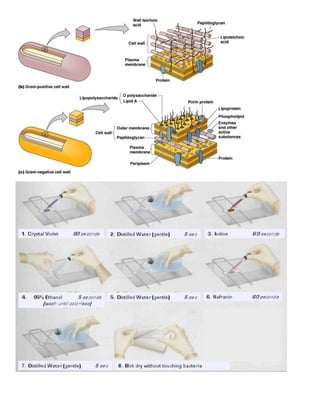
Gram's staining is a method used to differentiate bacterial species based on differences in their cell walls. It involves staining bacteria with crystal violet dye and rinsing with iodine solution or alcohol to reveal whether the bacteria takes a red or purple stain. Gram-positive bacteria retain the purple crystal violet dye after rinsing, while Gram-negative bacteria do not and appear red. The difference is due to the thicker peptidoglycan layer in Gram-positive cell walls.