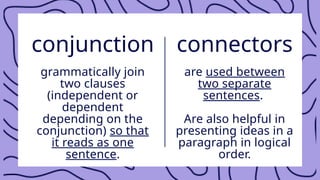
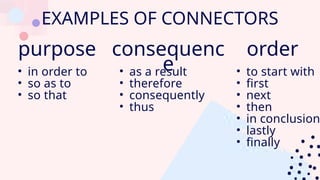
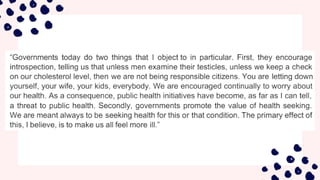
The document discusses logical connectors and their role in revealing the organizational structure and purpose of texts, such as conjunctions, contrast, addition, cause, and examples of connectors. It categorizes texts into four types: expository, descriptive, persuasive, and narrative, each with distinct purposes. Additionally, it outlines reading strategies like scanning, skimming, speed reading, and intensive reading to effectively comprehend different types of written material.