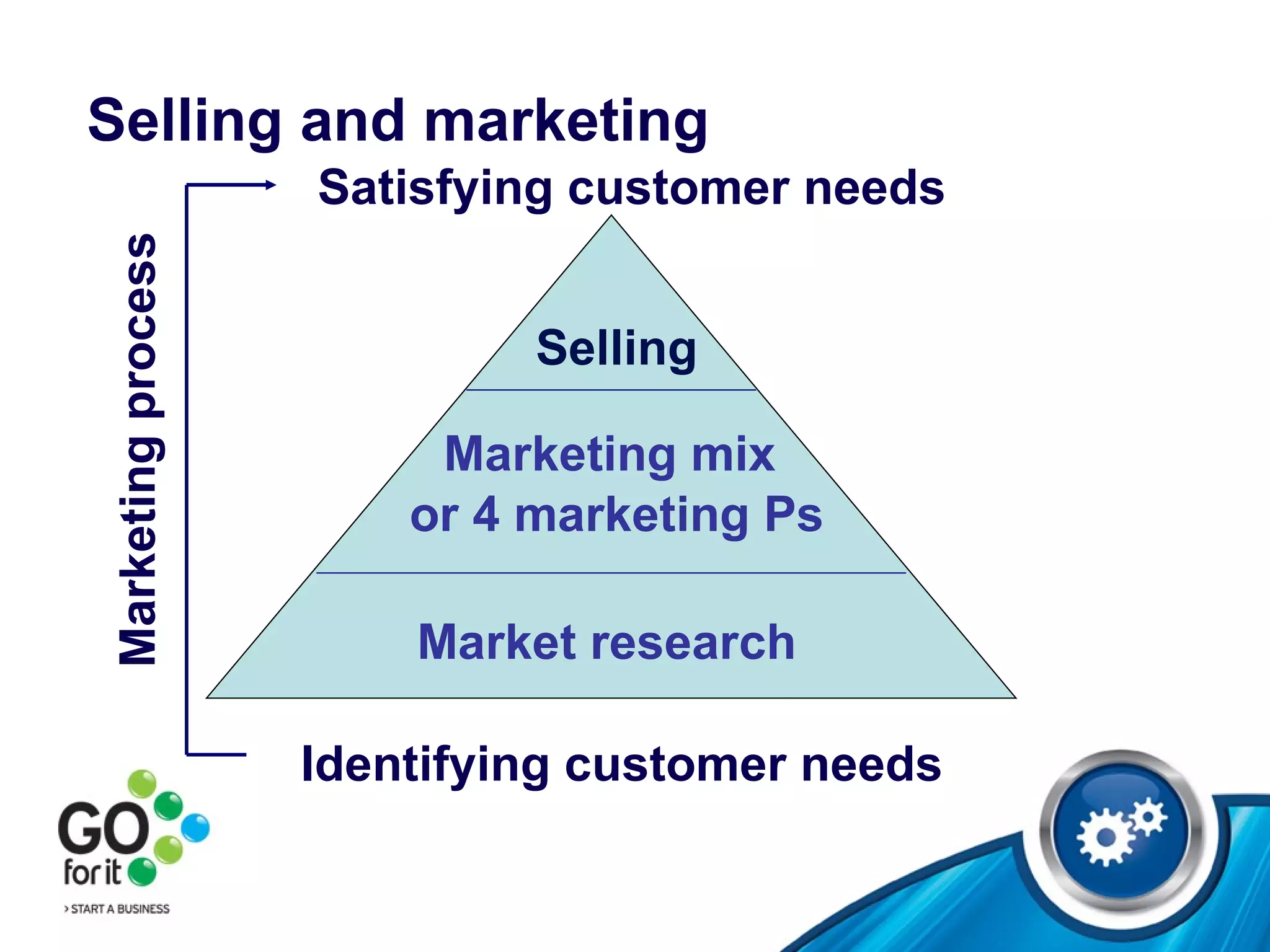
This document provides an overview of various topics related to selling and networking, including:
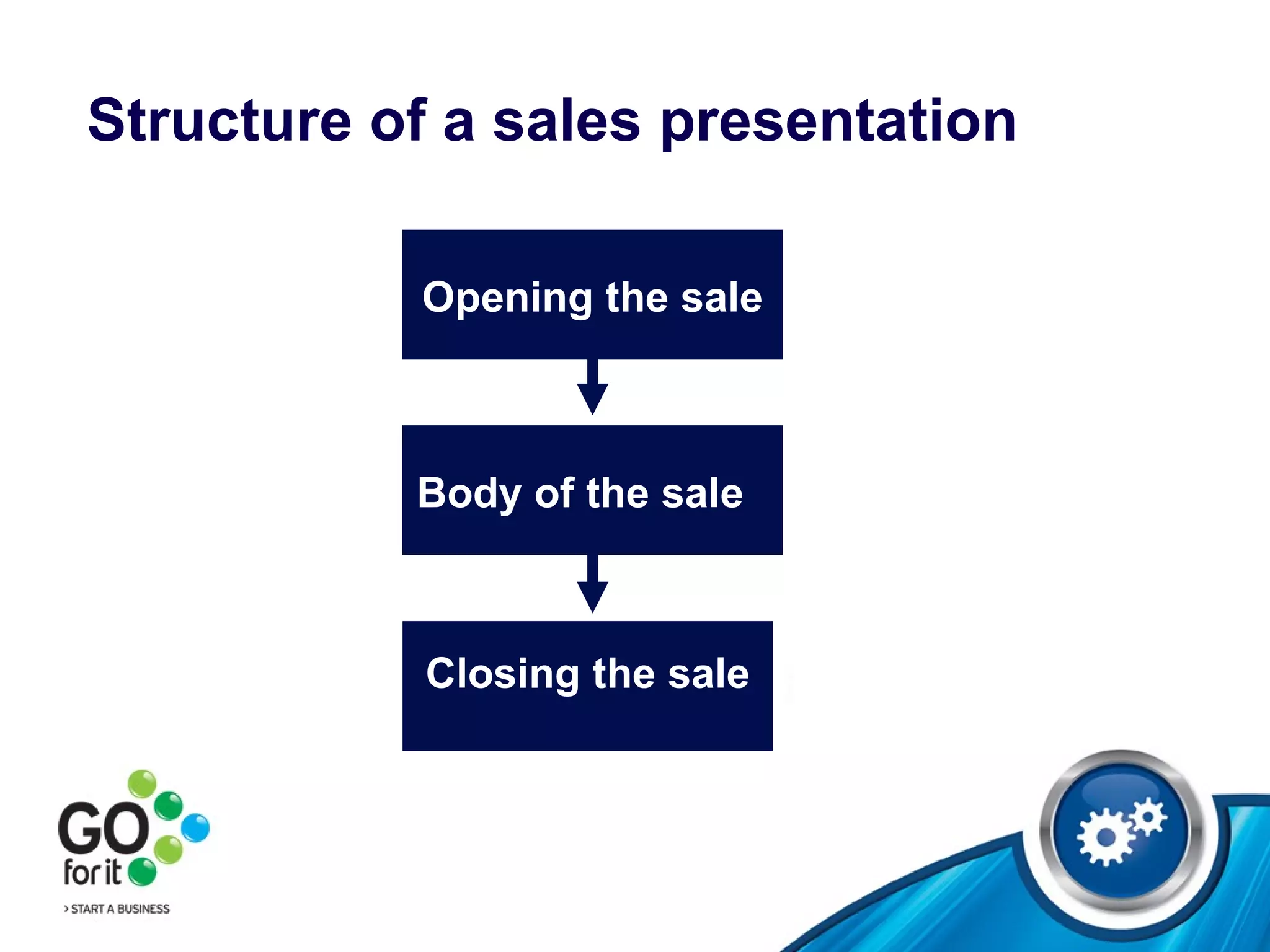
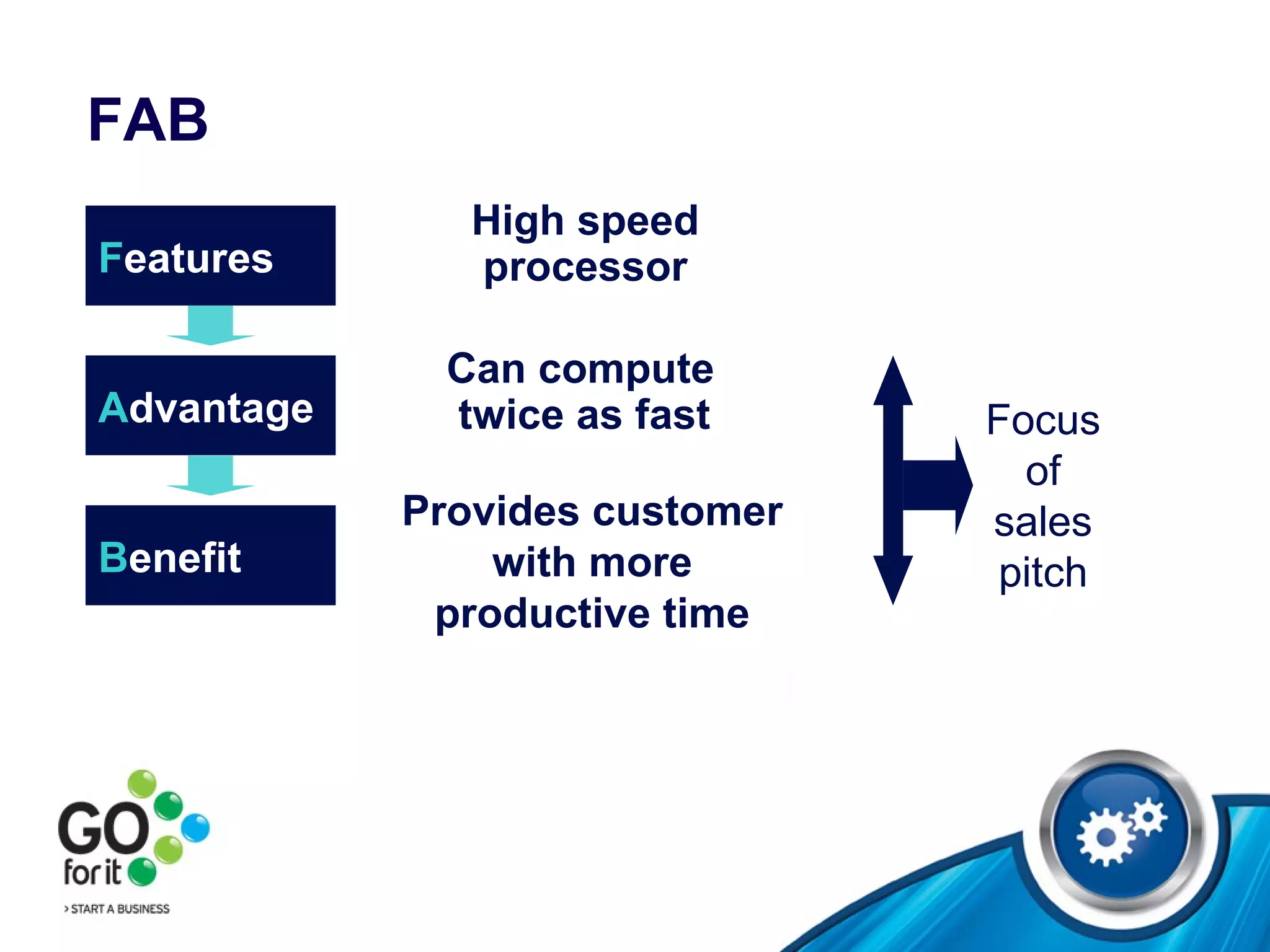
1) The selling process and how to find prospects through referrals, databases, directories, and networking. It discusses opening, body, and closing techniques for sales presentations.
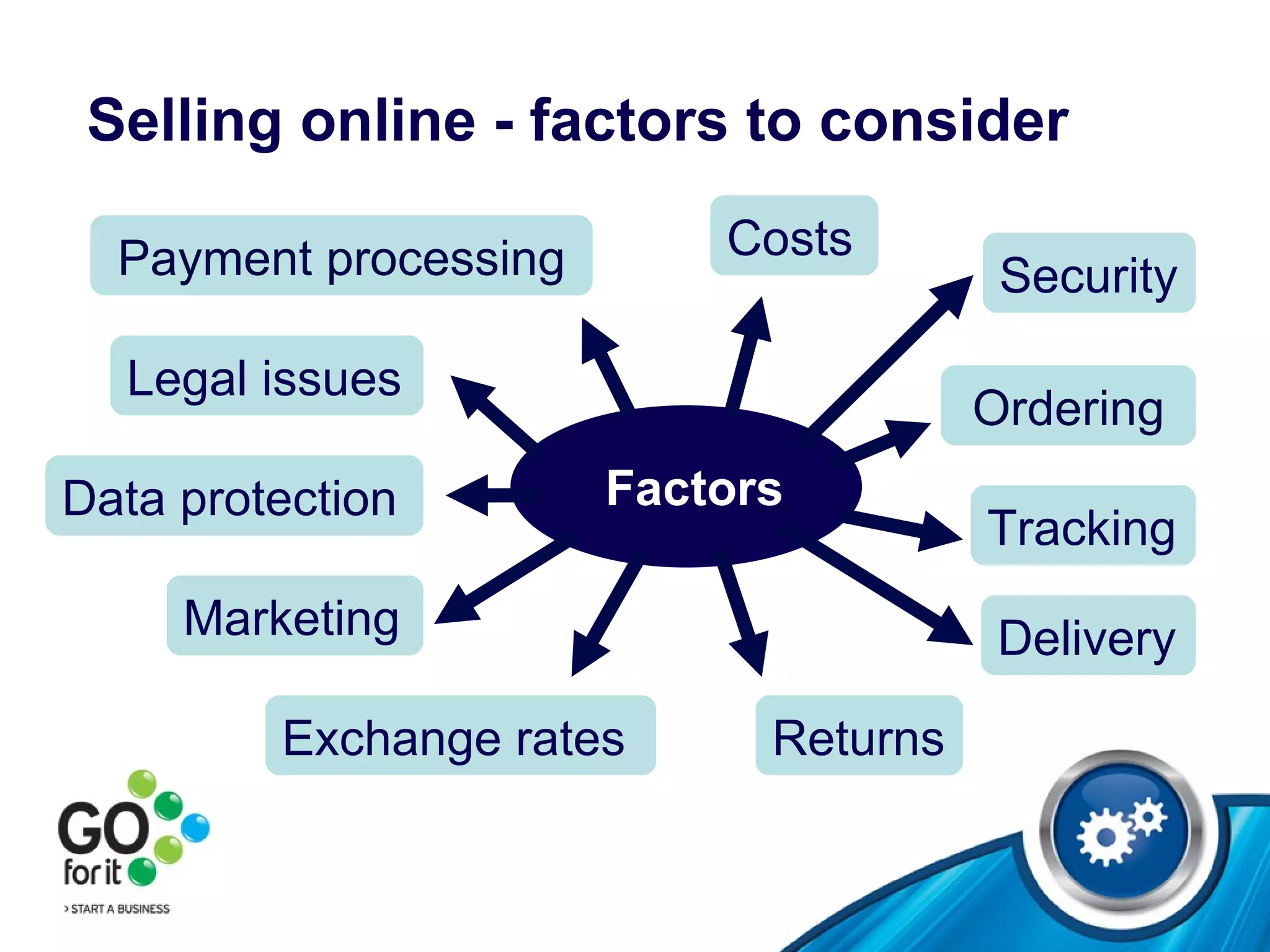
2) Factors to consider for selling online and overseas, such as payment processing, security, and legal issues.
3) The benefits of good customer care like repeat sales and referrals, and tactics like follow-up calls and loyalty schemes.
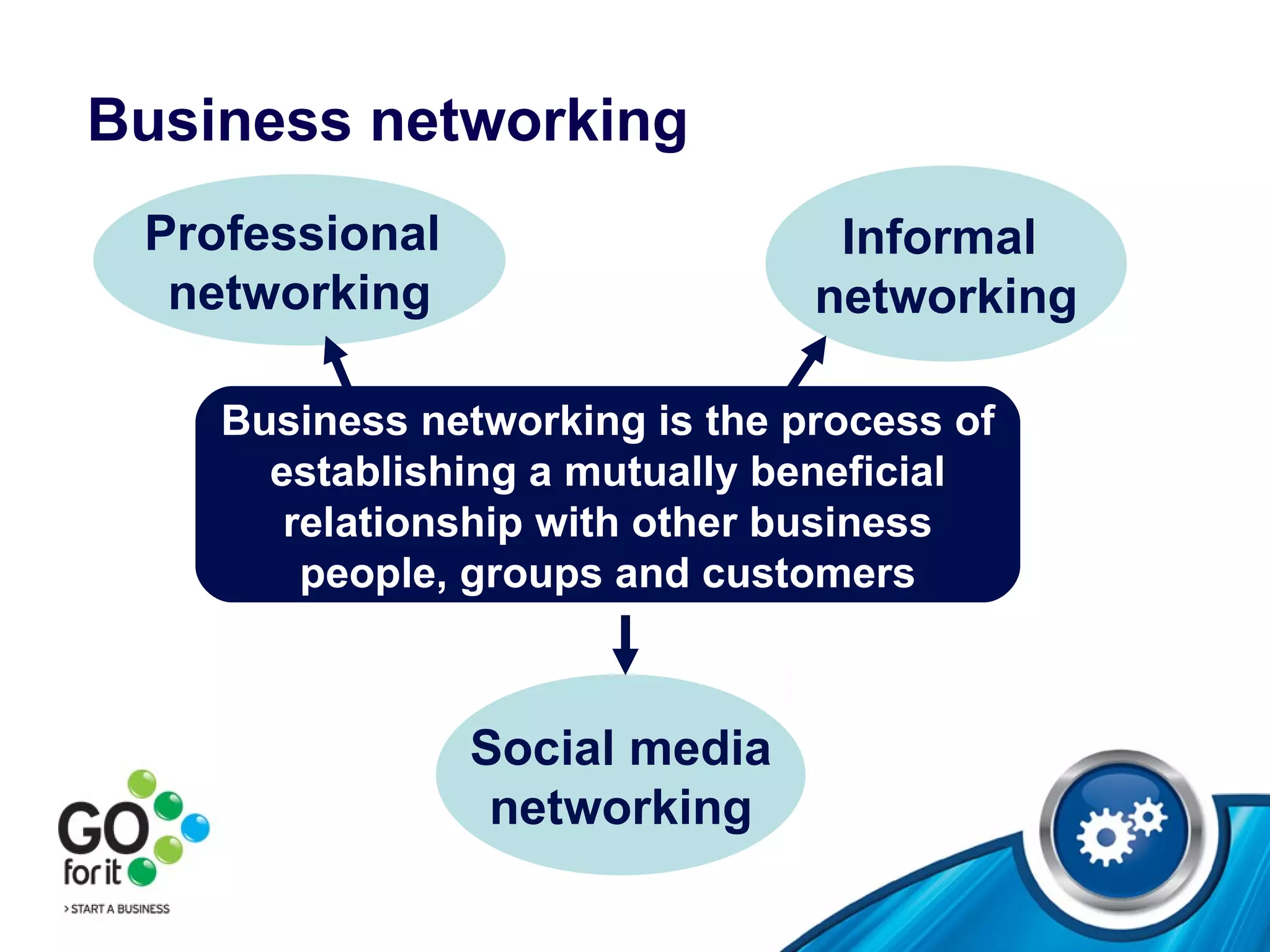
4) Types of business networking including professional events, social media, and maintaining contacts through regular communication and providing referrals.
5) Key considerations for tendering like costs, strategy fit,