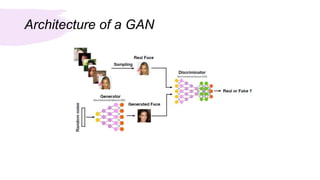
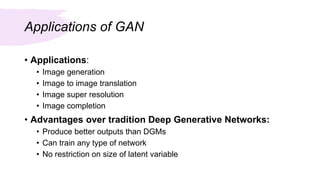
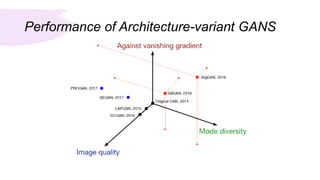
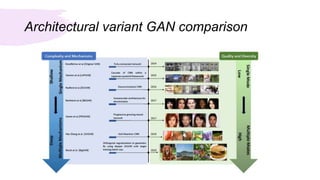
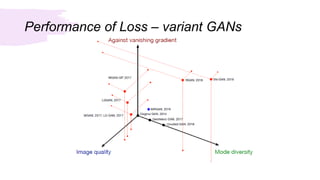
This document summarizes a survey of Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) in computer vision. It introduces GANs and discusses their applications in image generation, translation, super resolution and completion. It then outlines challenges with GANs like generating high quality diverse images and stable training. GANs are classified into two categories - architecture-variant GANs which modify network architecture, and loss-variant GANs which modify the loss function. Several examples of each category are described along with their performance and ability to address issues like vanishing gradients or improve image quality through techniques like progressive training. In conclusion, the document reviews GAN variants aimed at improving training stability and image quality.