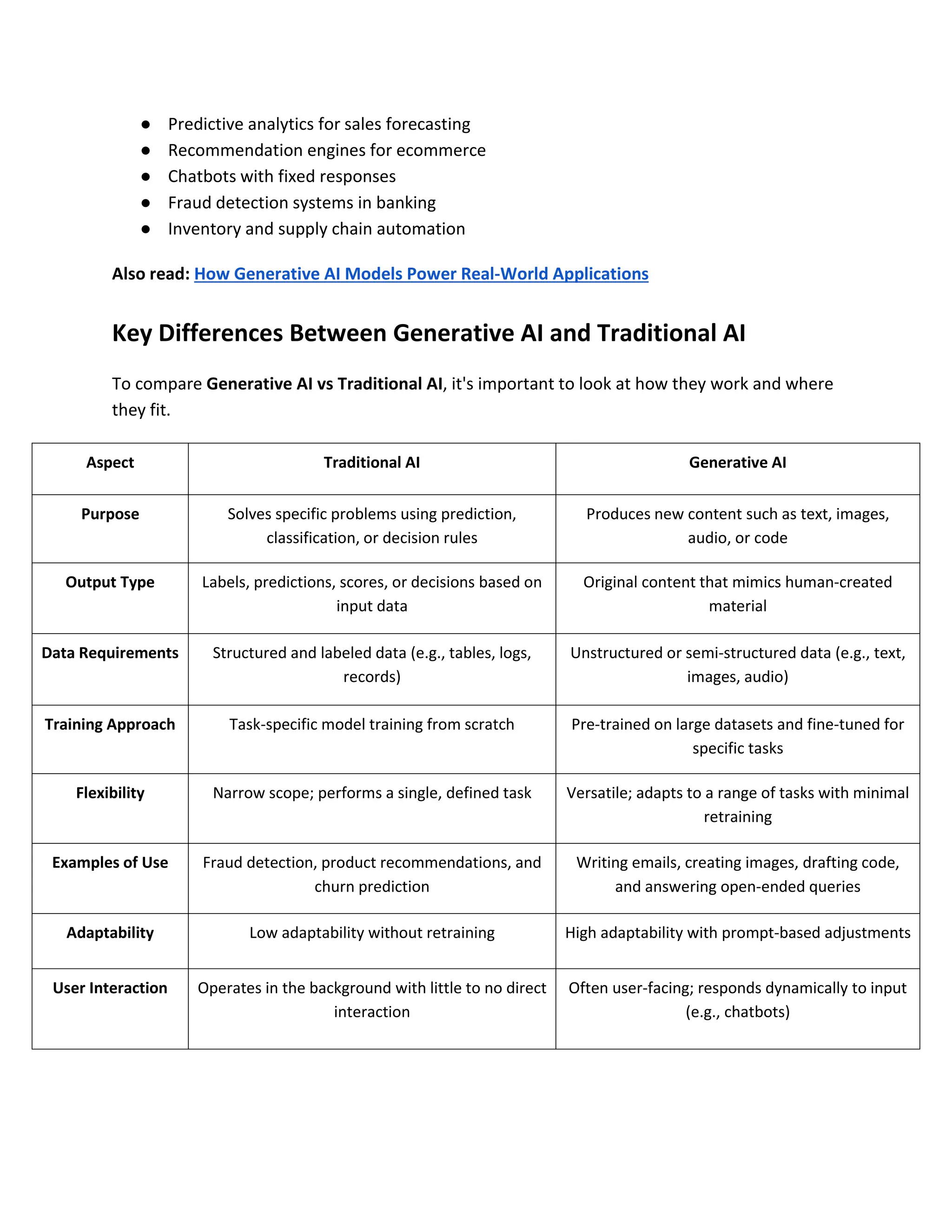
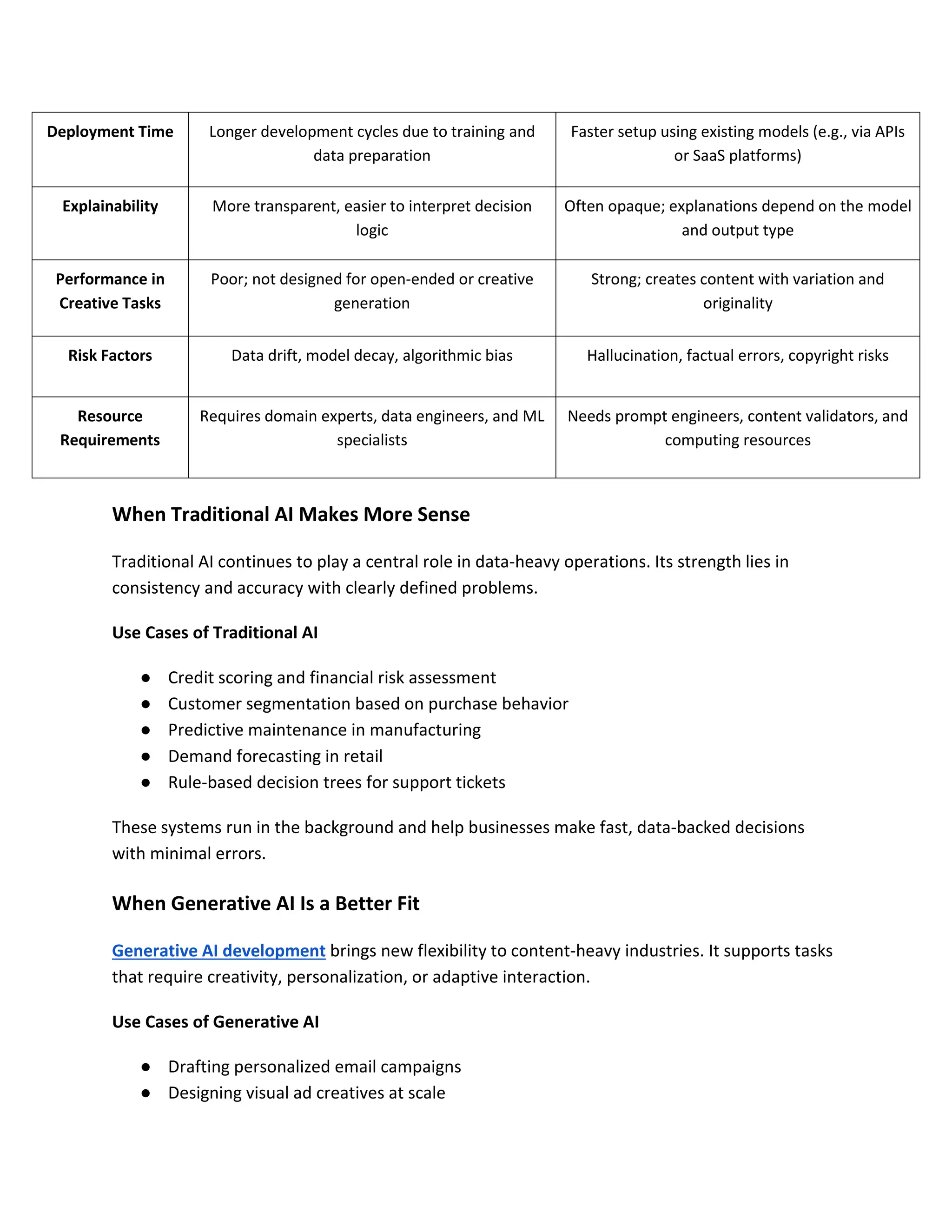
This blog breaks down the key differences between Generative AI and Traditional AI, helping business owners understand which one suits their needs. It explains how each type works, where they are most useful, and the real-world results they offer.
Whether you're curious about AI tools that create content or those that follow rules to solve tasks, this post gives a clear side-by-side look. Ideal for decision-makers looking to pick the right AI path for their business goals without getting lost in technical terms.
#GenerativeAIandTraditionalAIDifferences