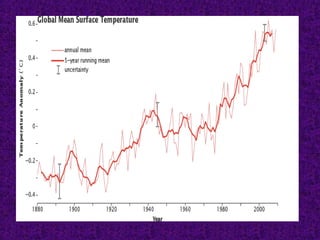
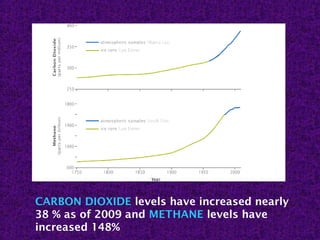
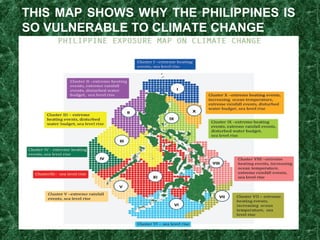
Global warming is caused by increased levels of greenhouse gases from human activities like burning fossil fuels. The greenhouse effect occurs naturally and makes Earth habitable, but human activities have enhanced the effect. Burning fossil fuels and other activities have increased carbon dioxide and methane levels, trapping more heat in the lower atmosphere and leading to warming temperatures worldwide. This global warming will cause significant climate change impacts like sea level rise and more extreme weather unless reduced. The Philippines is especially vulnerable to these impacts due to its geography and development.