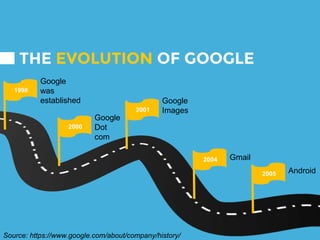
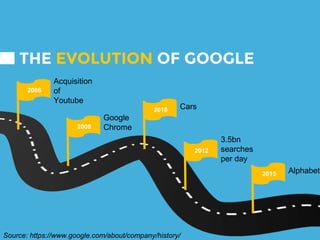
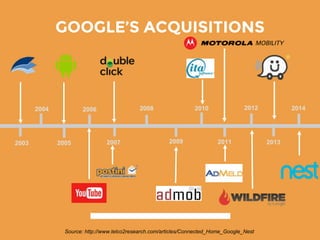
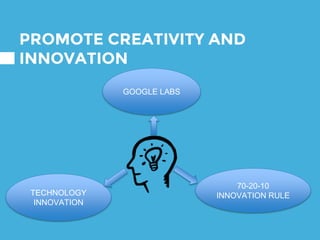
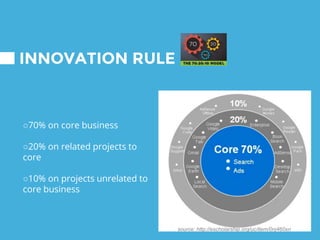
The document provides an overview of Google's strategy and evolution from 1998 to present. It discusses Google's mission to organize the world's information and make it accessible, their diversification strategy including acquisitions and strategic partnerships. It also outlines their approach to technology innovation including Google Labs, the 70-20-10 rule, and cultivating an innovative work culture. Regarding IT strategy, it highlights how Google customizes servers, develops custom software, and promotes choice and interesting work to support their search business through a unique and unconventional approach.