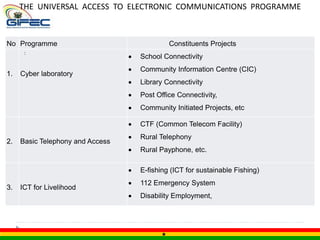
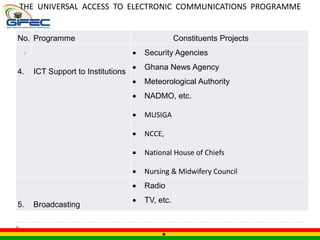
This document summarizes Ghana's Universal Service Fund (GIFEC). It outlines GIFEC's vision to bridge the digital divide, and its mission to provide basic telecom services to underserved communities. It describes GIFEC's management structure and various programs to connect schools, libraries, and communities to the internet through cyber labs and community information centers. The document also discusses GIFEC's achievements in connectivity and ongoing challenges around sustainability and ownership.