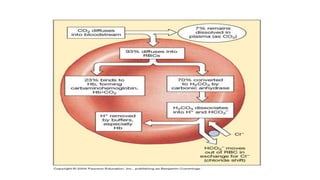
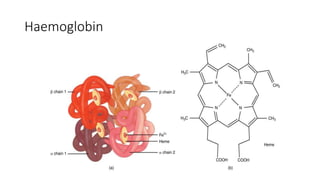
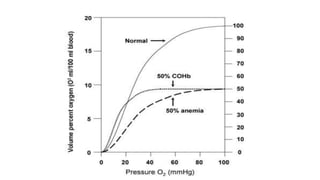
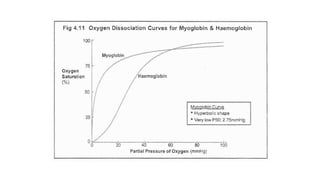
The document summarizes gas transport in the body. It describes how oxygen moves from the alveoli in the lungs to tissues via diffusion and binding to hemoglobin in red blood cells. Hemoglobin has a higher affinity for oxygen when carbon dioxide levels are higher, facilitating unloading of oxygen to tissues. Carbon dioxide is transported primarily as bicarbonate in plasma and binds reversibly to hemoglobin as well. The oxygen content of arterial blood and cardiac output determine the oxygen flux or amount of oxygen delivered to tissues per minute to meet metabolic demands.













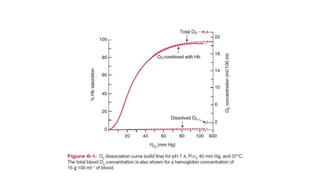






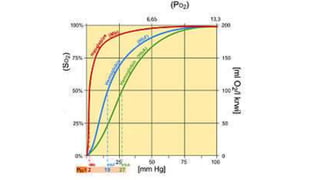
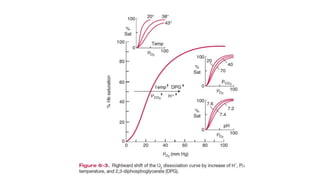
![Physiological significant
• Flat upper part acts as a buffer-
• PO2 can drop to 80mmHg, yet Hb remained highly saturated (96%) with
oxygen keeping the arterial [O2] high despite impairment in saturation in the
lungs
• Steep lower part allows large O2 unloading and maintain O2 diffusion
gradient (from capillary to cell) by only a small drop in PO2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gastransport-221106062350-a67dca3a/85/Gas-Transport-pptx-22-320.jpg)




![Oxygen content
• 98% is carried bound to Hb in RBC, only 2% of O2 in arterial blood is
present as dissolved O2
• One gram of Hb can combine with 1.34 ml O2 when 100% saturated
• Functional Hb saturation= [HbO2] x ( [HbO2] + [DeoxyHb]
(1 gm pure Hb binds 1.39mls O2)
• Fractional saturation = ( [HbO2] x 100/total [Hb] )
where total [Hb] = [HbO2] + [DeoxyHb] + [metHb] + [COHb]
(Physiological value ~ 1.34 to 1.37 ml.O2/gmHb)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gastransport-221106062350-a67dca3a/85/Gas-Transport-pptx-31-320.jpg)
![• Total O2 content of arterial blood
CaCO2 = [1.34x(Hb)xSaO2] + [PaCO2 x kO2]
• CaCO2=O2 content (mlO2/dl Blood)
• Hb= hemoglobin concentration (g/dl)
• SaO2= O2 saturation of Hb
• kO2= O2 solubility constant (0.003ml O2/mmHg/dl of blood)
• Normal blood contains 15 gm of Hb/dl of blood
• CaCO2= (1.34x15x1) + (0.003x100)
= 20.4 mls/dl blood
• Thus normal O2 content is about 20.4ml O2/ dl of blood
(if 100% saturated)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gastransport-221106062350-a67dca3a/85/Gas-Transport-pptx-32-320.jpg)
![O₂ Consumption by cell ~250mlsO₂/min
• Arterial point PaO₂ 100mmHg, SaO₂97.5% = 19.9mls O₂/dL
• Venous point PaO₂ 40mmHg, SaO₂ 75%
CaCO2 = [1.34x(Hb)xSaO2] + [PaCO2 x kO2]
= 15.1 + 0.12
= 15.22 O₂/dL
O₂ Consumption 19.9.-15.2= 4.7mls O₂/dL
~ 5x50=250mls O₂/min](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gastransport-221106062350-a67dca3a/85/Gas-Transport-pptx-33-320.jpg)

![• Oxygen Flux equation
oxygen flux = chemical O2 delivery + Dissolved O2 delivery
= [CO x (Hb) x SaO2 x k] + [CO x PaO2 x 0.003]
= [50 x 15 x 0.99 x 1.34] + [50 x 100 x 0.003]
= 995 + 15
= approx 1000 mls O2/ min
k – Huffner’s number (1.34mlO2/gm.Hb)
CO in dl/min; Hb in gm/dl](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gastransport-221106062350-a67dca3a/85/Gas-Transport-pptx-35-320.jpg)