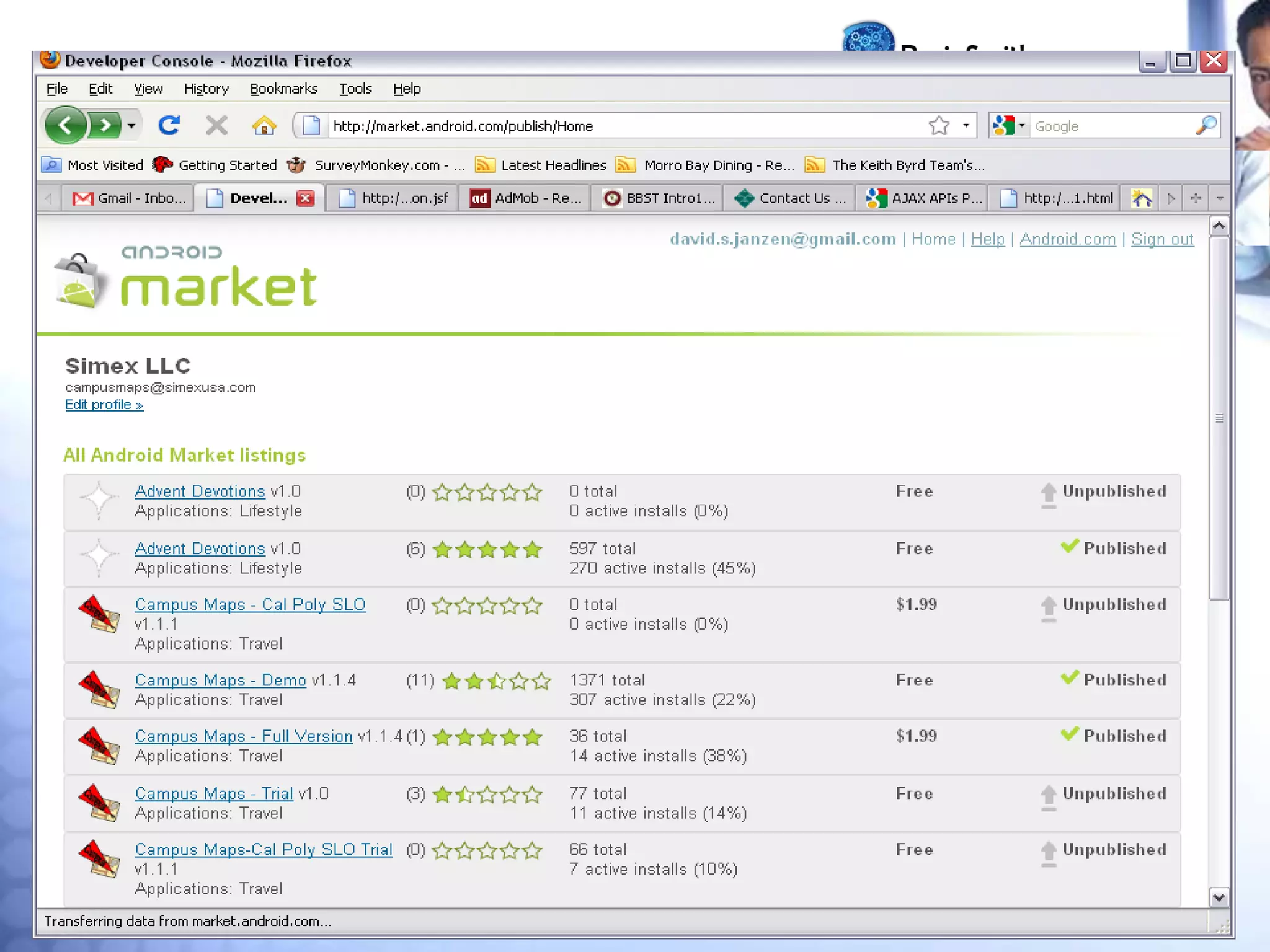
This document provides an overview of getting started with Android development. It discusses how to make money from Android apps through paid apps, ads, or services to other developers. It also covers publishing apps to the Android Market, a quick tour of common and less common Android features, the Android design philosophy focusing on responsiveness, and leveraging the web to keep apps fast.