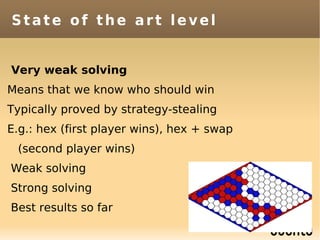
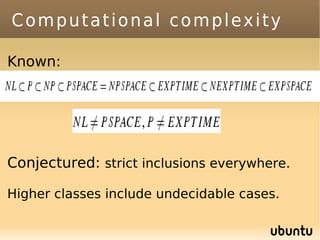
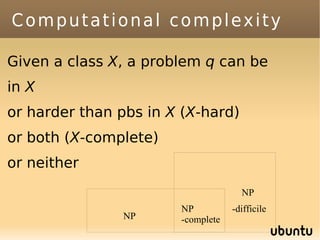
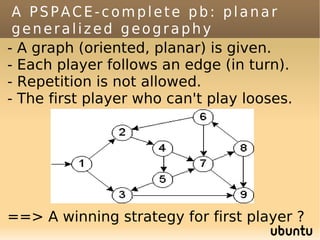
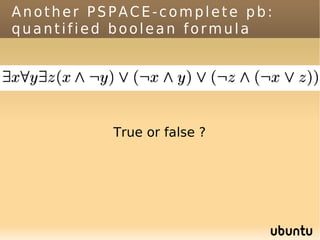
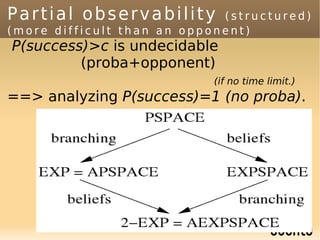
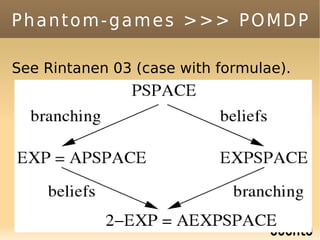
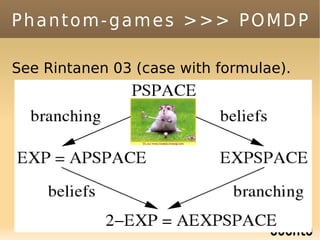
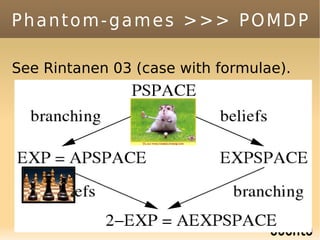
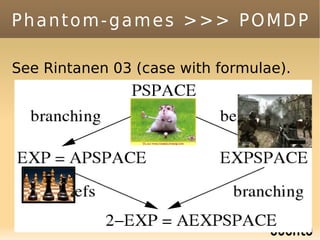
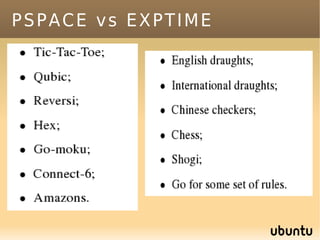
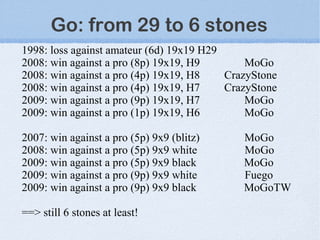
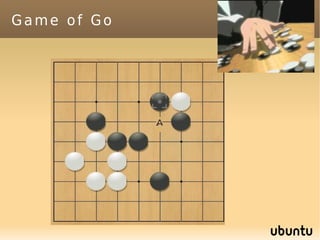
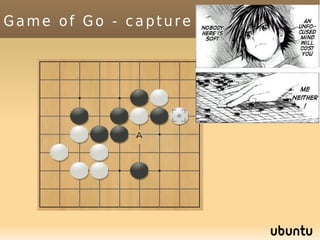
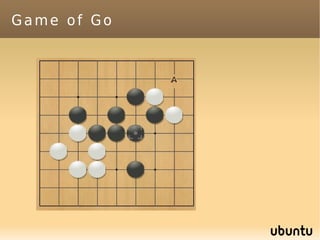
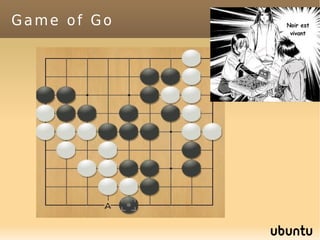
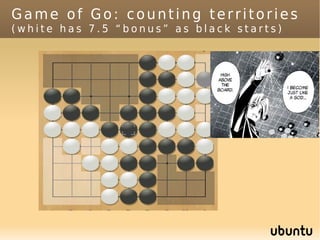
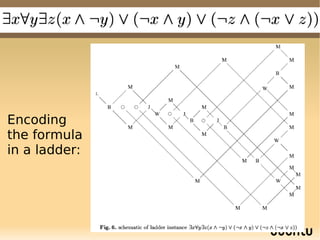
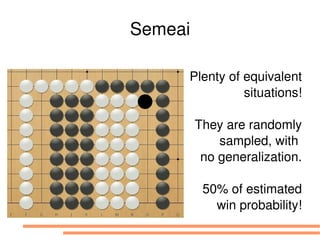
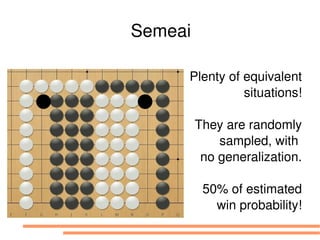
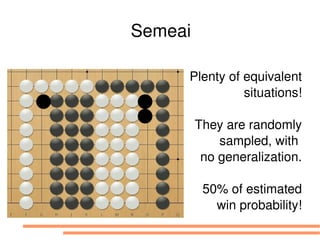
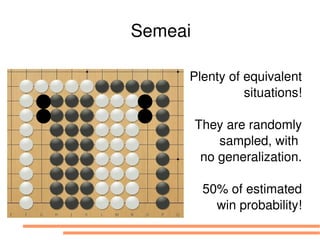
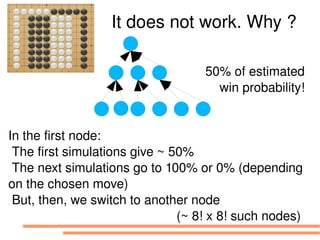
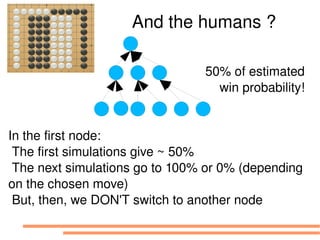
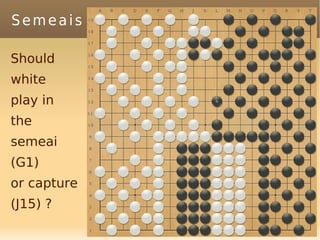
The document discusses bandit-based Monte Carlo planning, focusing on games such as Go, and explores complexity measures, computational complexity, and various game types including partially observable games. It highlights the evolution of AI performance in games like draughts and chess, the intricacies of decision-making in complex game scenarios, and the relationship between game complexity and human versus machine competition. The work also contemplates ongoing challenges for Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS) methods in handling large and partially observable game environments.