Embed presentation
Downloaded 14 times



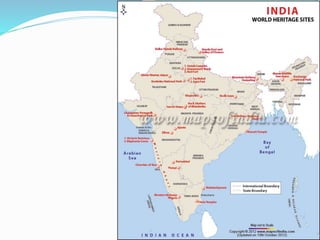

![Over the years, 30 more sites have been
inscribed, the latest being the Great Himalayan
National Park in 2014.[4] Of these 32 sites, 25
are cultural sites and the other seven are natural
sites. A tentative list of further sites/properties
submitted by India for recognition includes 51
sites. The cultural sites in India are marked by
their brilliant craftsmanship on stone. Most of
the temples of India which are inscribed on this
list are built in stone, without any mortar and
with sculpture carved on it.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/geological-151018021814-lva1-app6891/85/Geological-6-320.jpg)

The document defines geoheritage as the geological features of a place that are intrinsically important sites or culturally important sites that provide insights into the formation of Earth or the history of science. These include igneous, metamorphic, sedimentary, and other attributes at all scales. The term geoheritage was first mentioned in 1991 at a conference in France, but the first use of the specific term was at a conference in the UK in 1994. India has 32 UNESCO World Heritage Sites recognized for their importance as cultural or natural heritage, including 25 cultural sites like temples built without mortar and carved stone sculptures, and 7 natural sites.





![Over the years, 30 more sites have been
inscribed, the latest being the Great Himalayan
National Park in 2014.[4] Of these 32 sites, 25
are cultural sites and the other seven are natural
sites. A tentative list of further sites/properties
submitted by India for recognition includes 51
sites. The cultural sites in India are marked by
their brilliant craftsmanship on stone. Most of
the temples of India which are inscribed on this
list are built in stone, without any mortar and
with sculpture carved on it.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/geological-151018021814-lva1-app6891/85/Geological-6-320.jpg)
