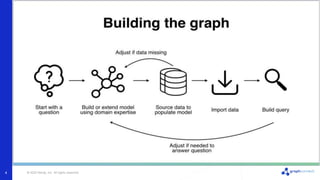
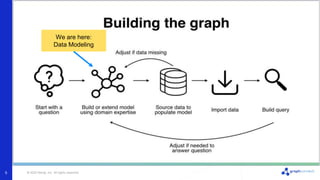
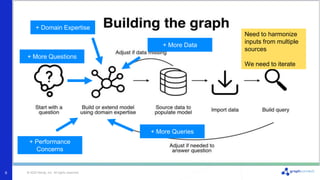
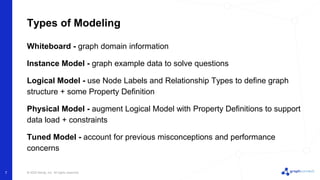
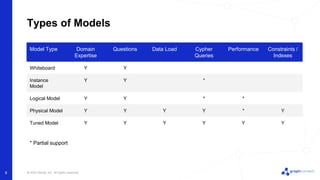
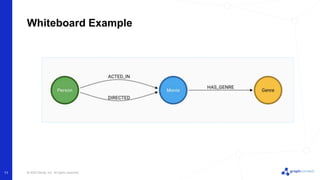
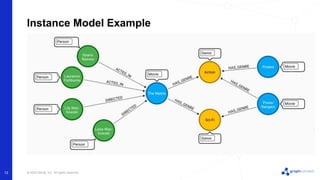
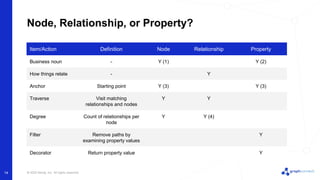
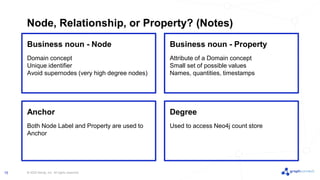
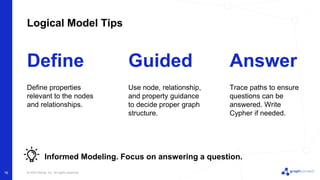
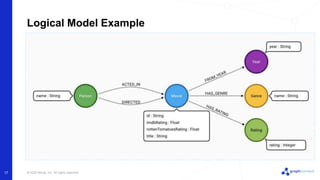
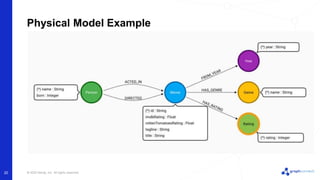
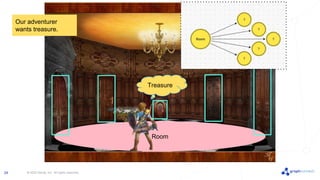
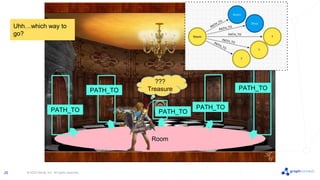
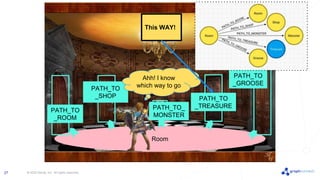
The document discusses best practices for graph data modeling in Neo4j. It describes different types of modeling including whiteboarding, instance modeling, logical modeling, physical modeling, and tuned modeling. Each type of modeling has a different focus such as conceptual understanding, answering questions, enabling data loading, and optimizing performance. The document provides tips for each modeling type and examples to illustrate graph structures. It also covers topics like relationship types, constraints, indexing, and validating the model.