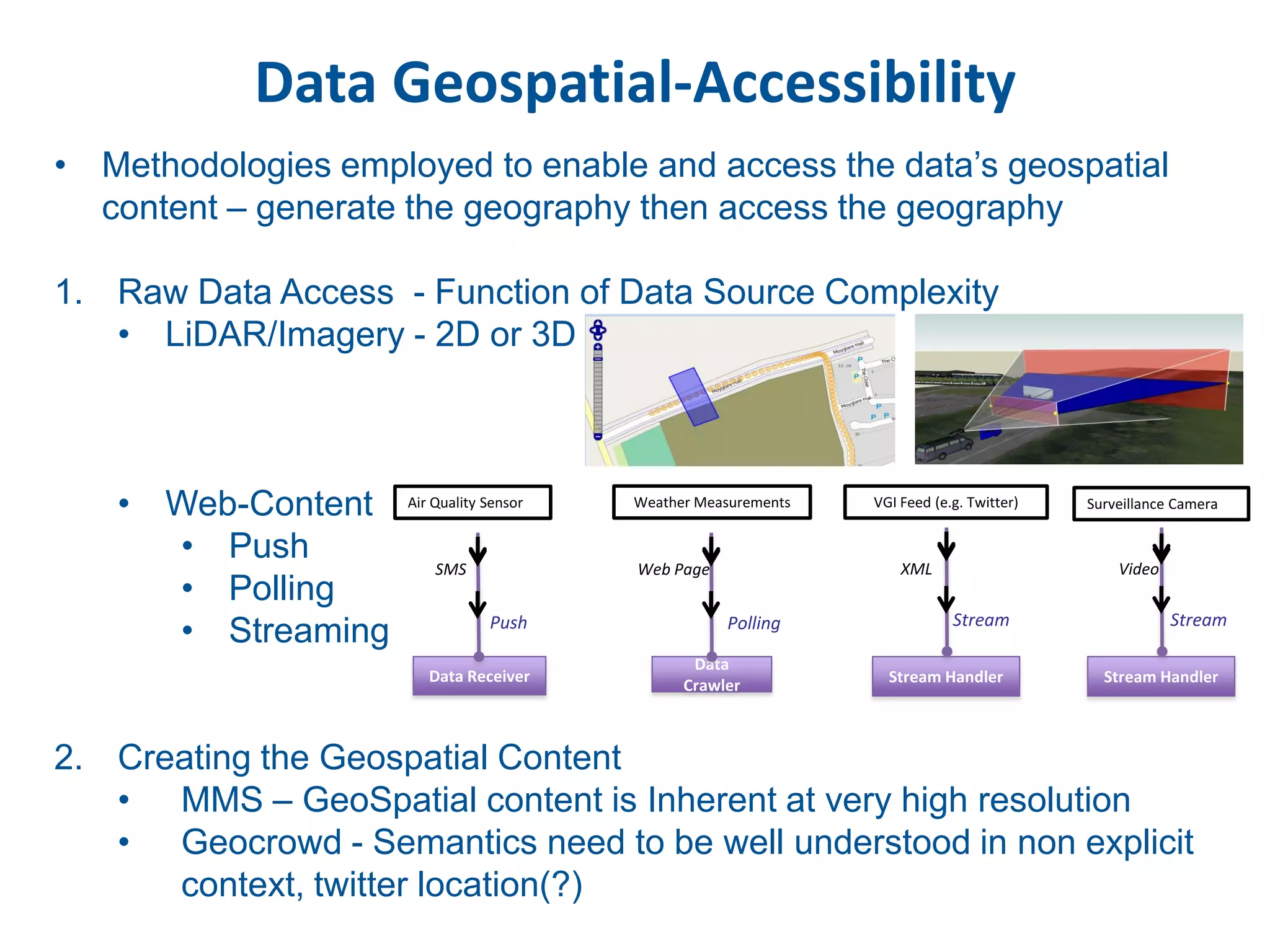
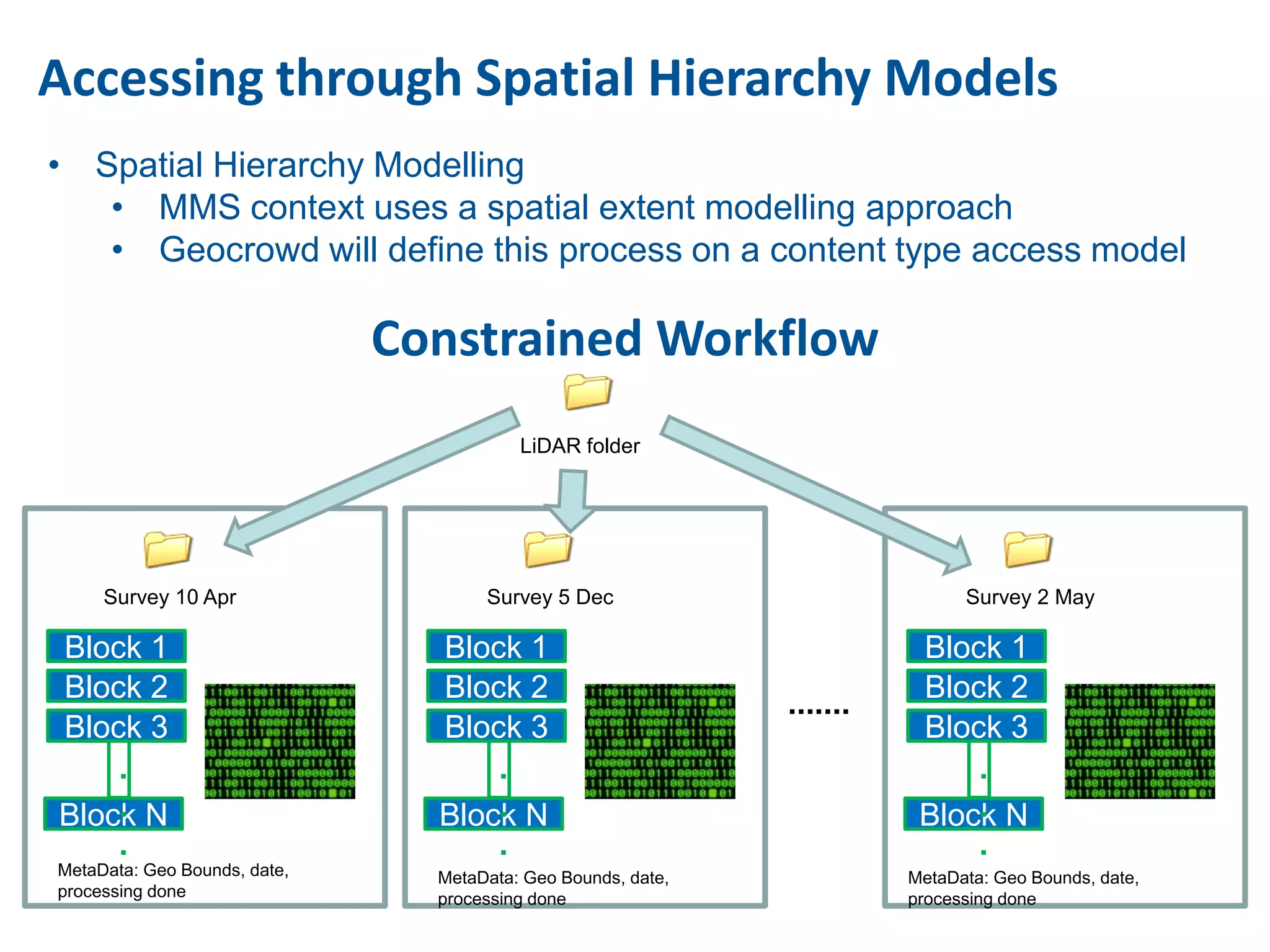
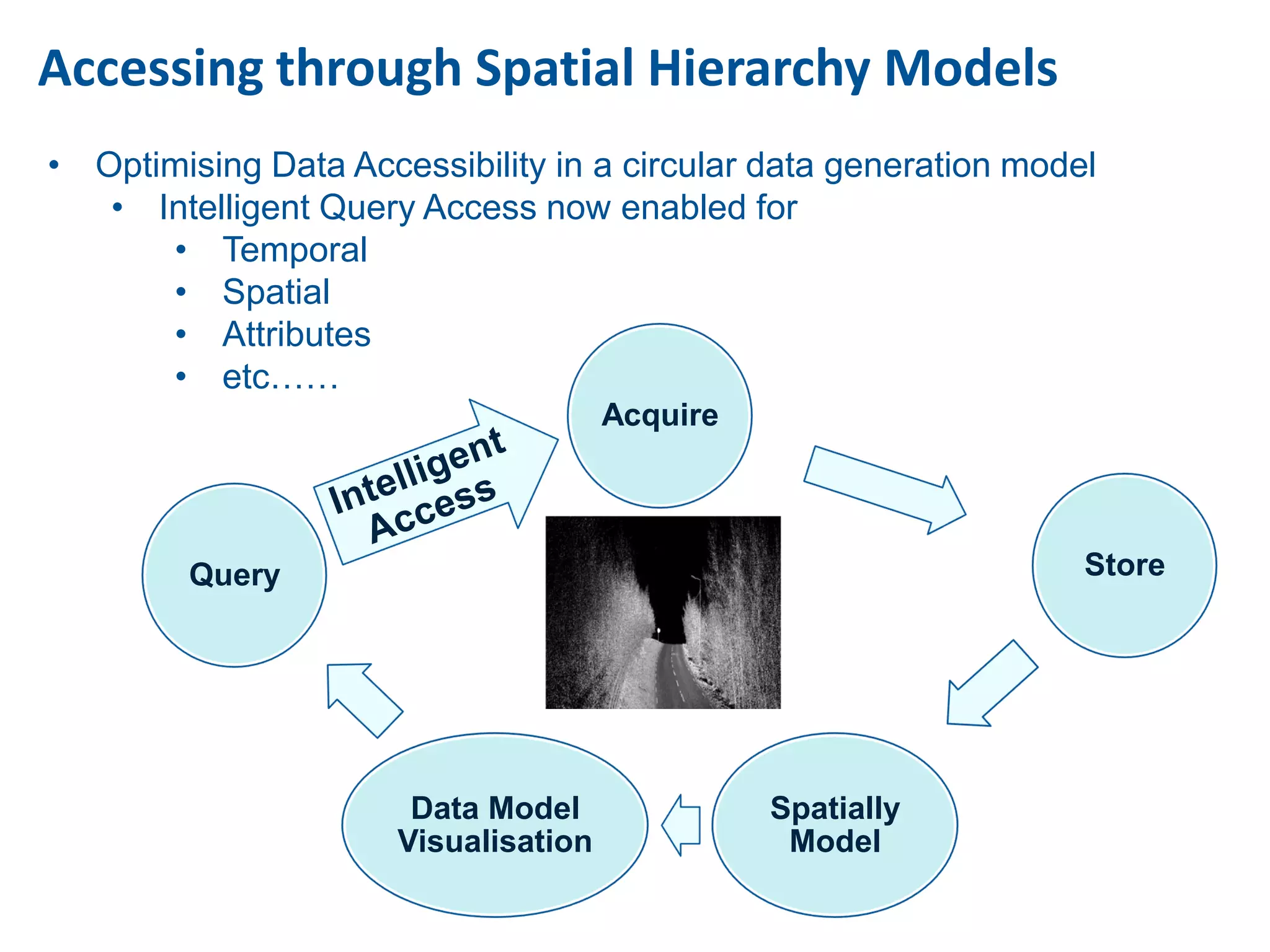
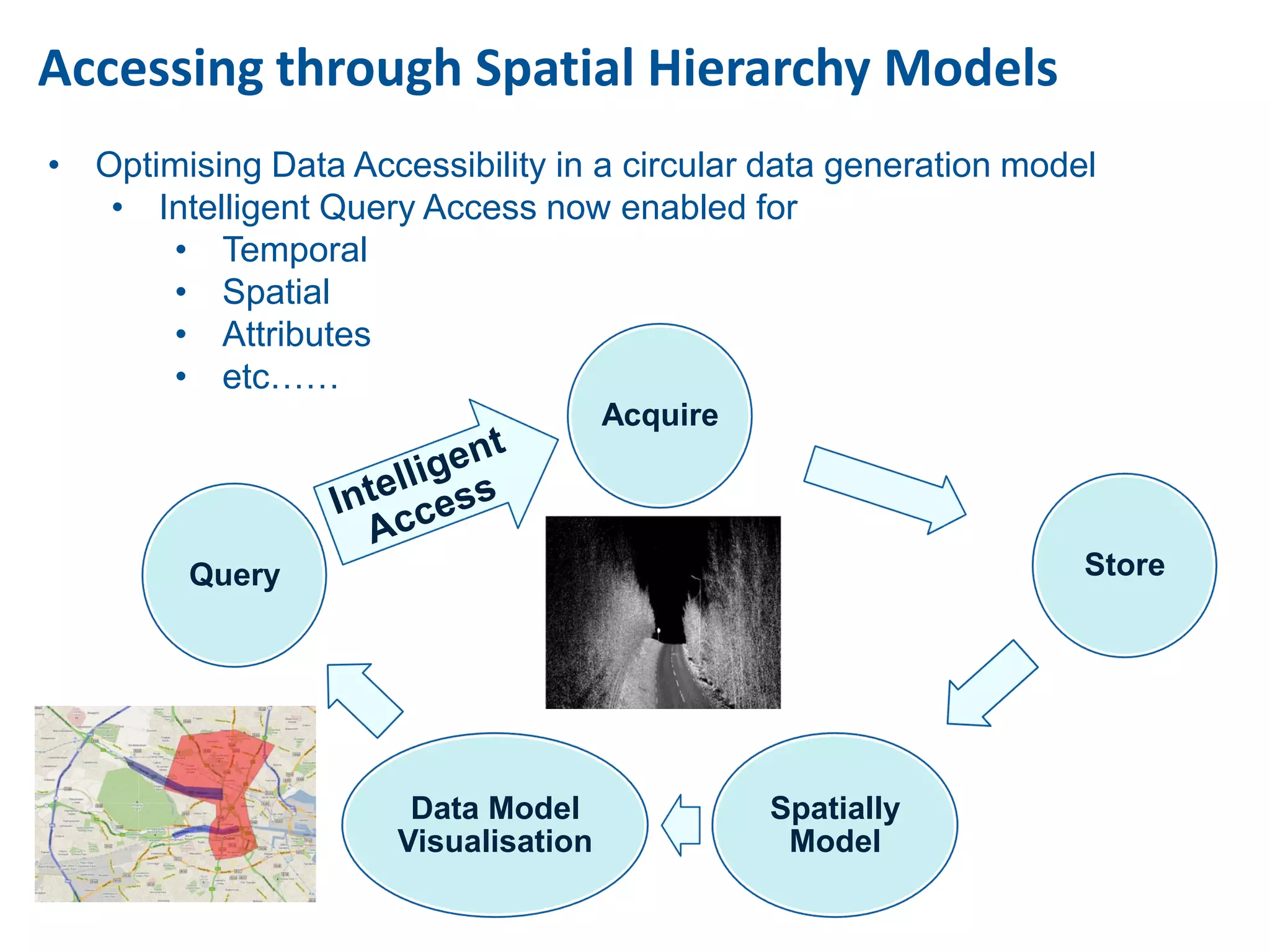
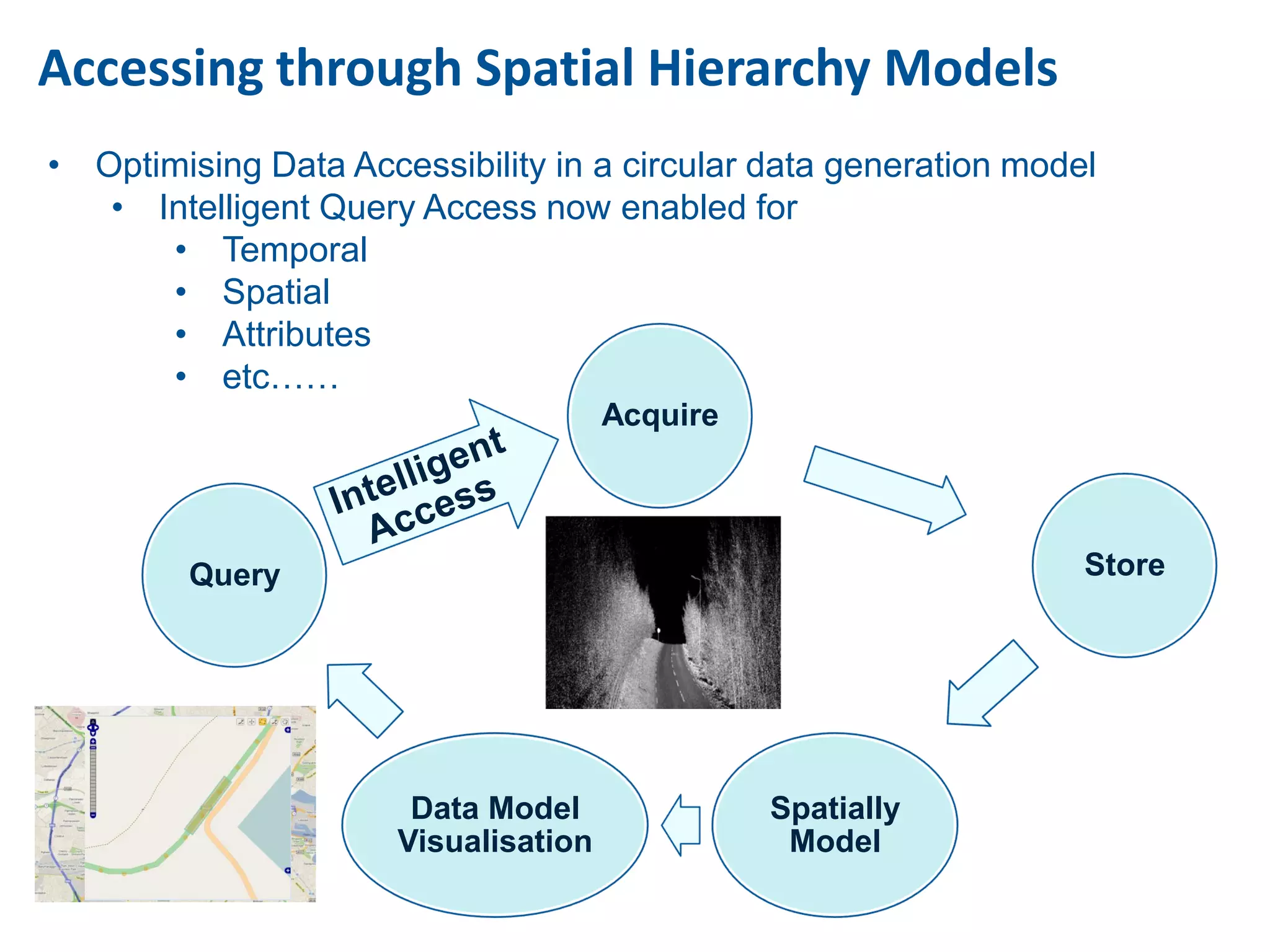
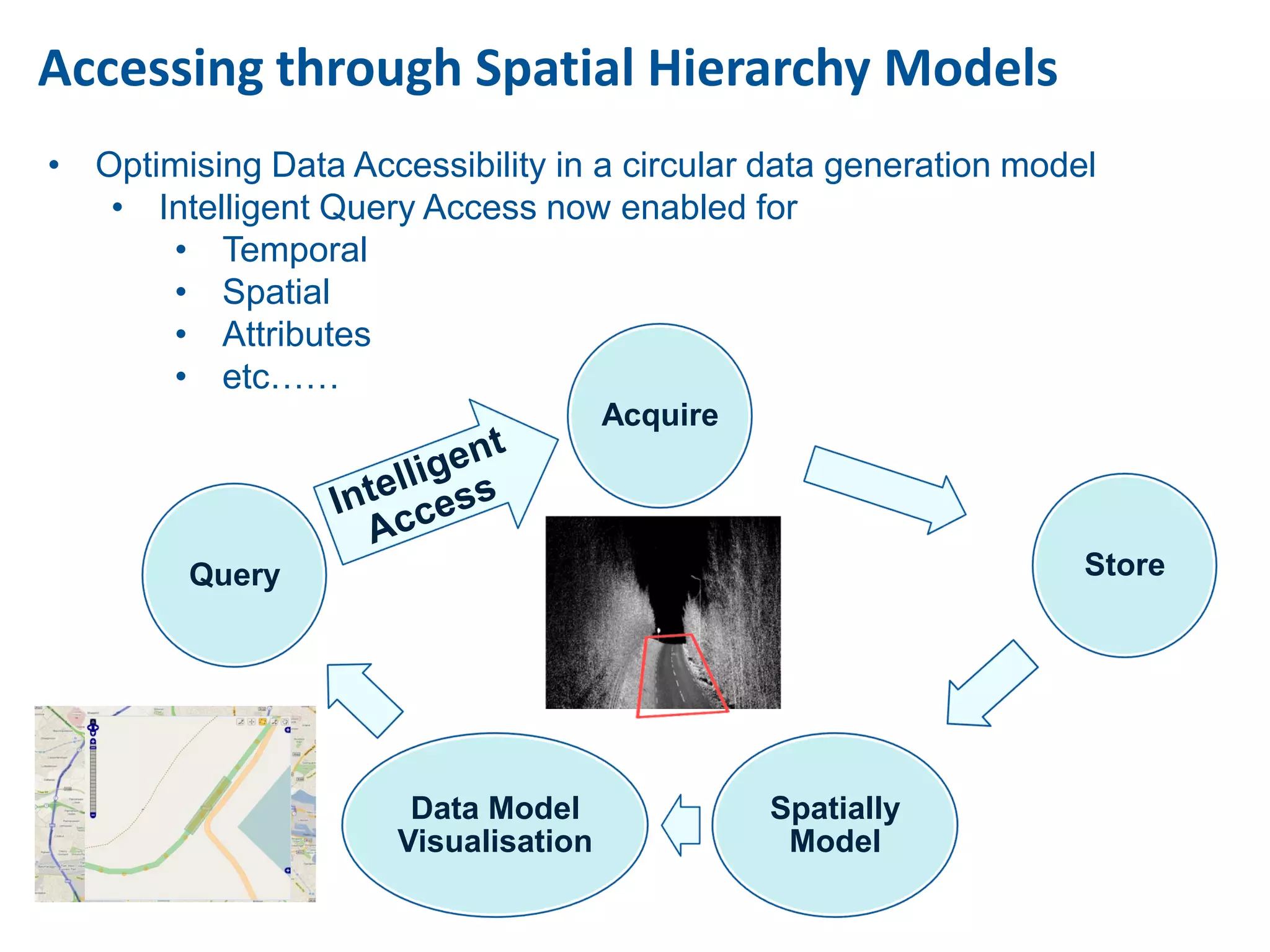
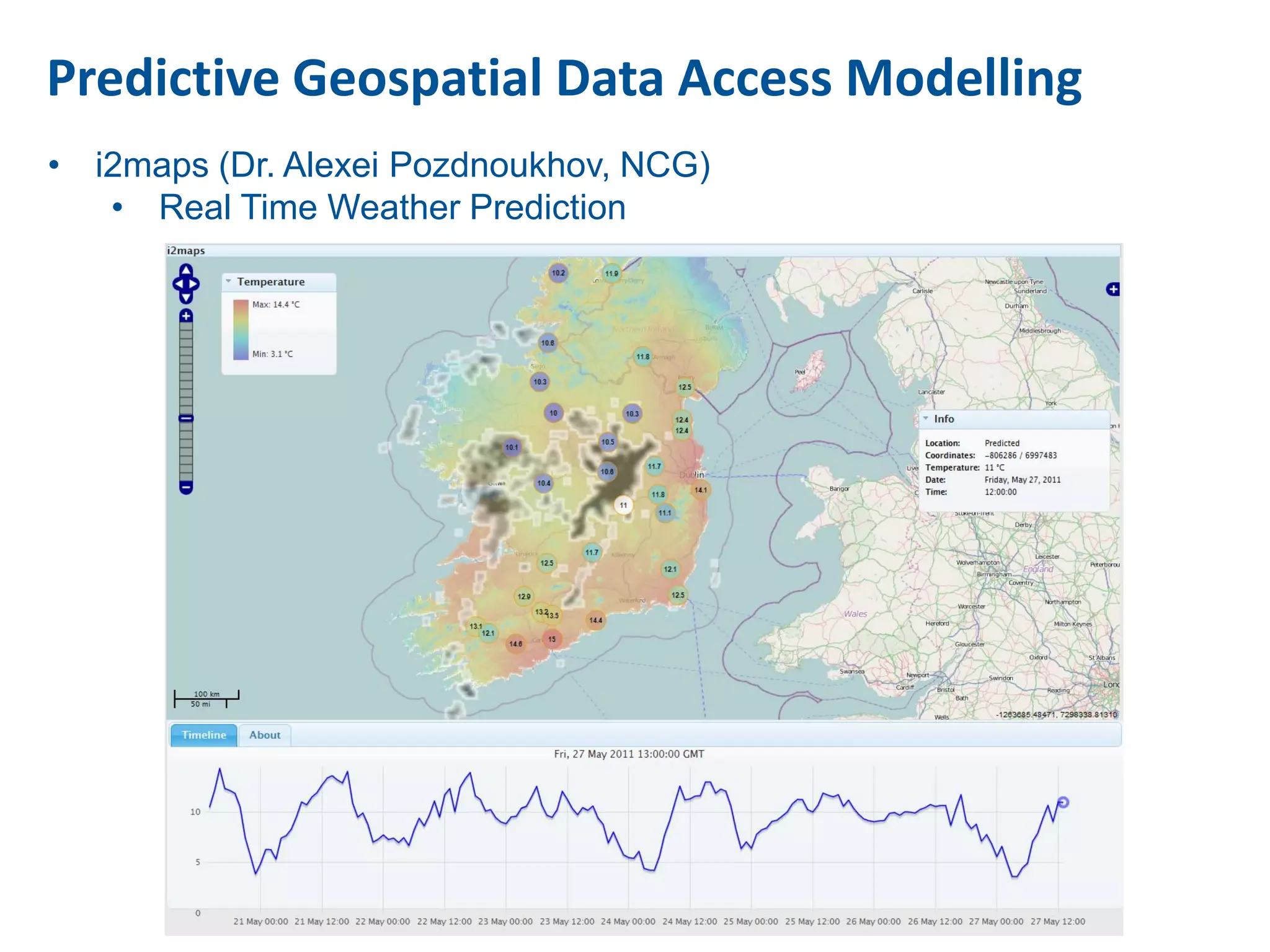
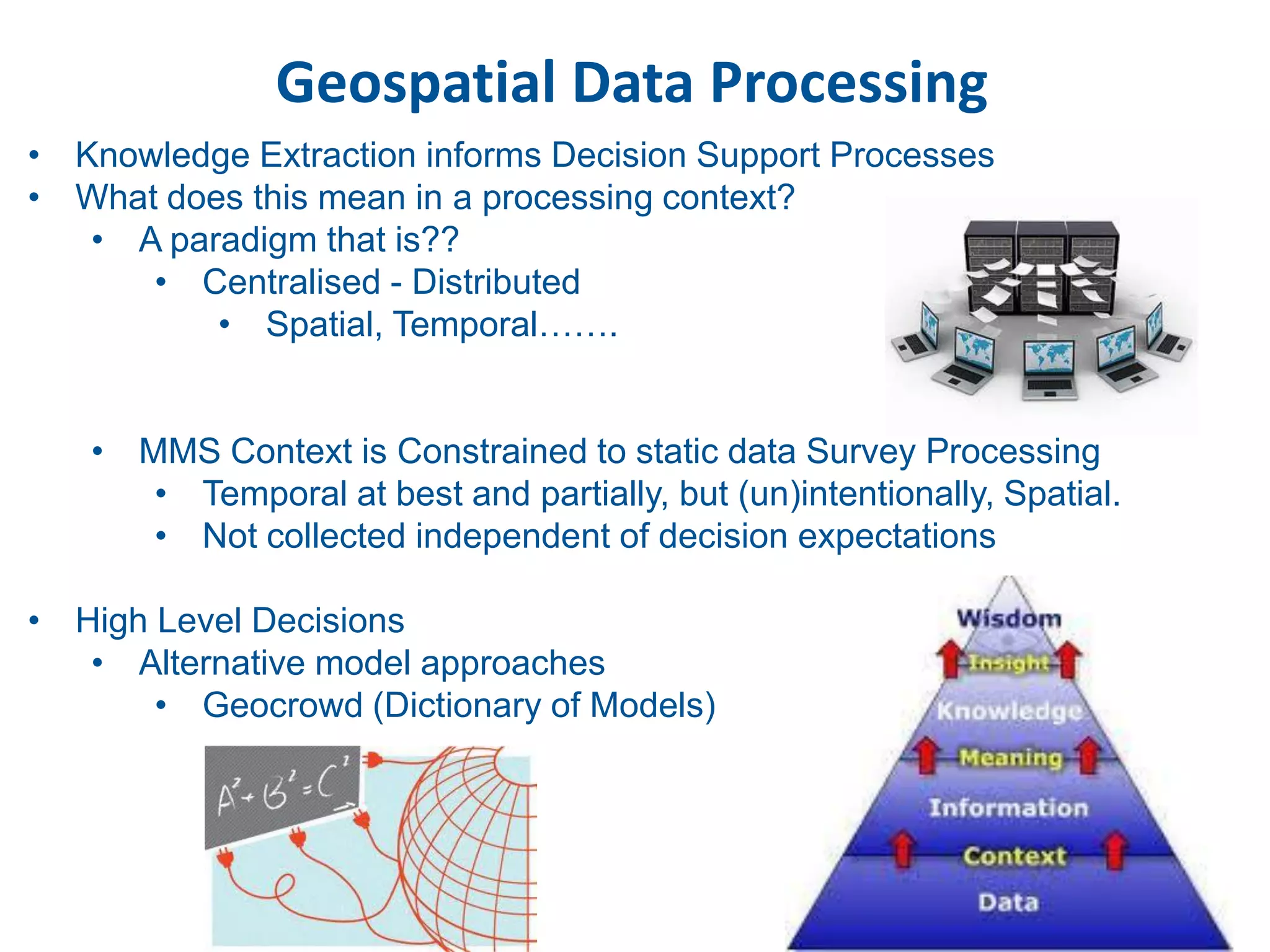
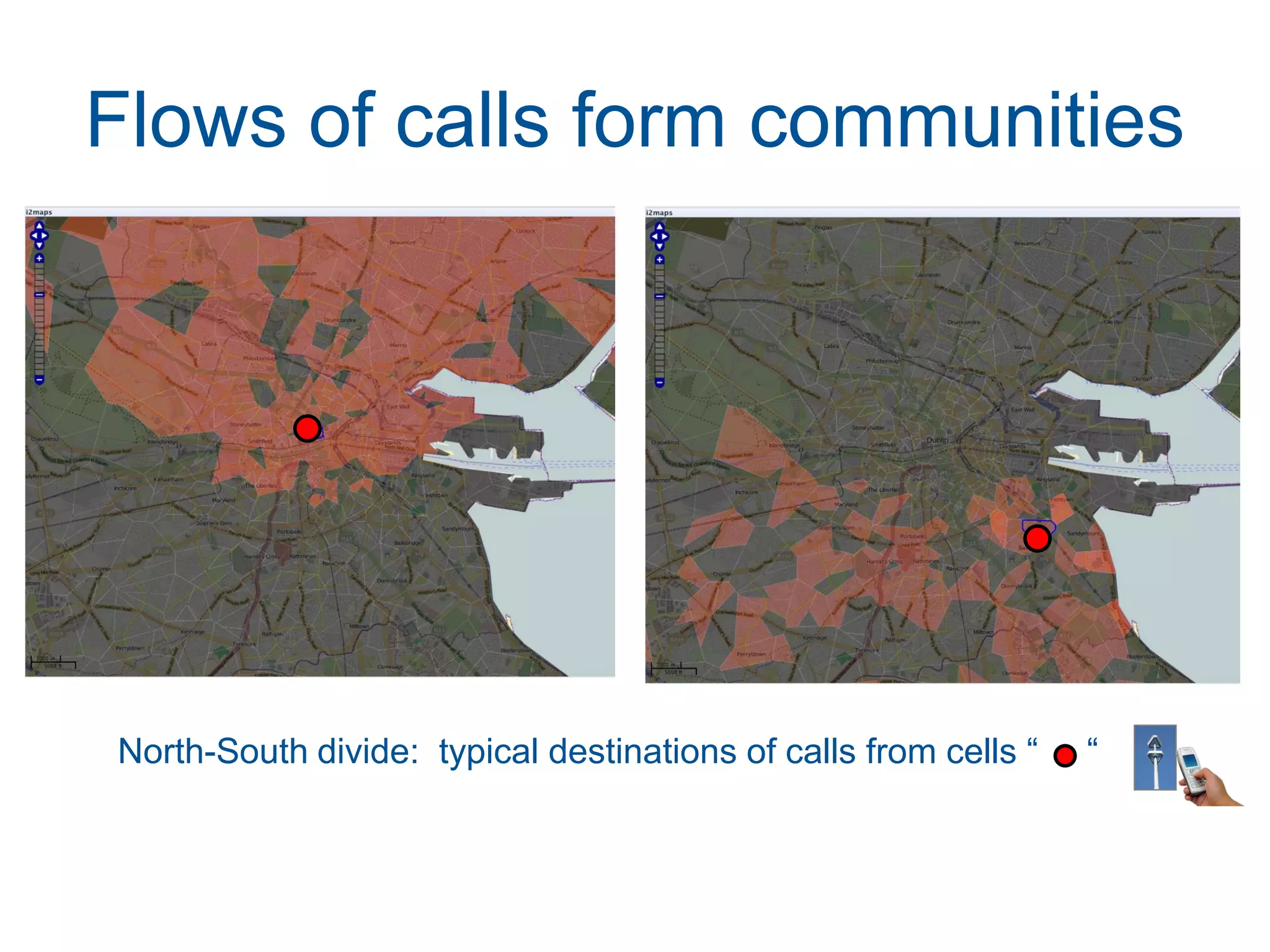
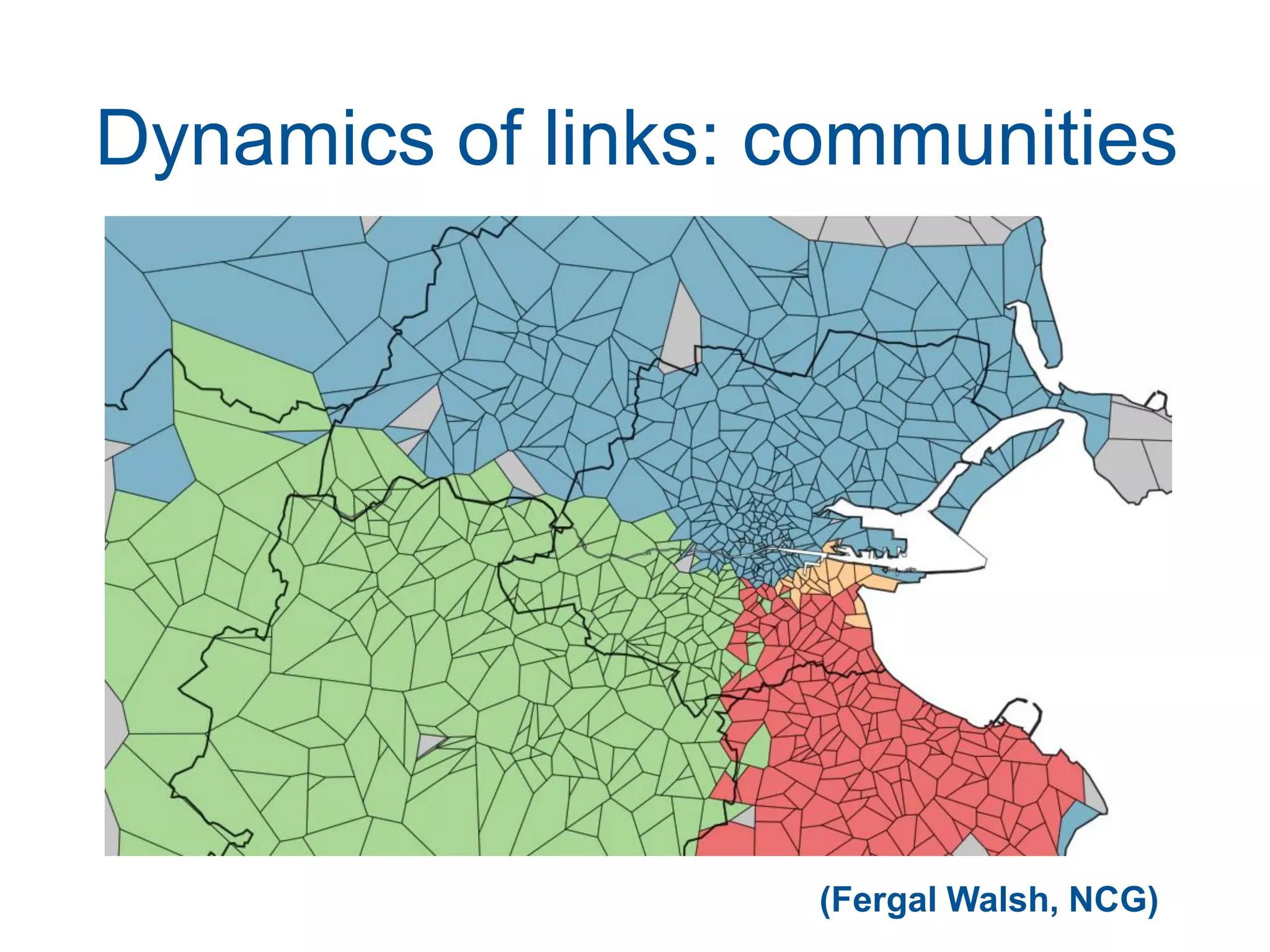
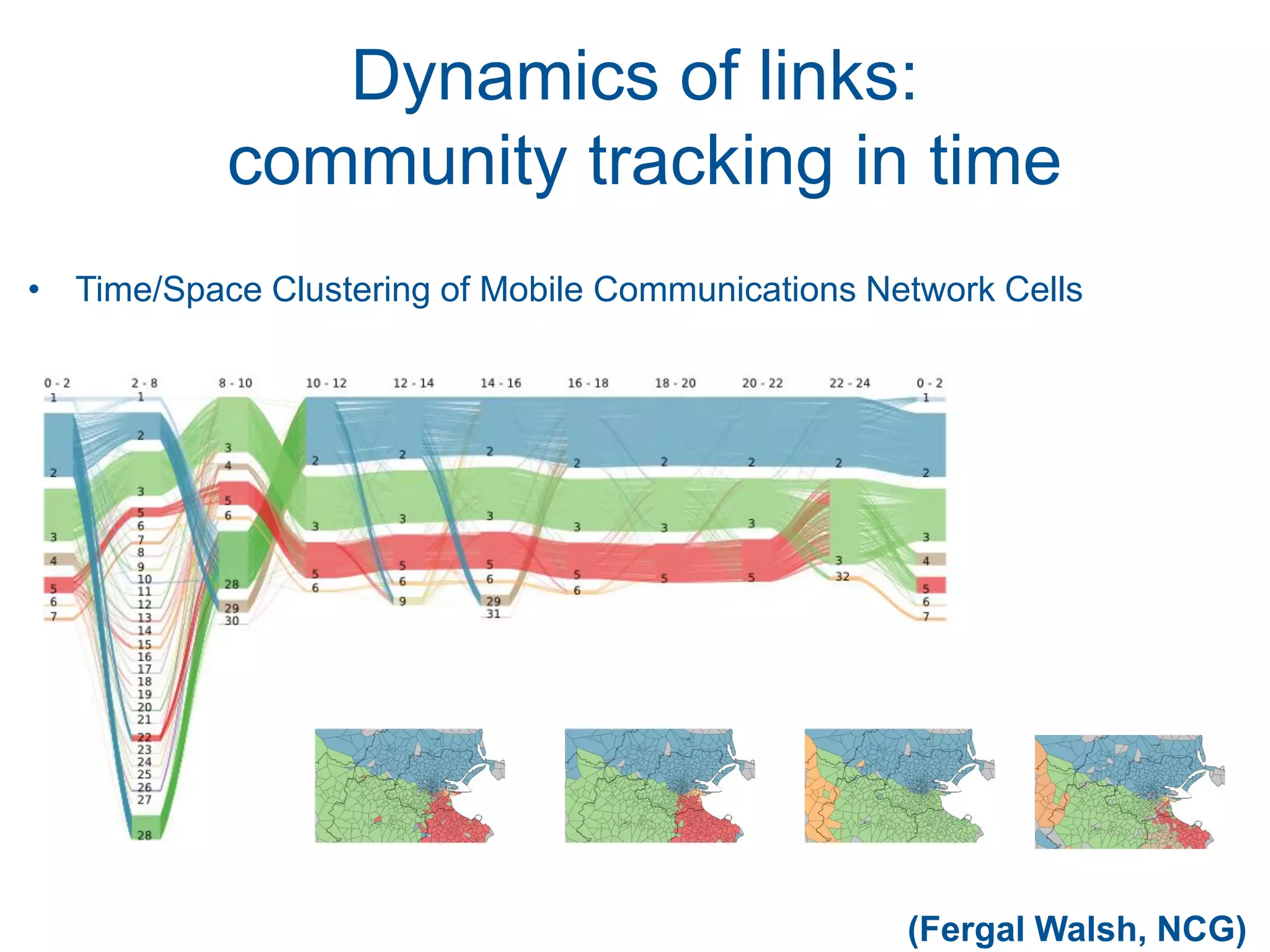
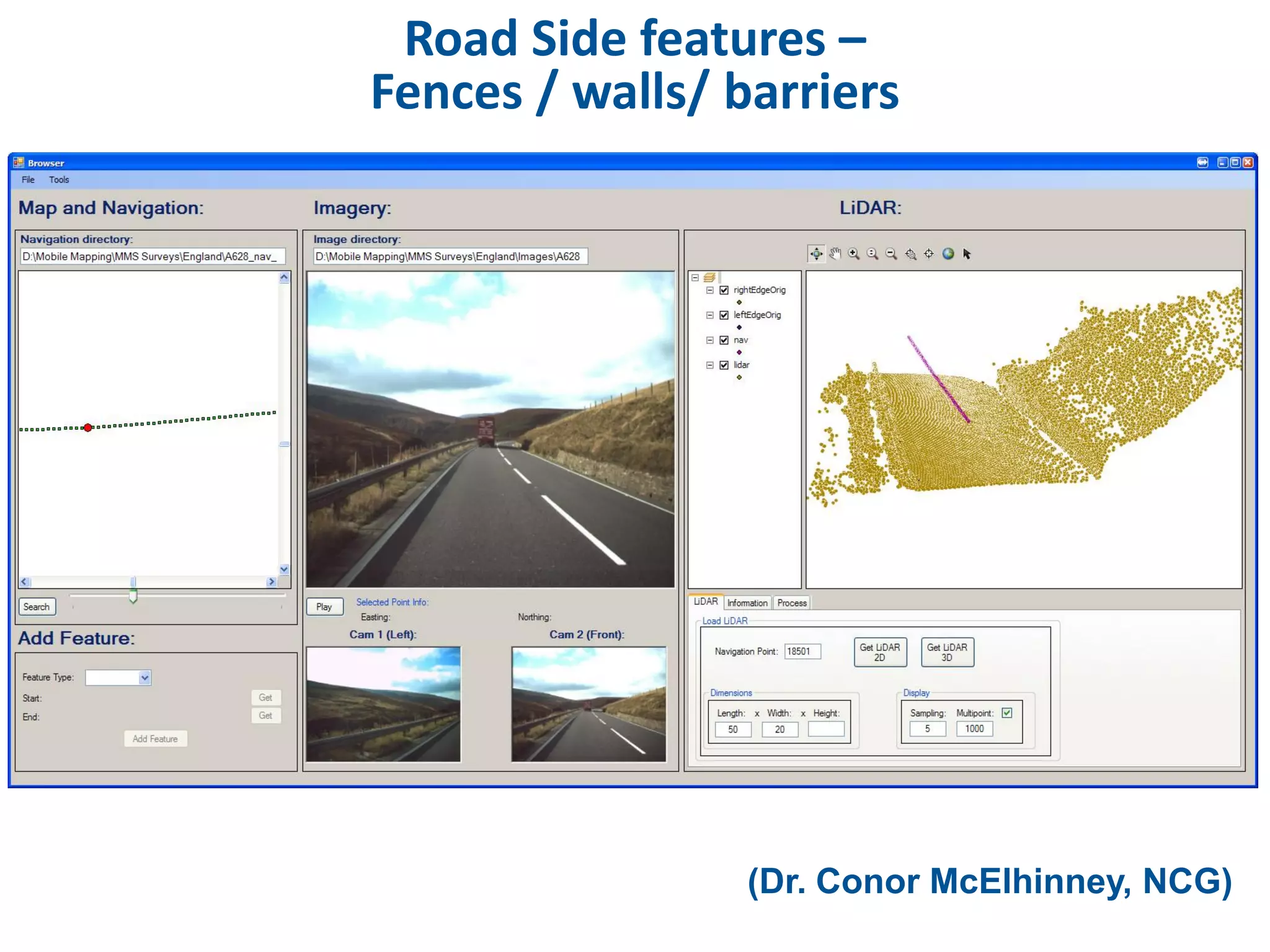
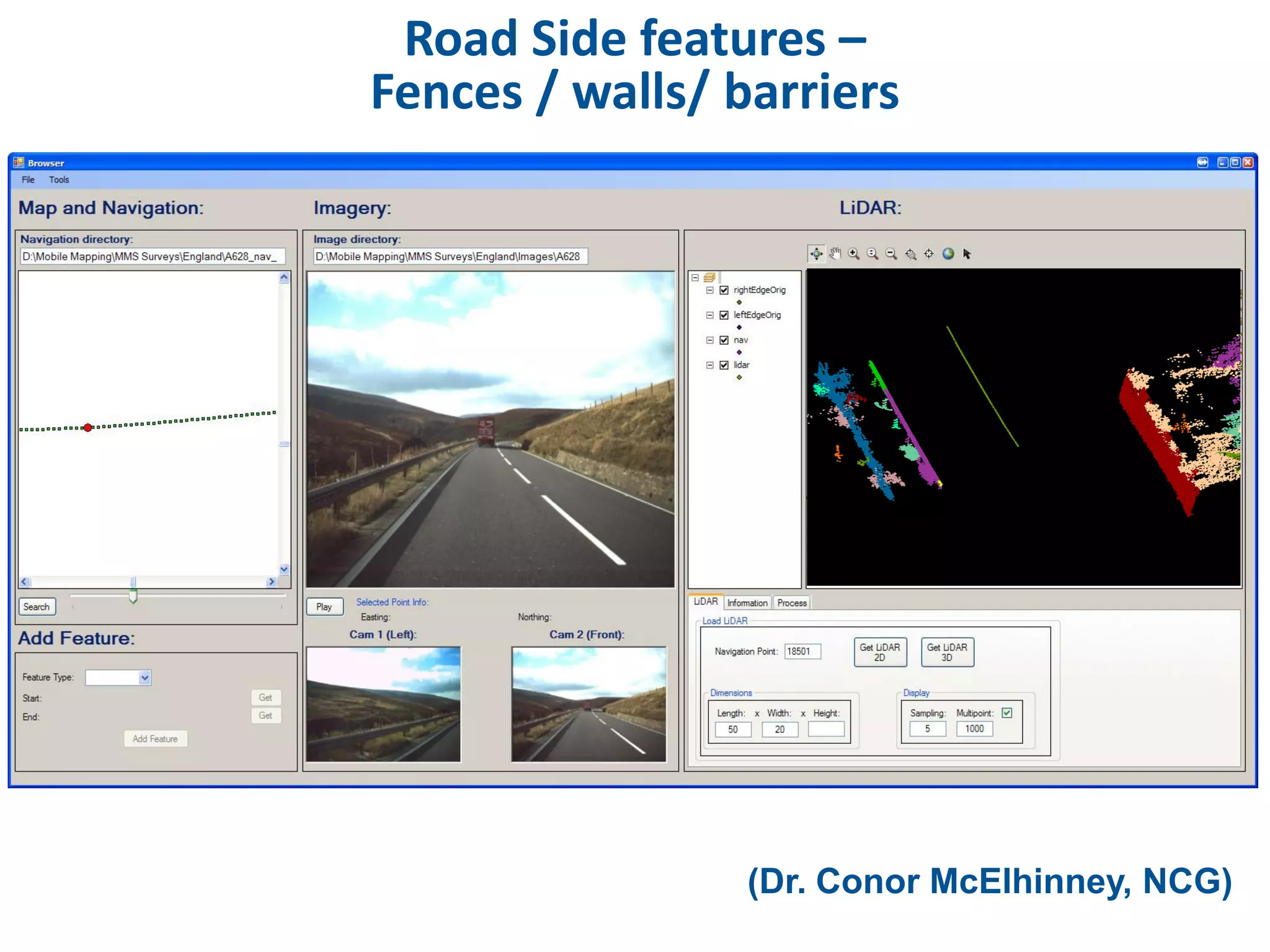
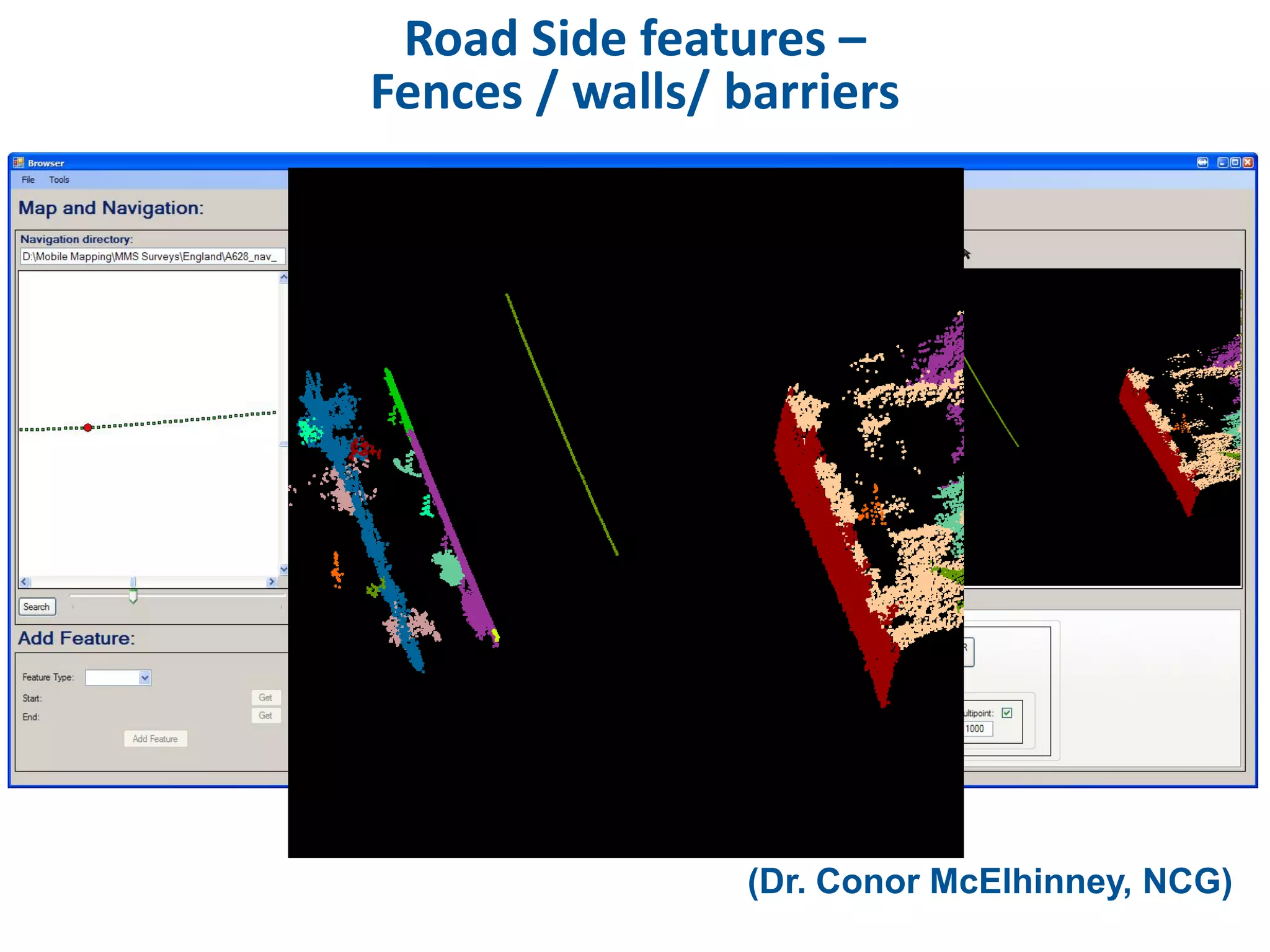
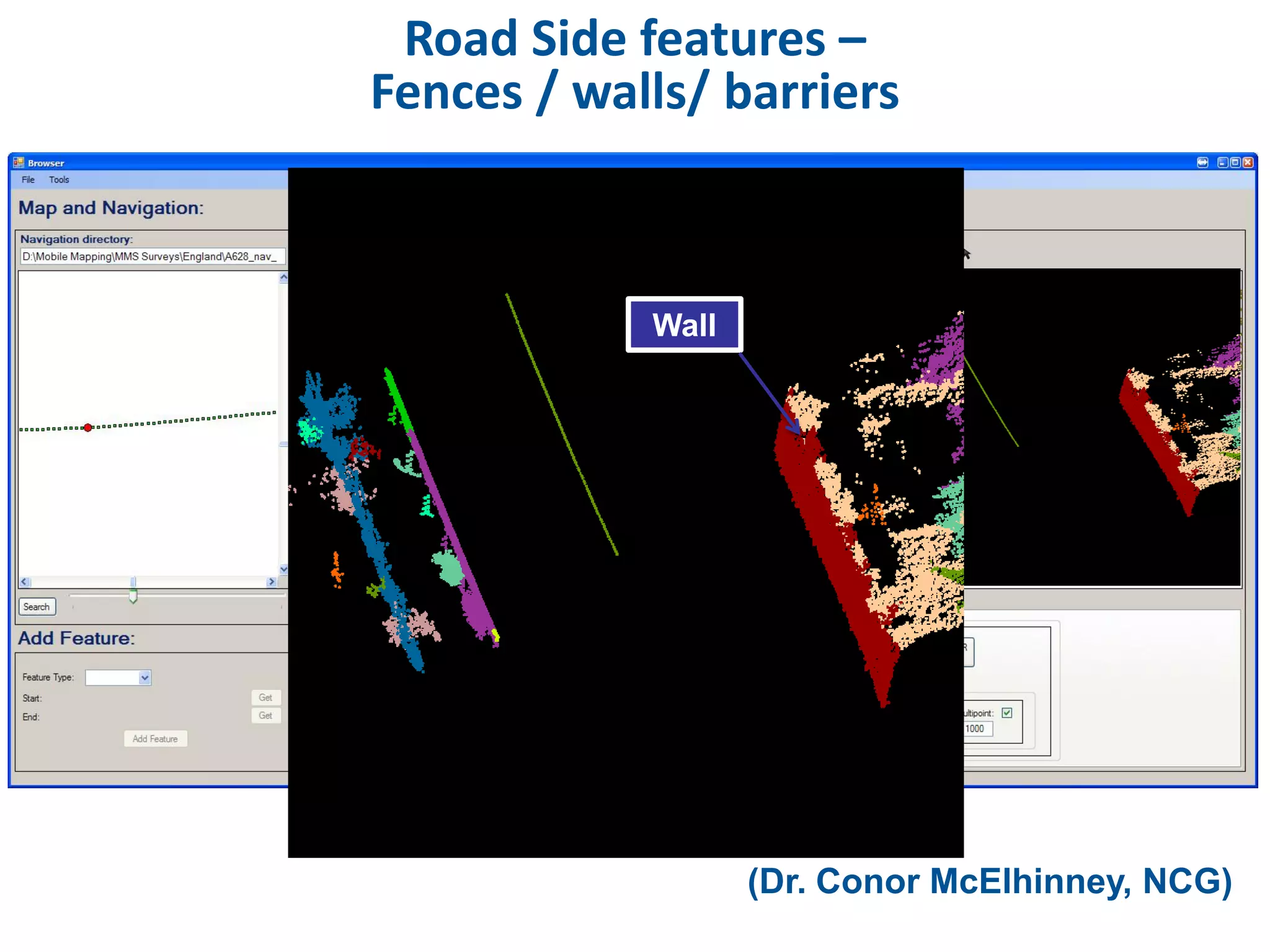
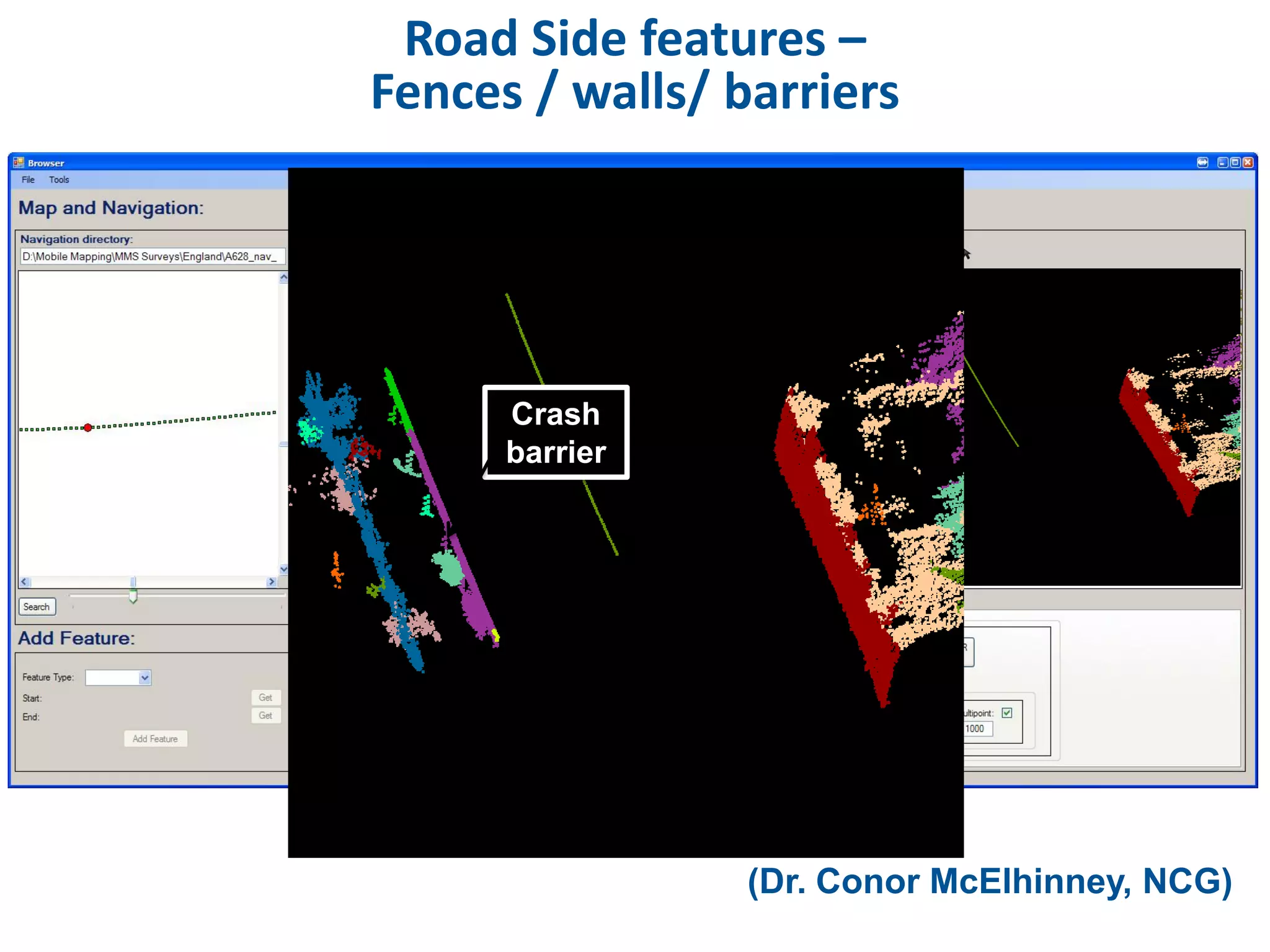
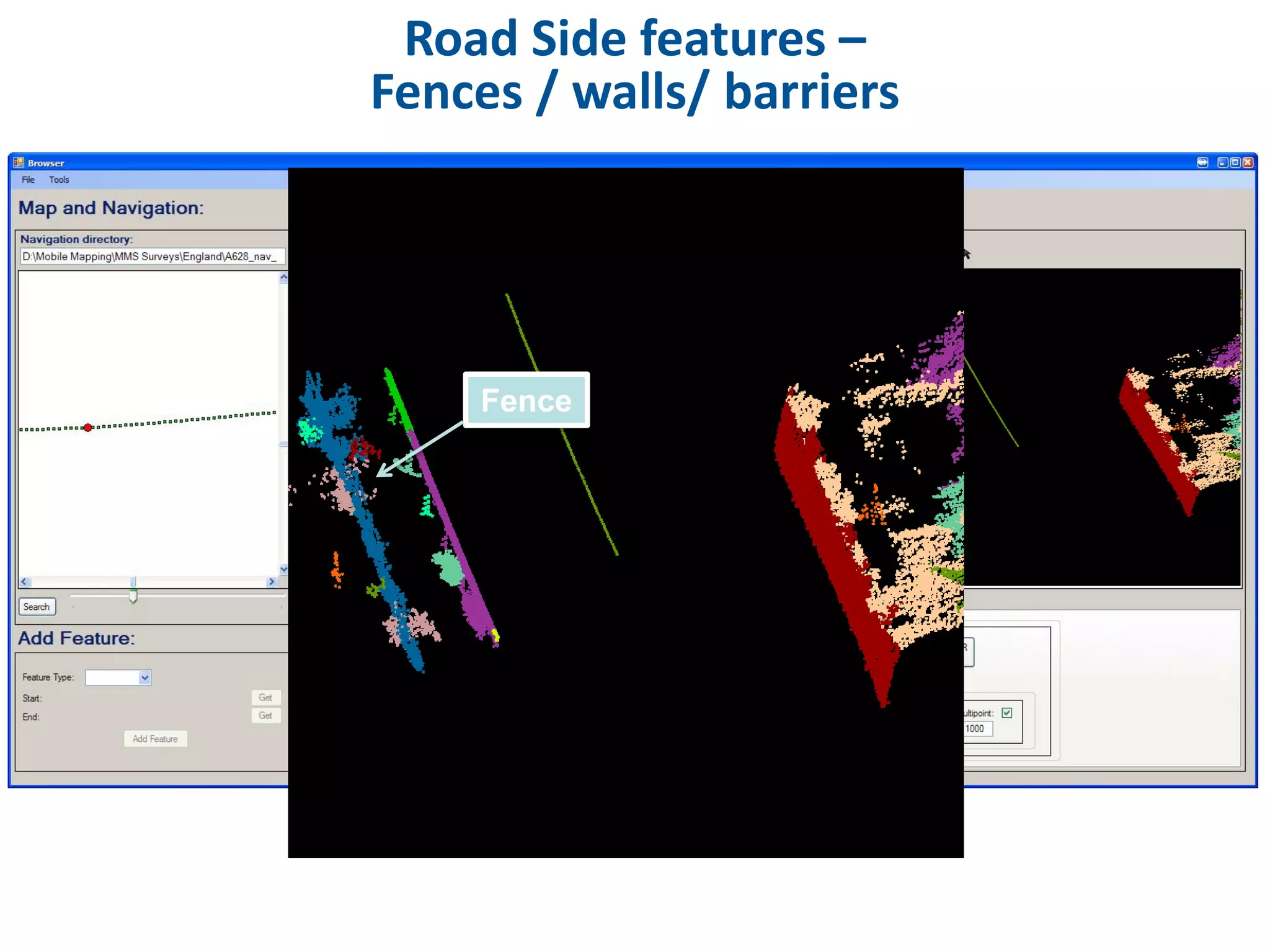
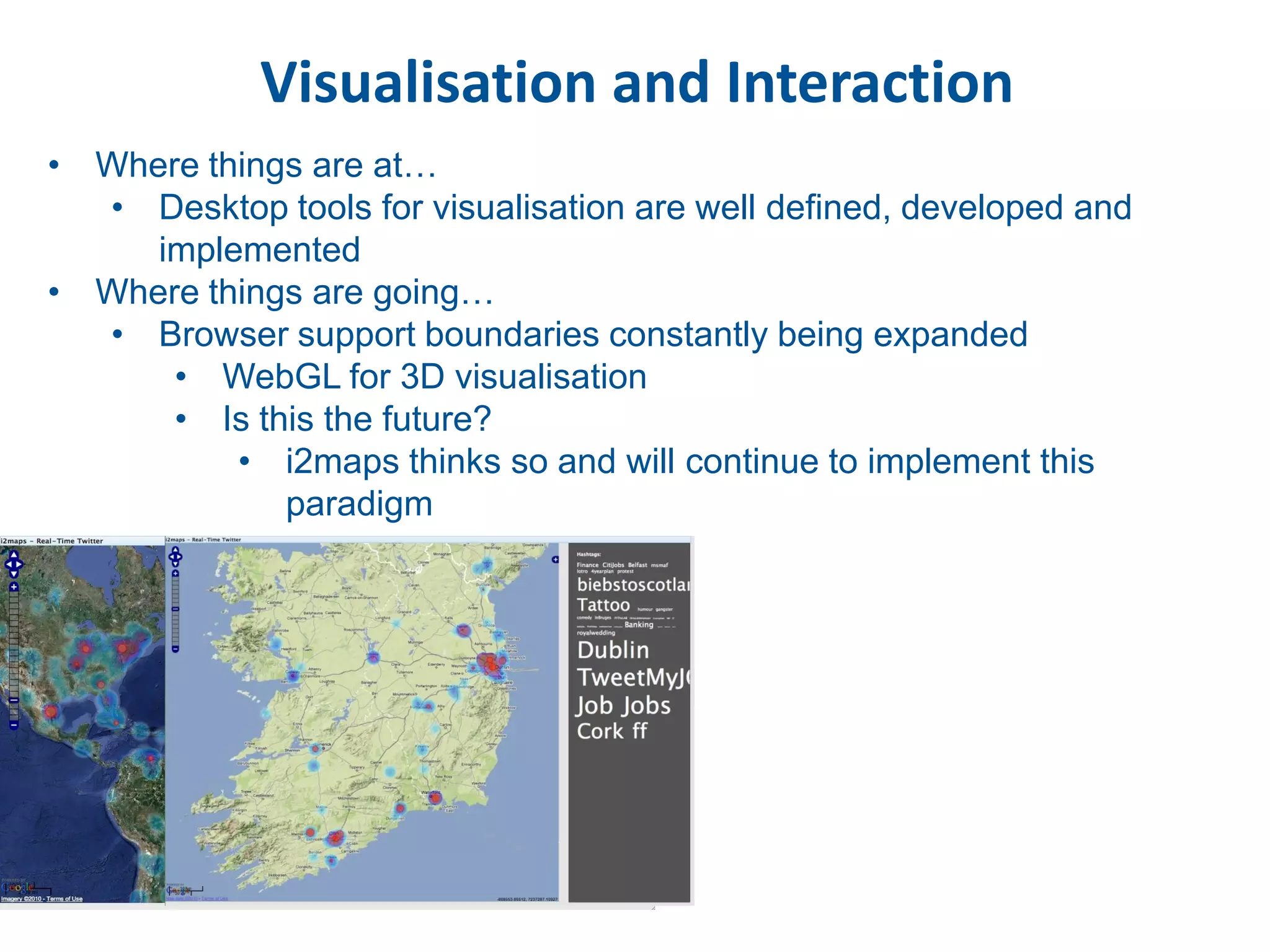
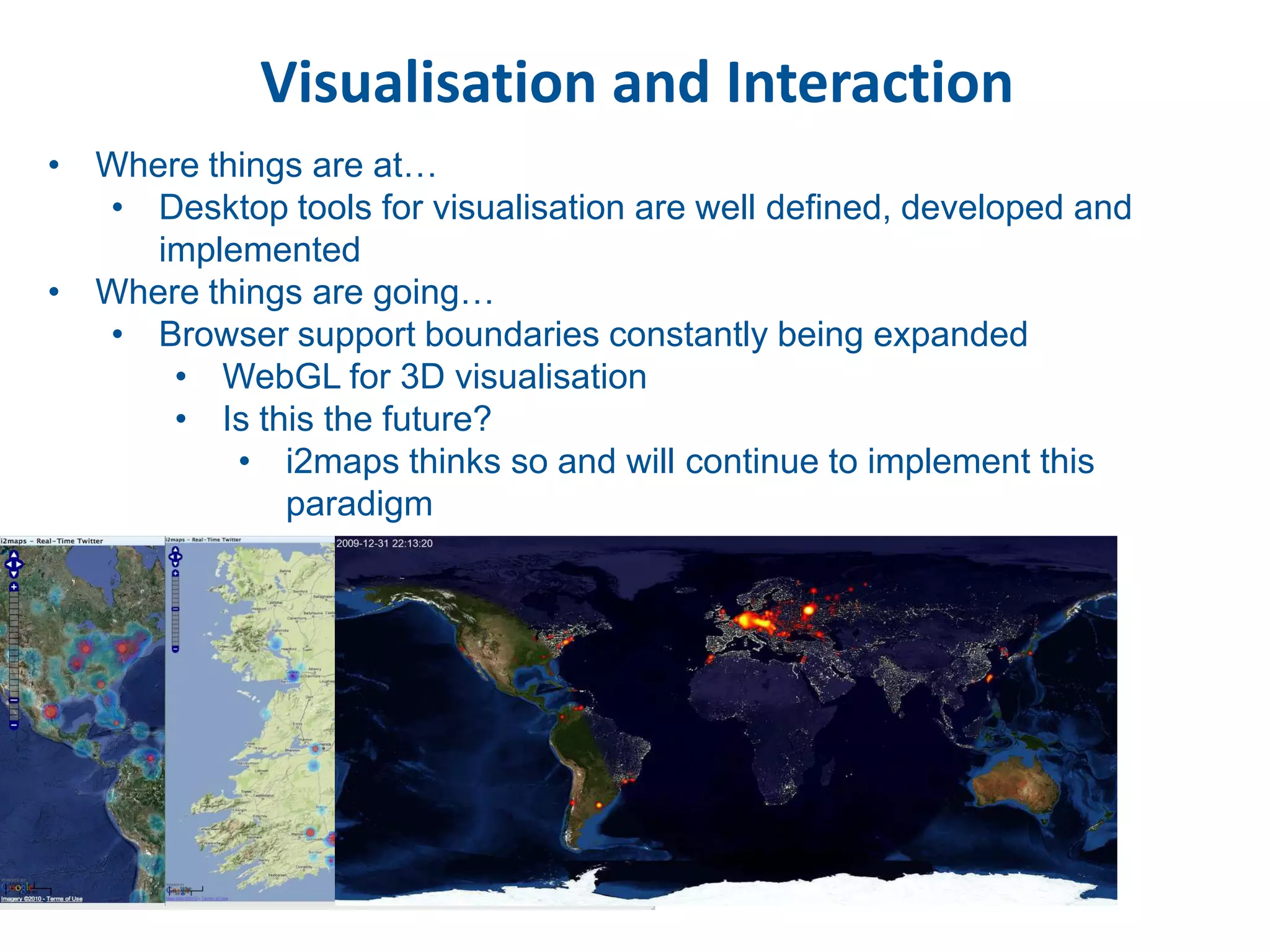
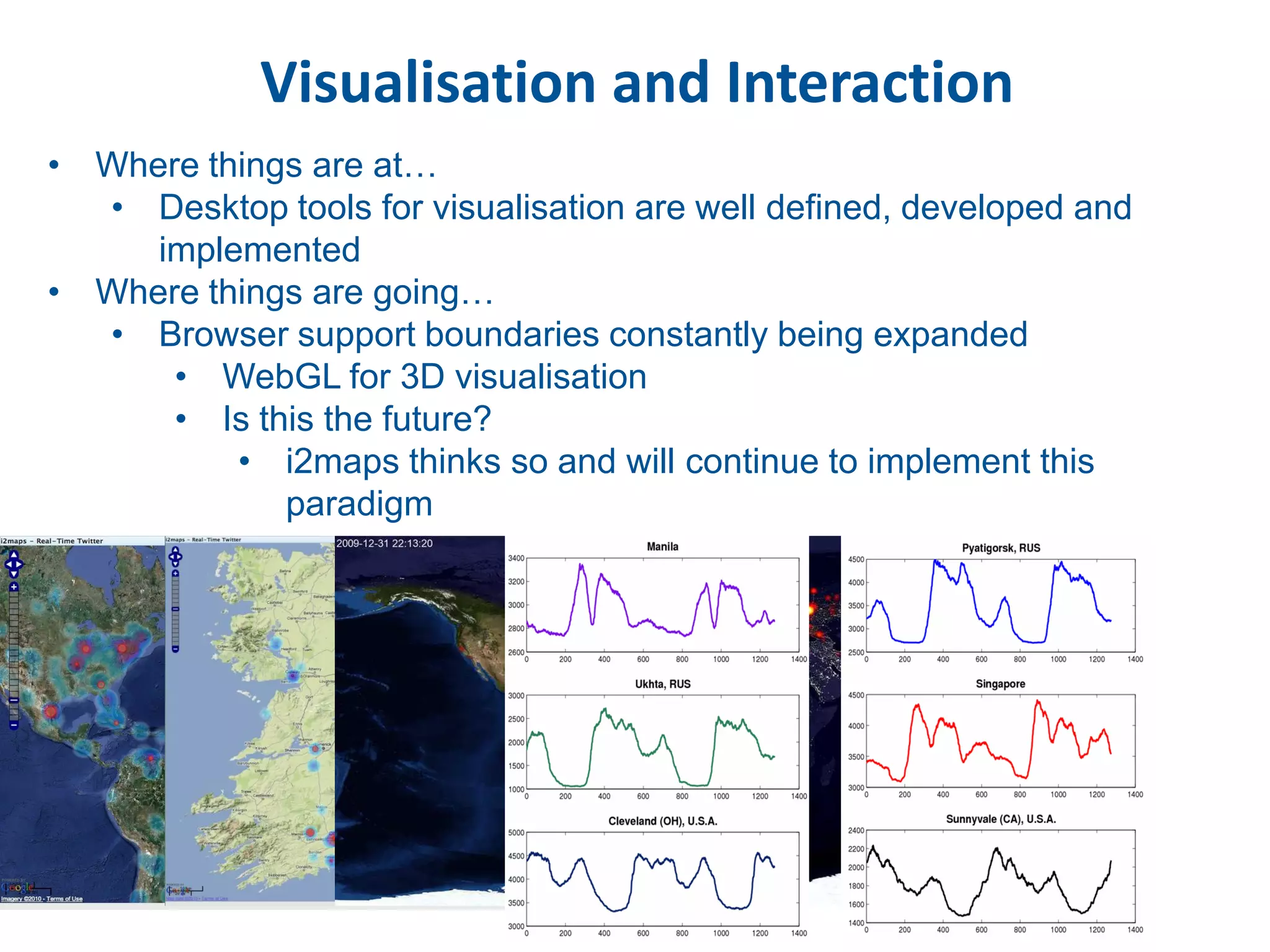
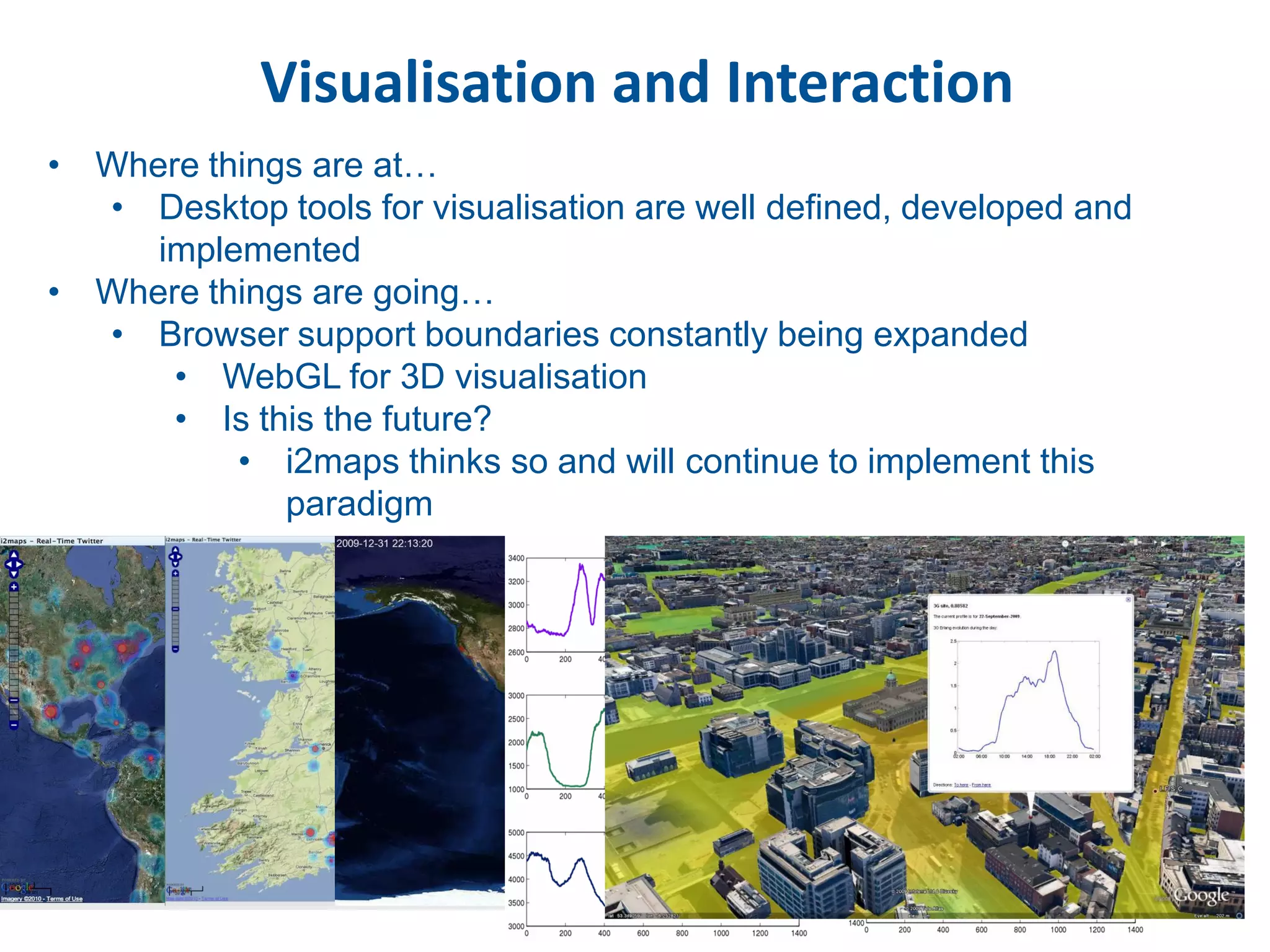
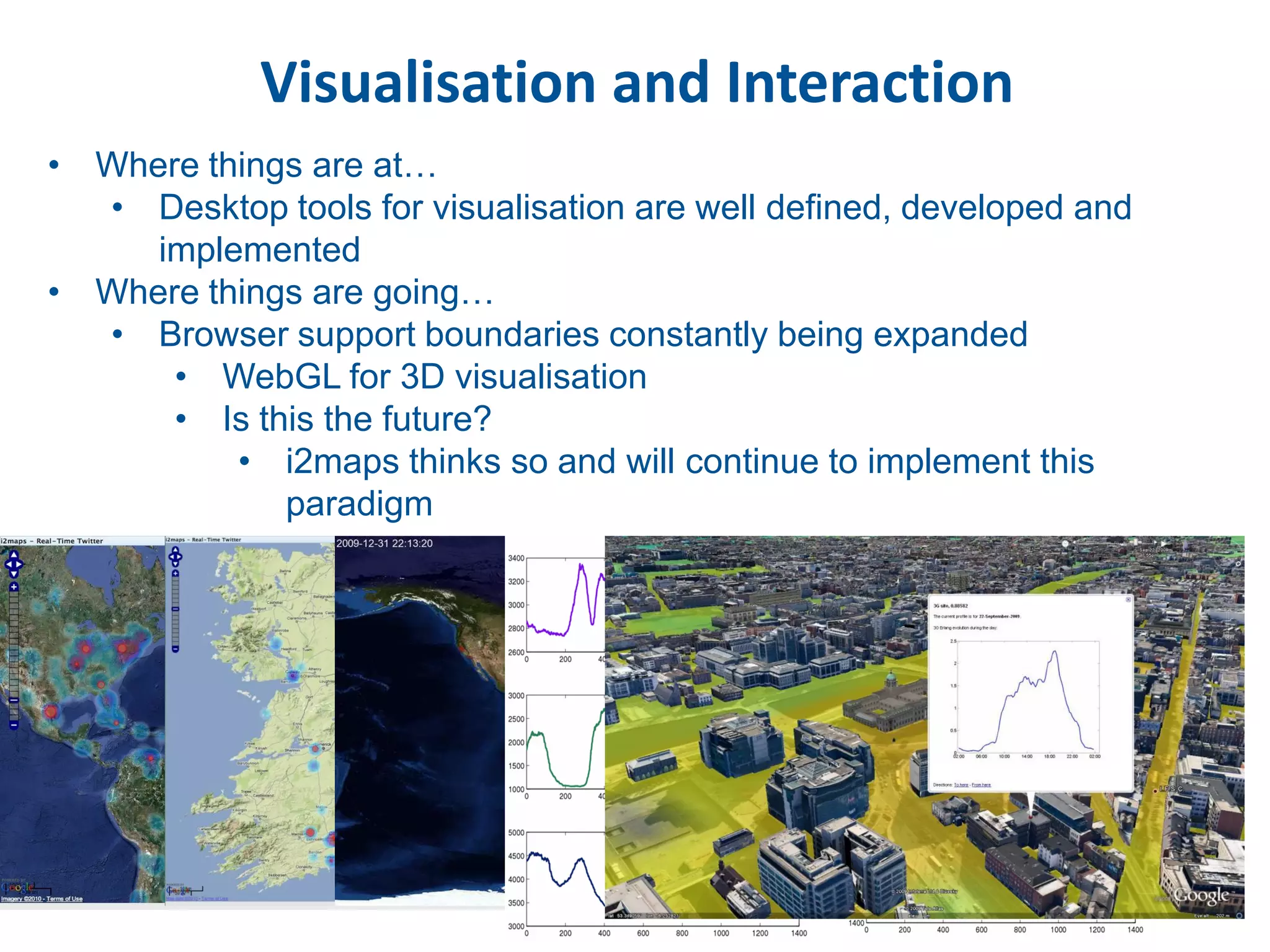
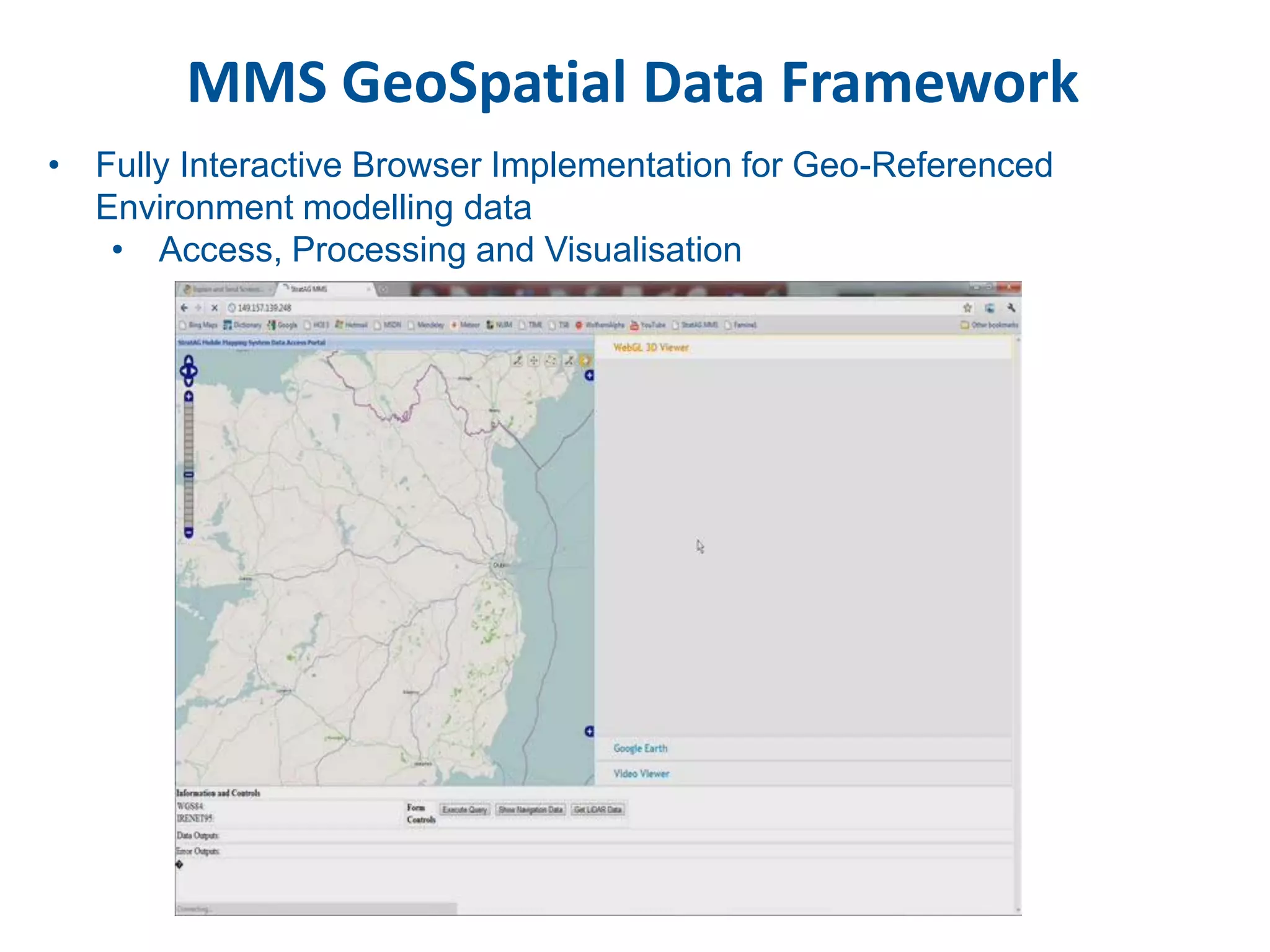
This document discusses methods for accessing, processing, and extracting knowledge from geo-referenced human activity data. It describes challenges in modeling geospatial data from different sources and accessing data through spatial hierarchy models. It also covers processing paradigms for knowledge extraction, including spatial workflow patterns and temporal dynamics in communities from data sources like tweets. Visualization and interaction techniques are discussed, including moving toward 3D web-based visualization using technologies like WebGL. Feature extraction from data is highlighted as informing risk assessment knowledge.