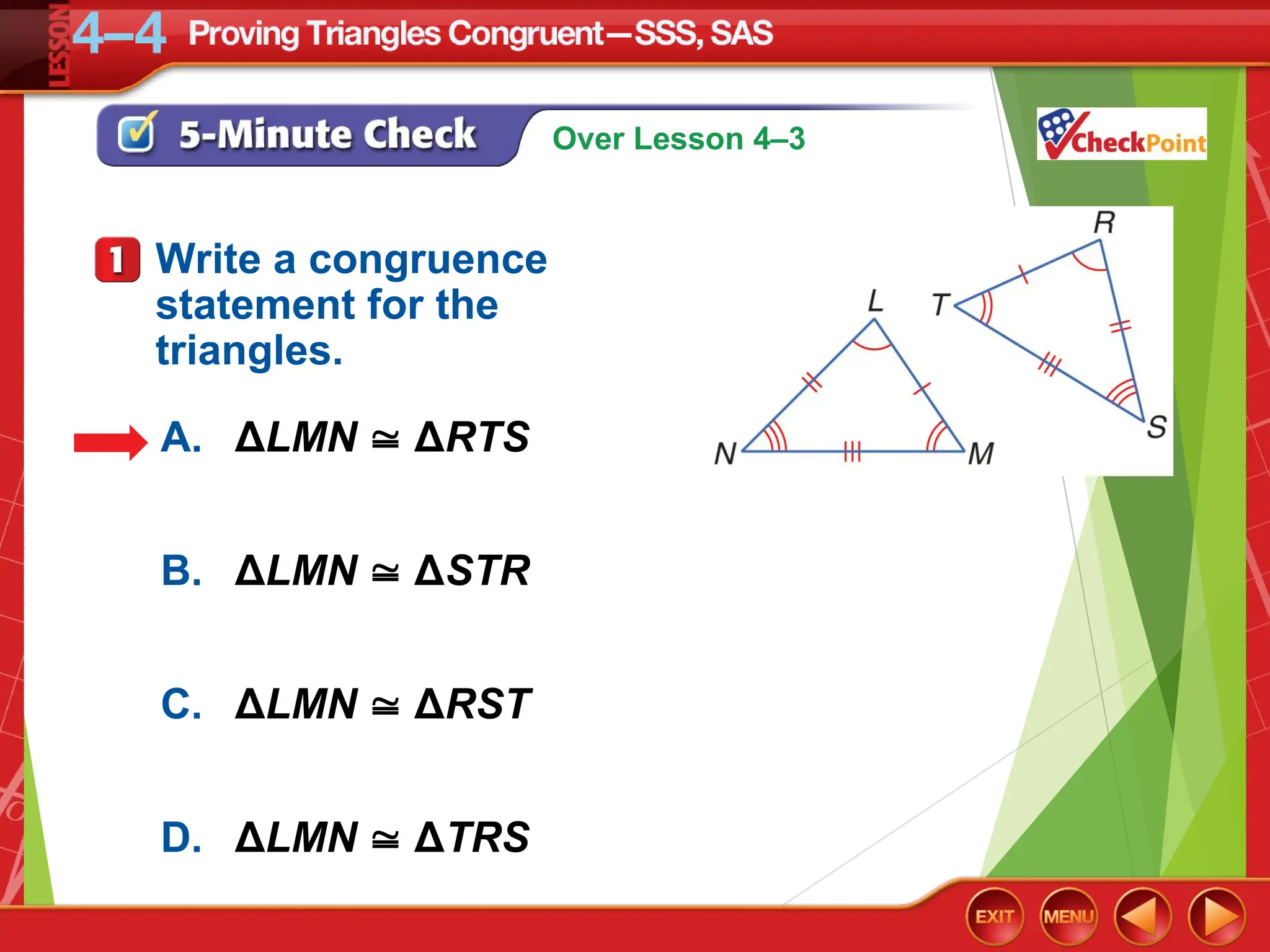
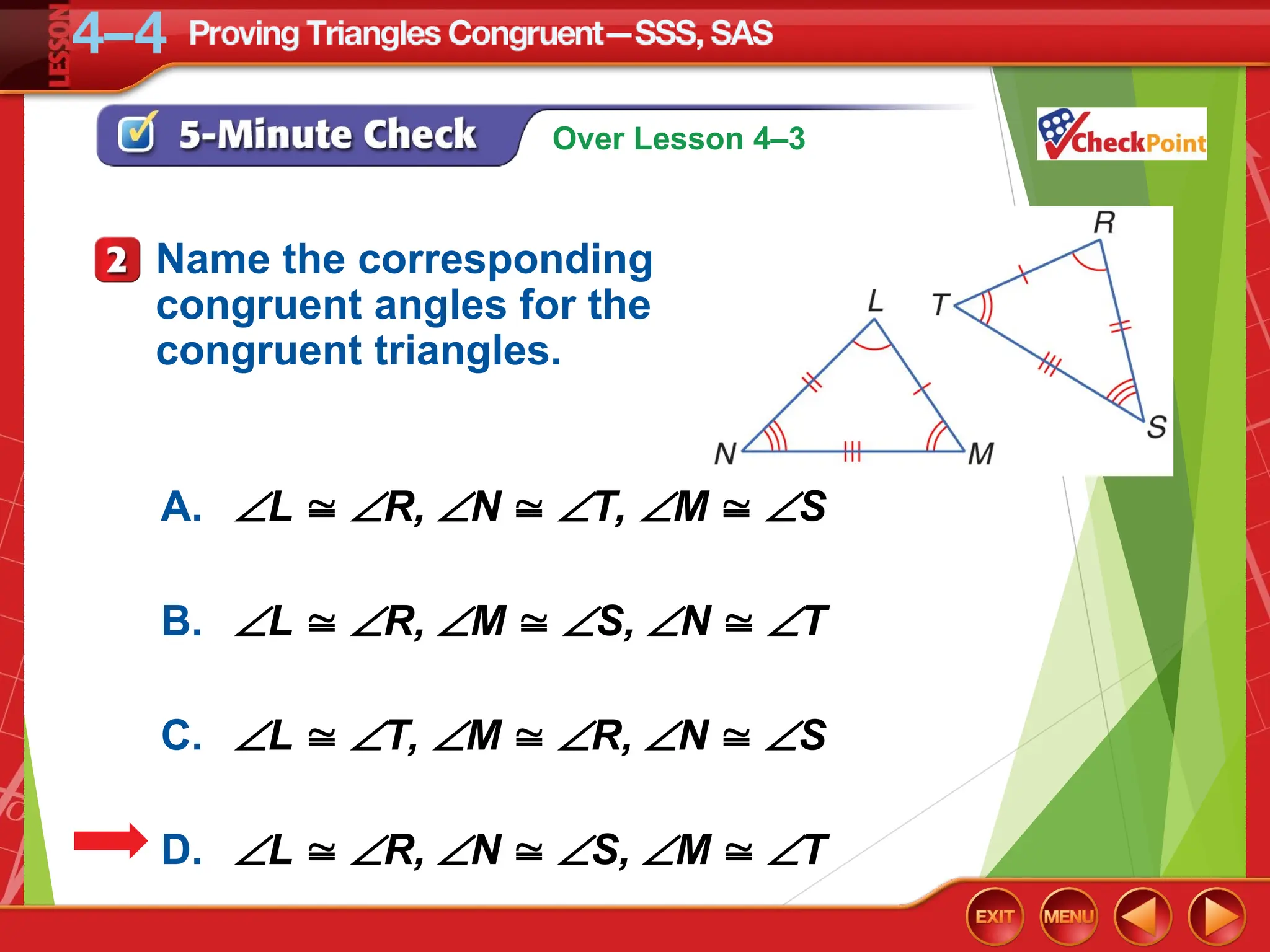
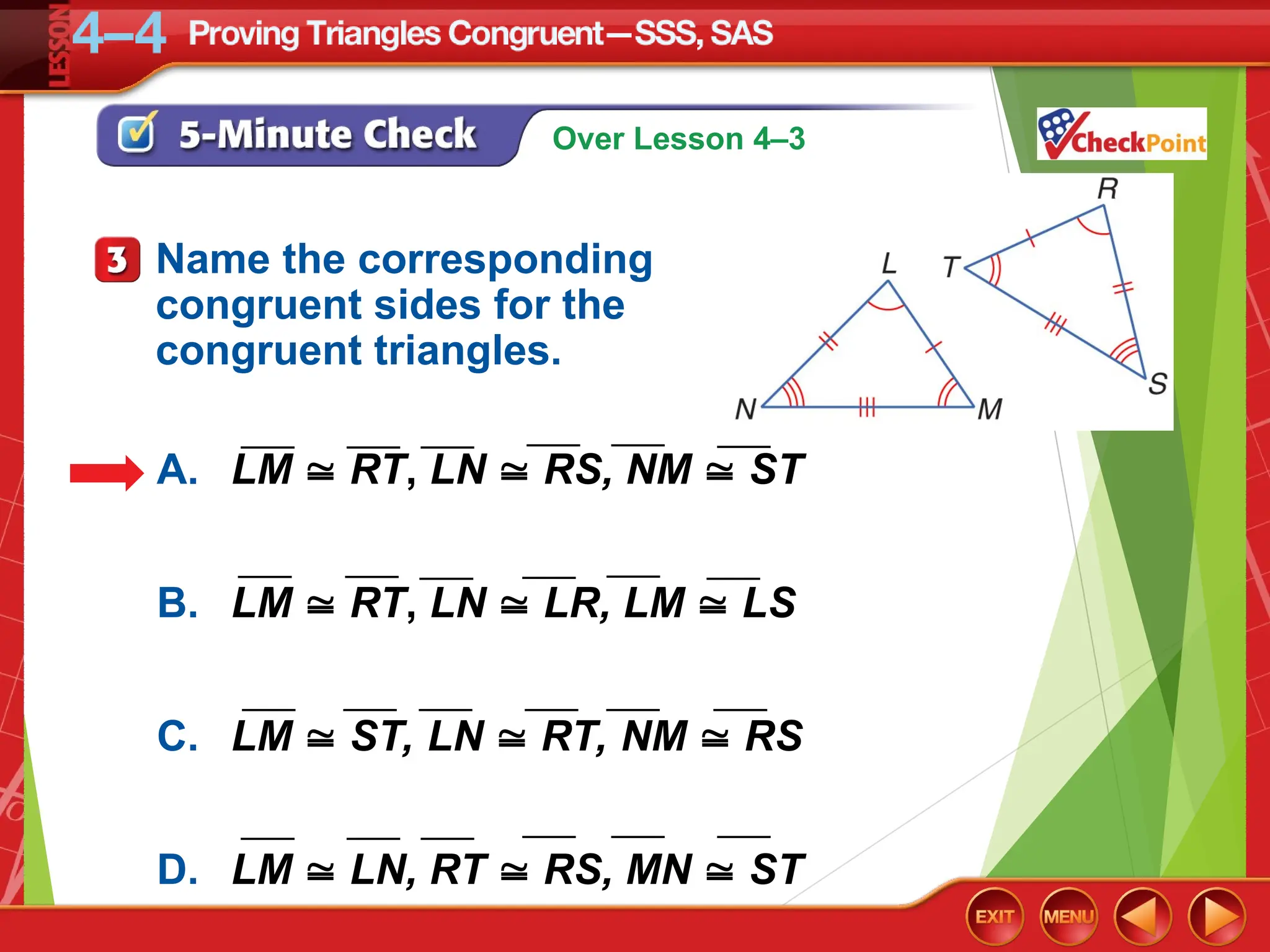
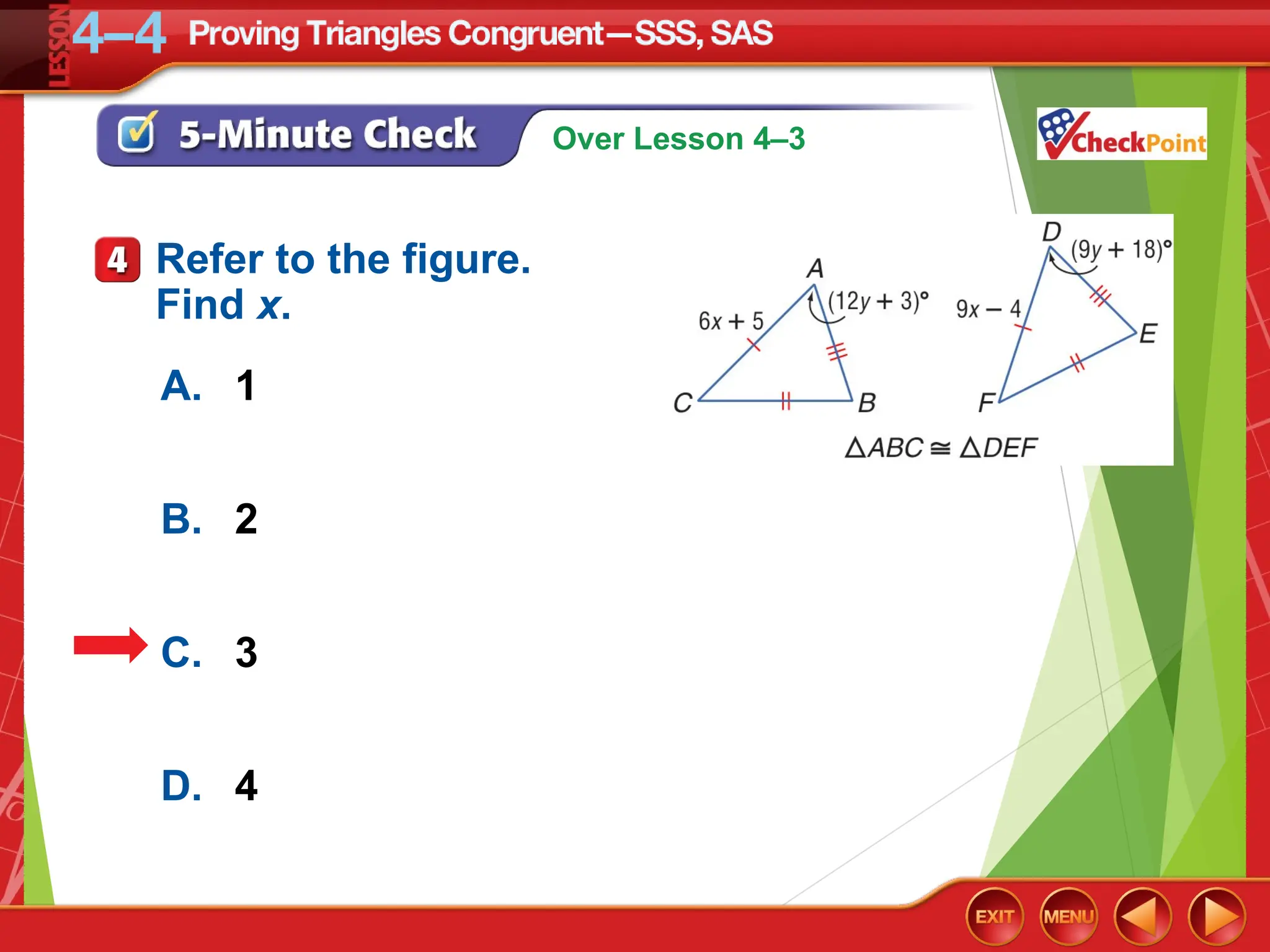
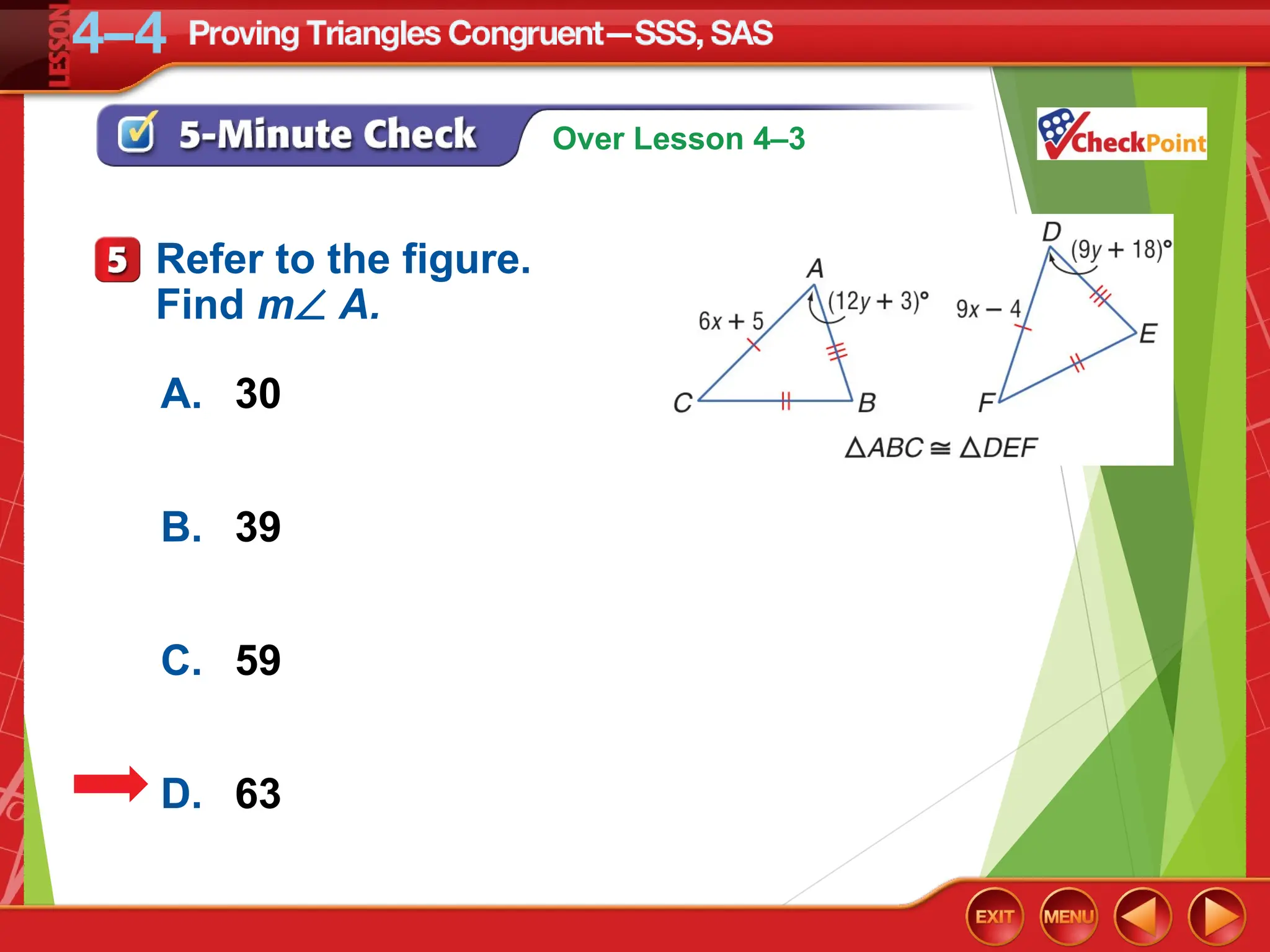
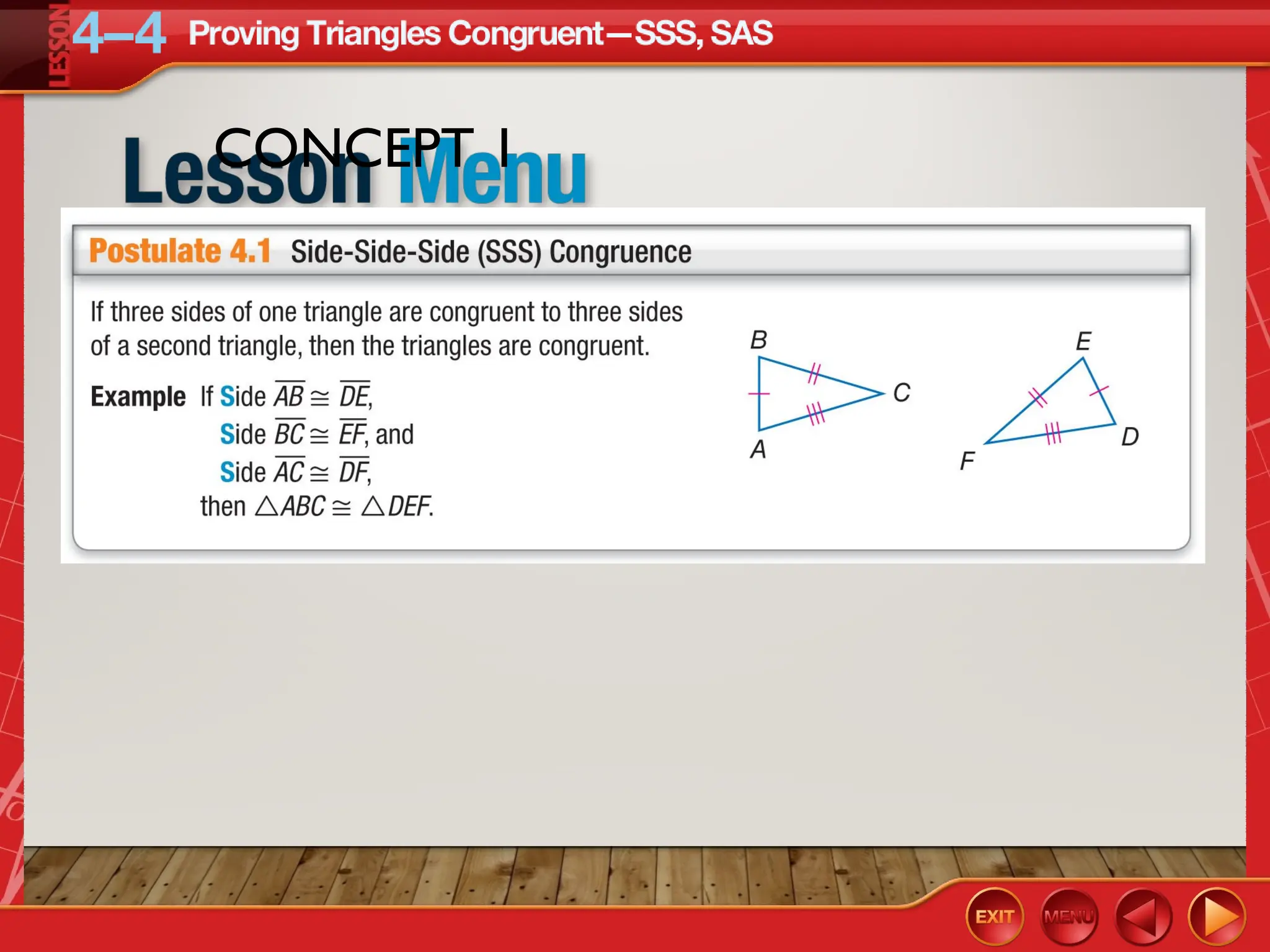
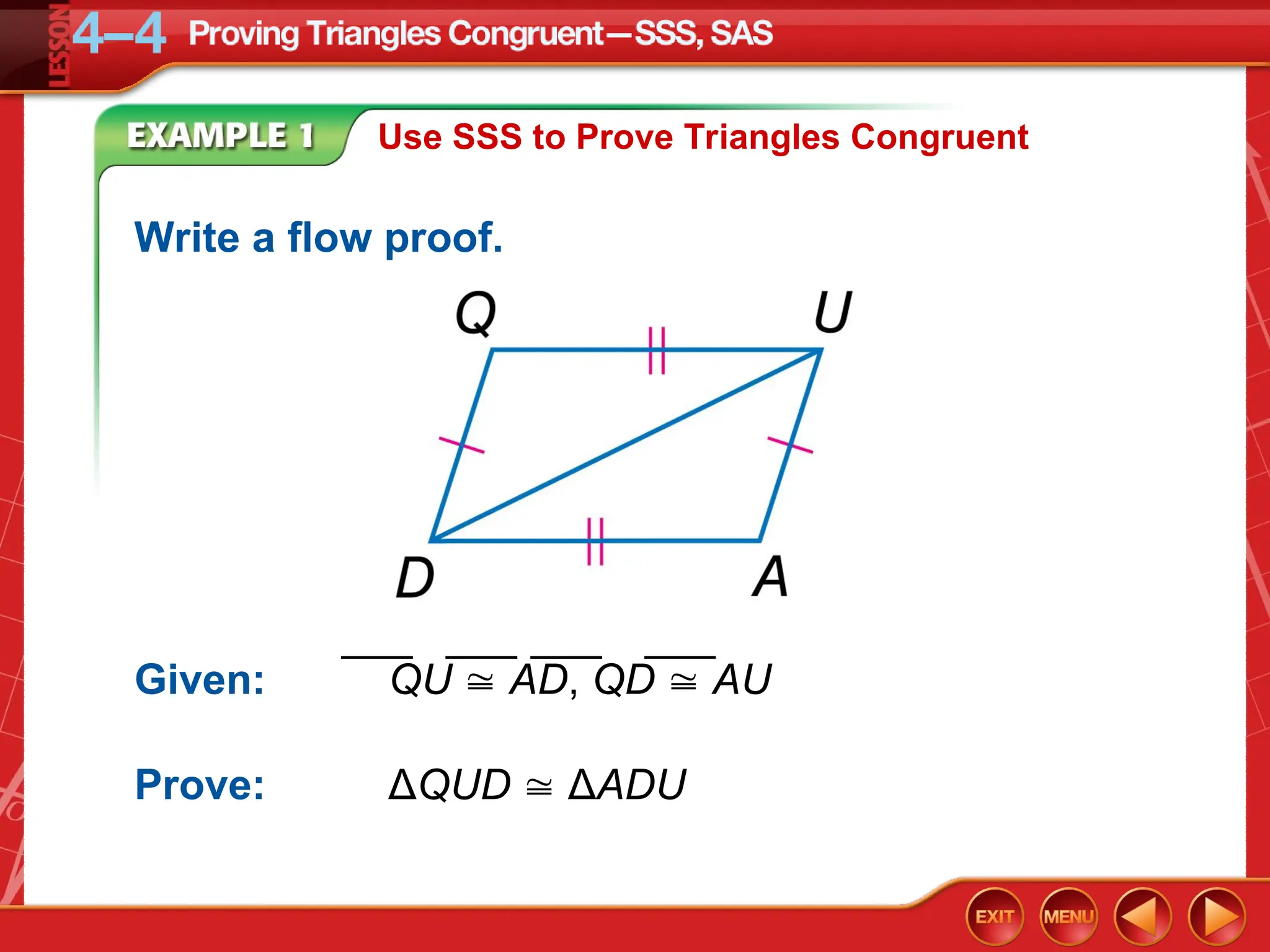
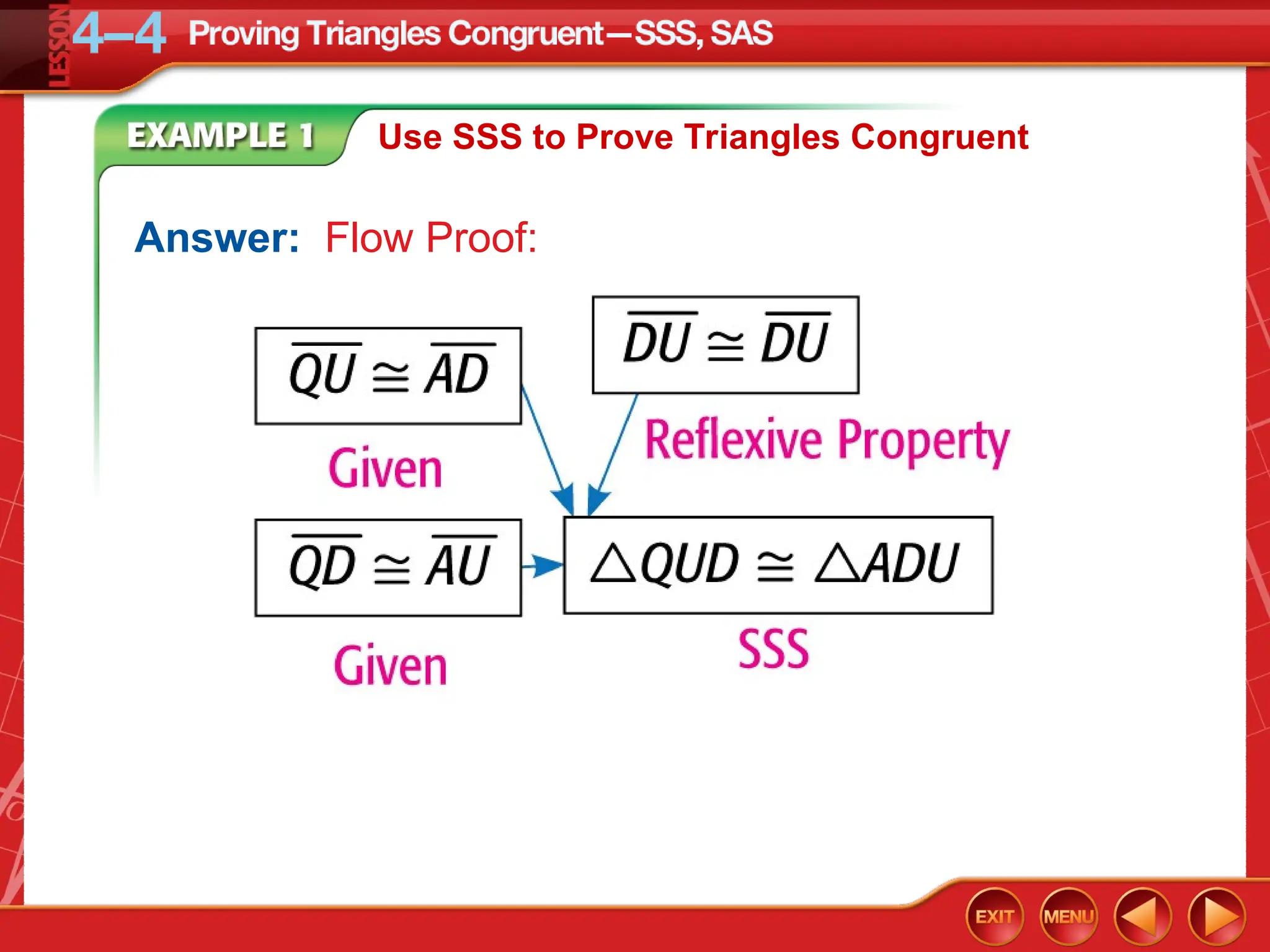
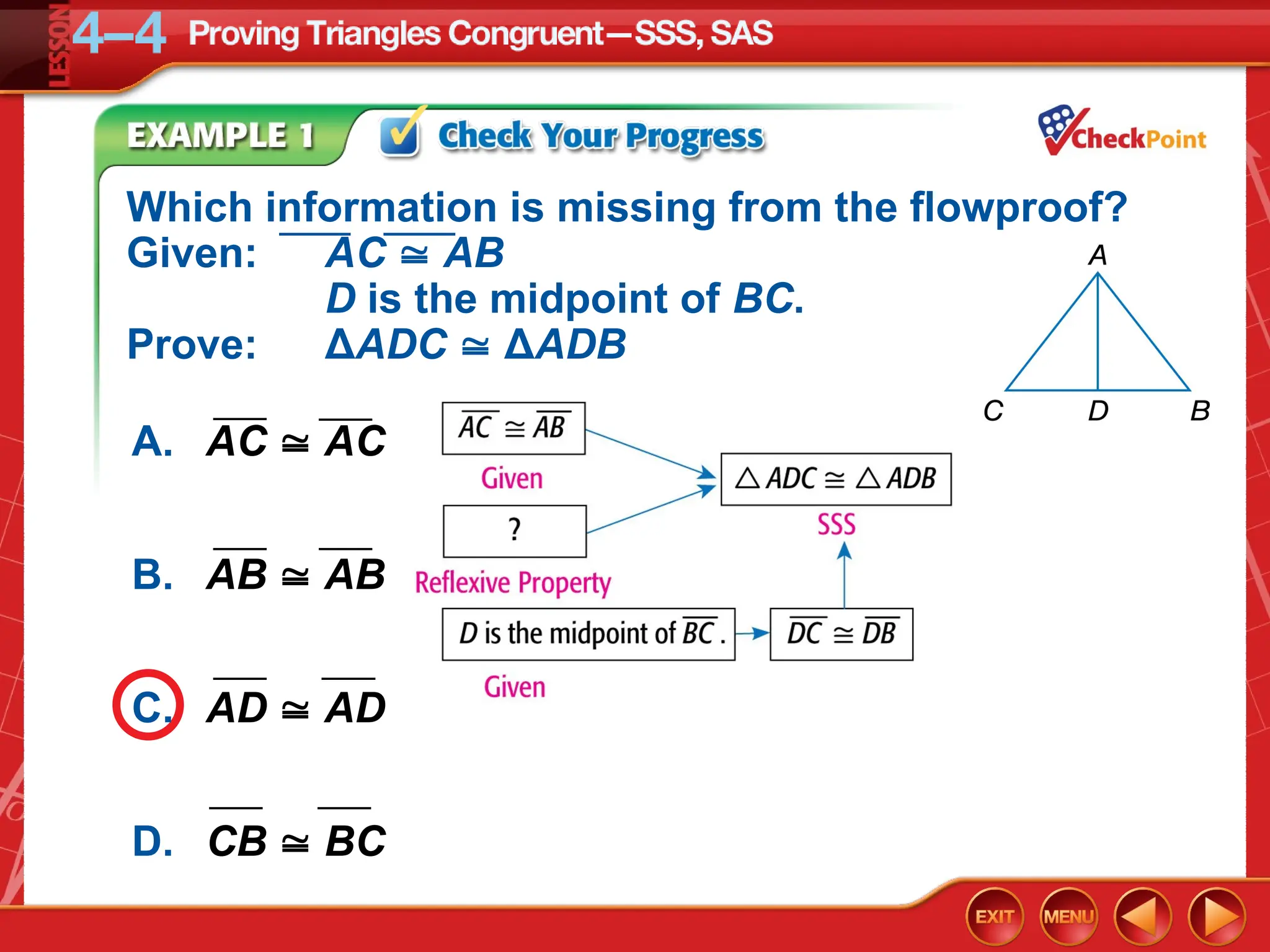
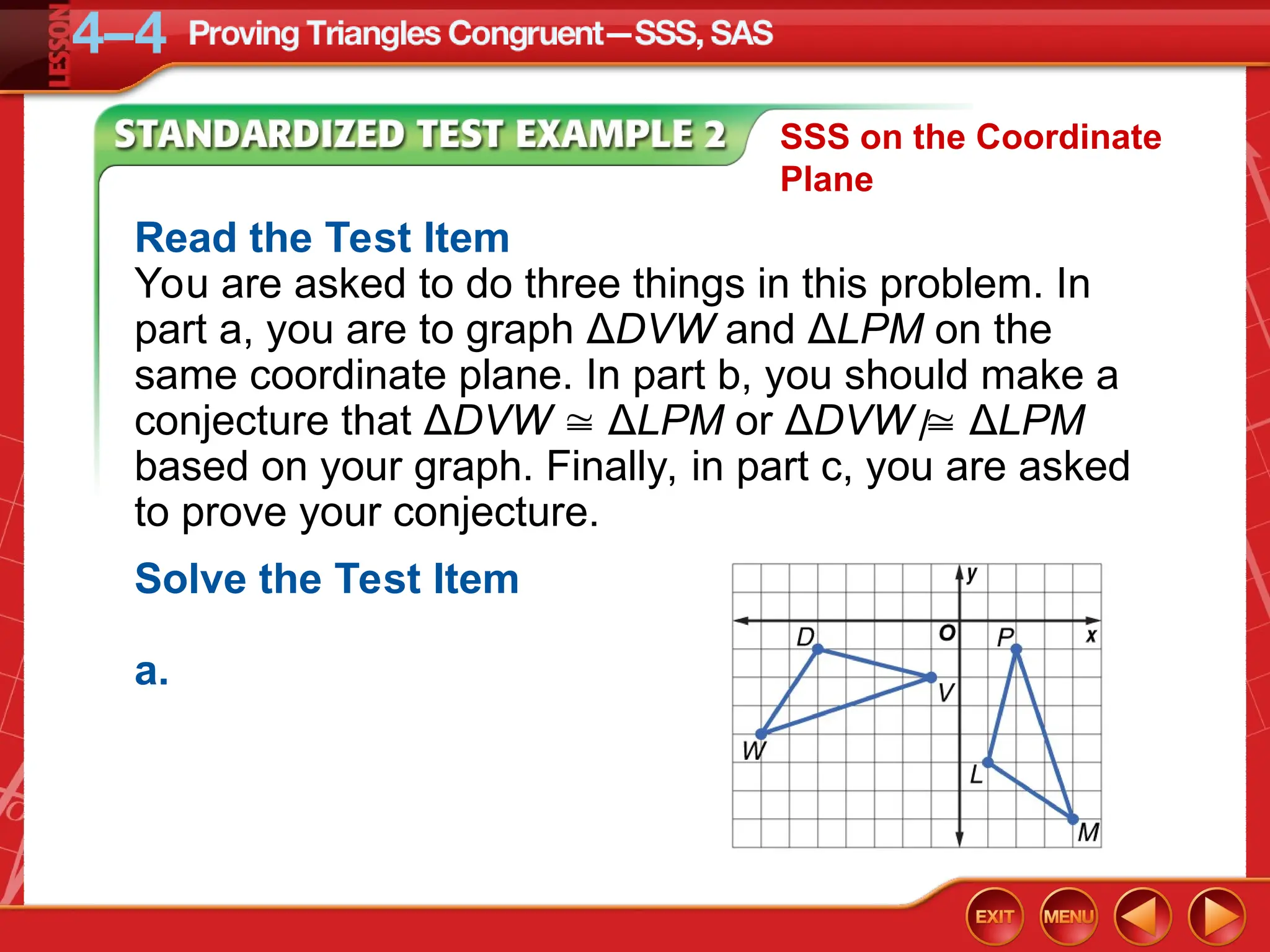
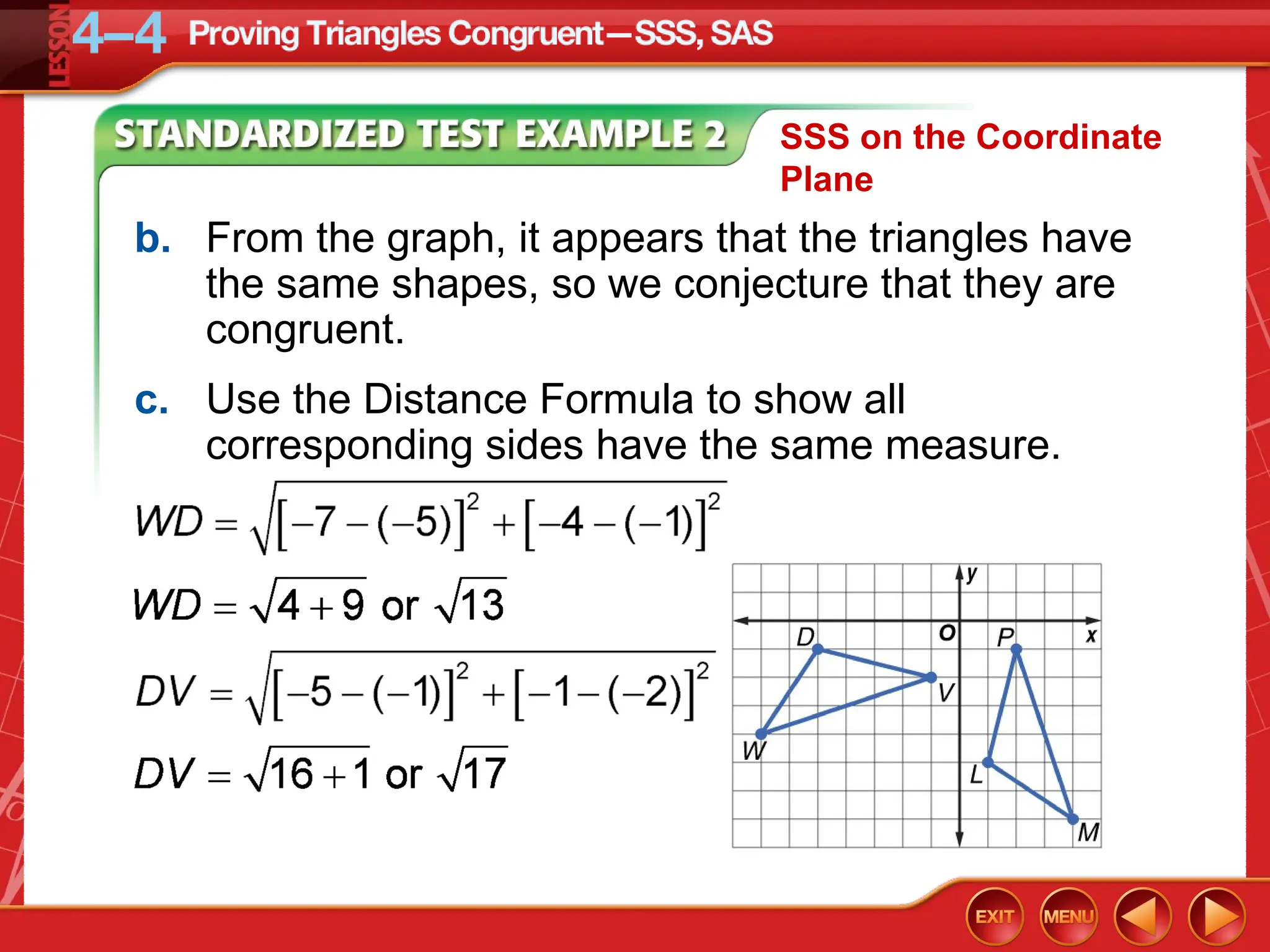
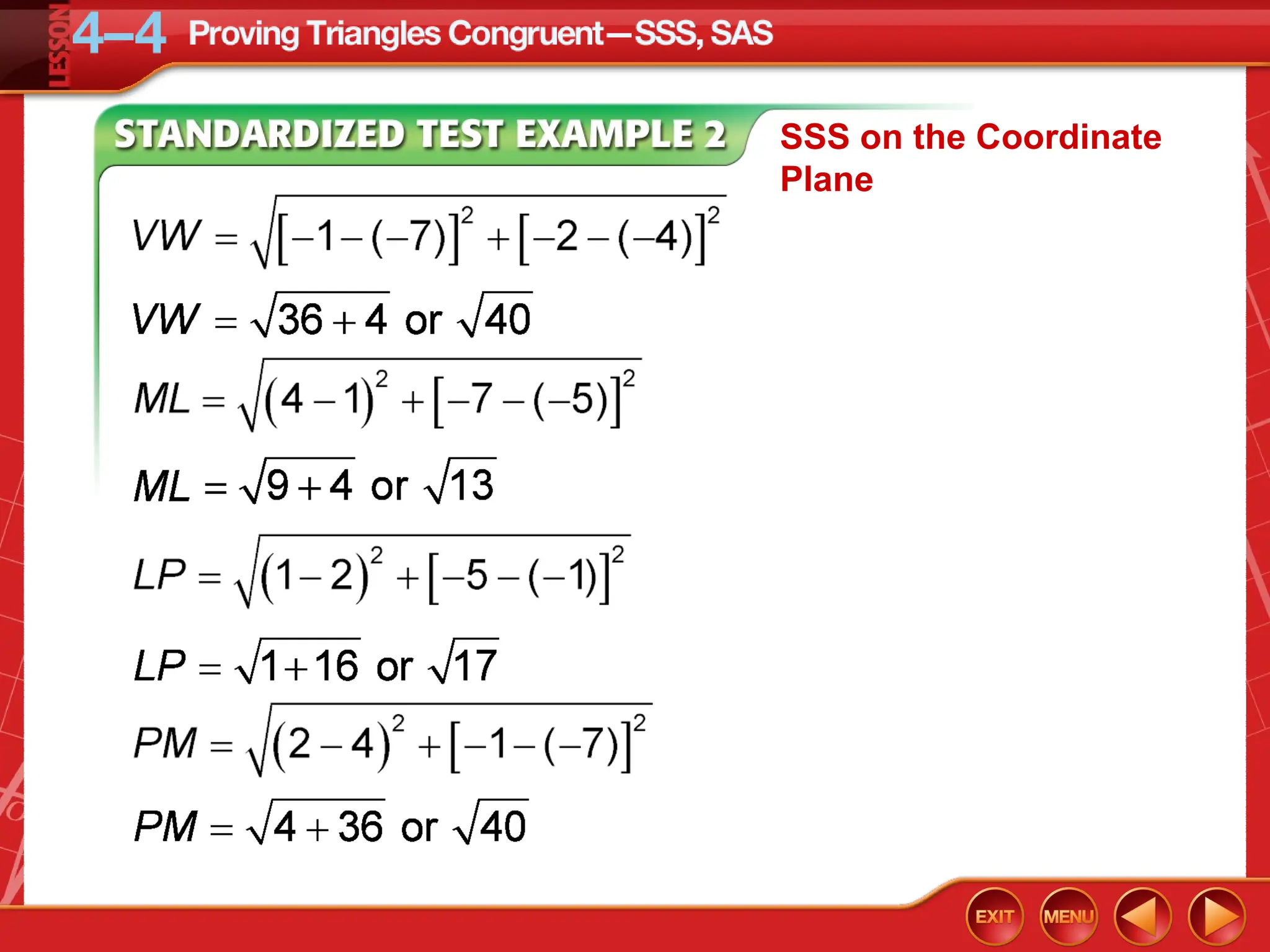
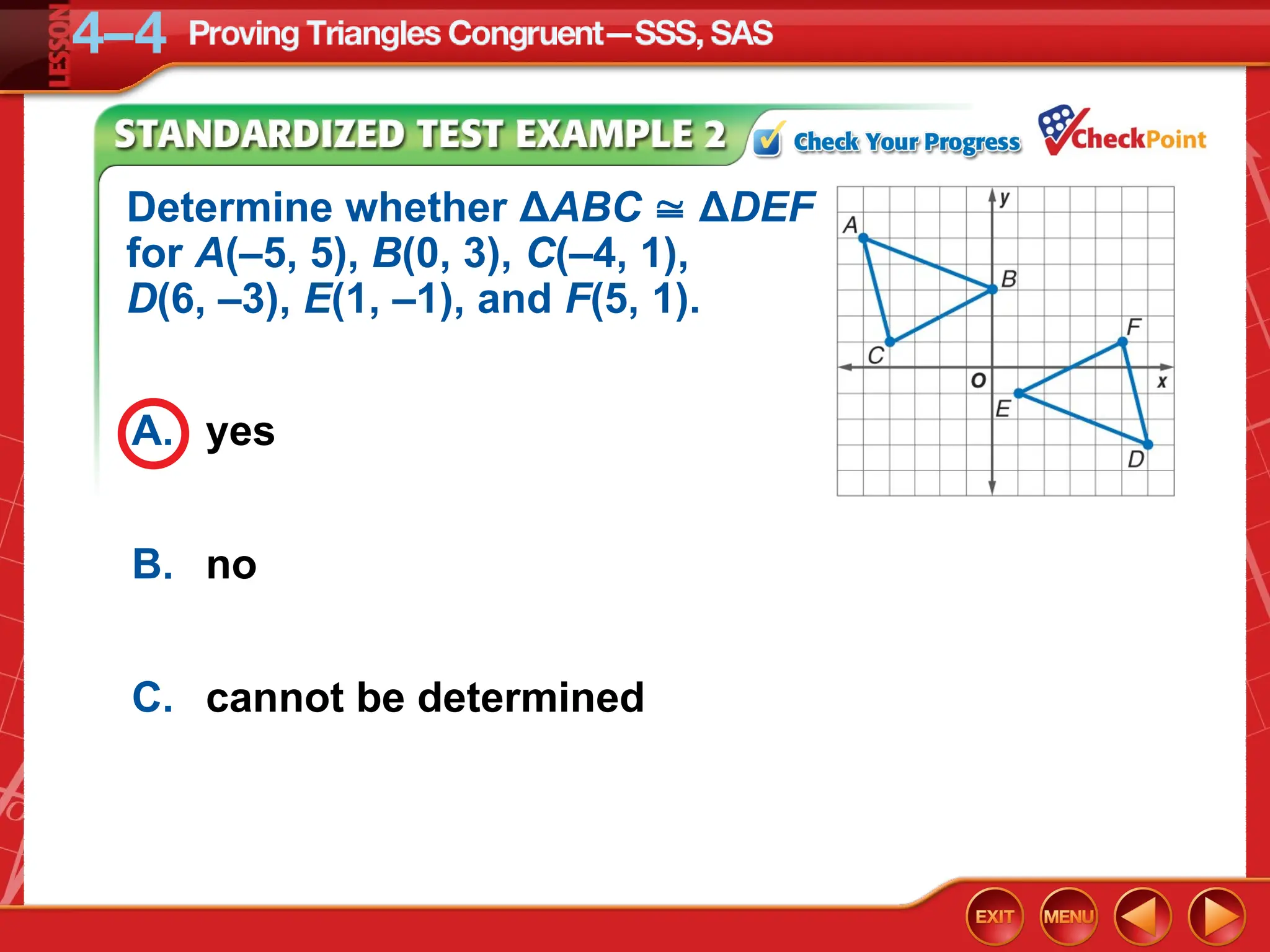
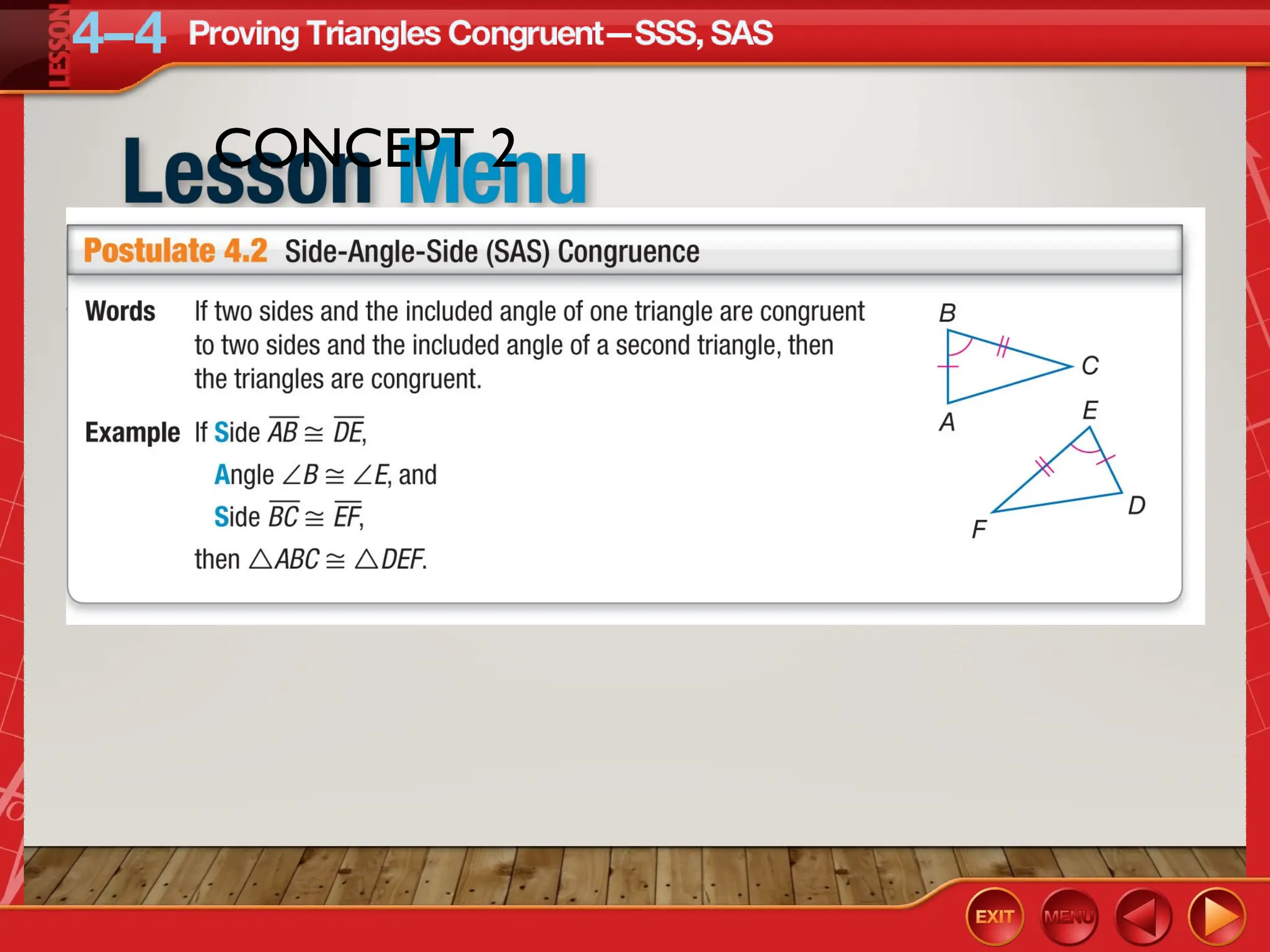
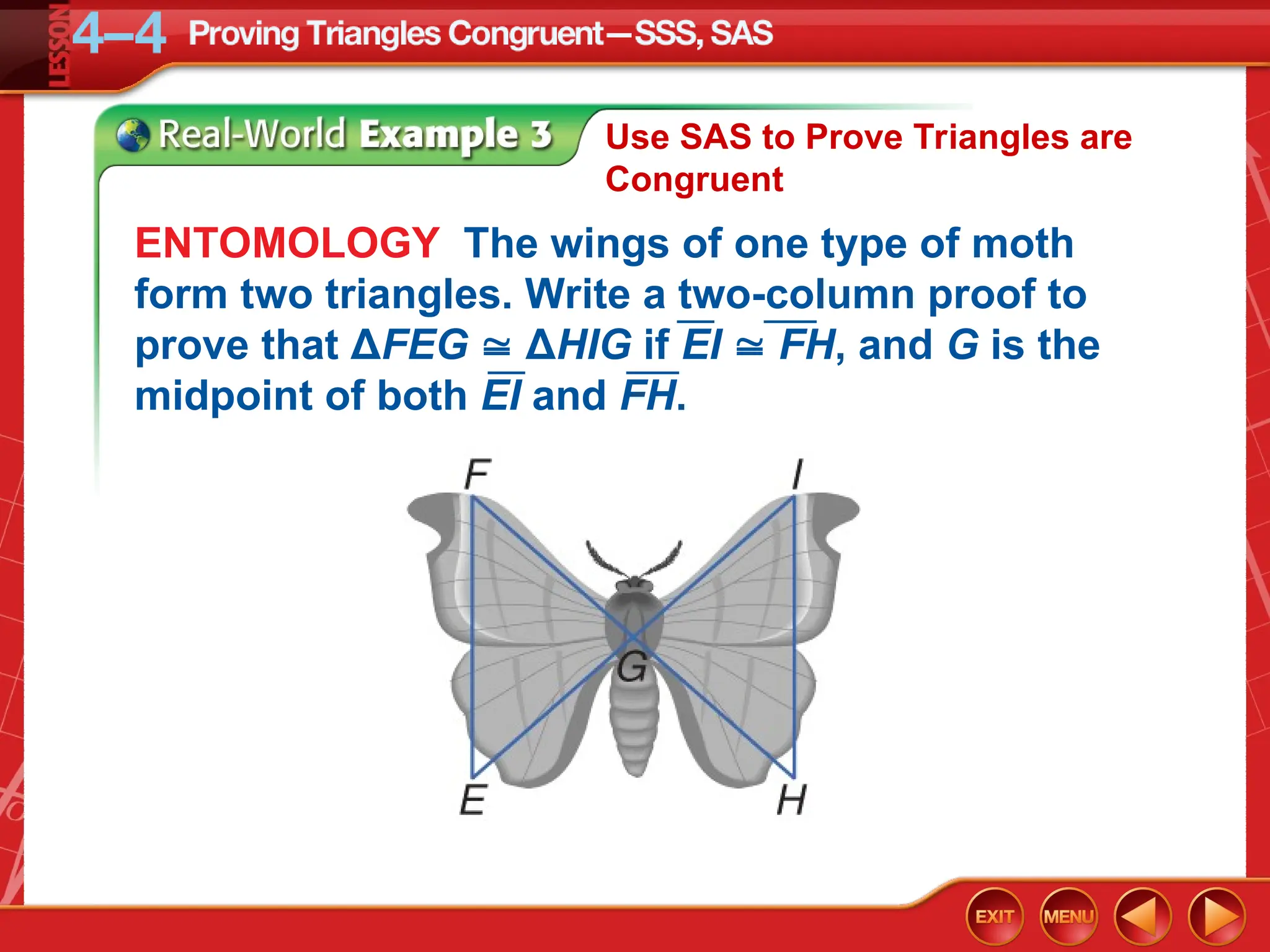
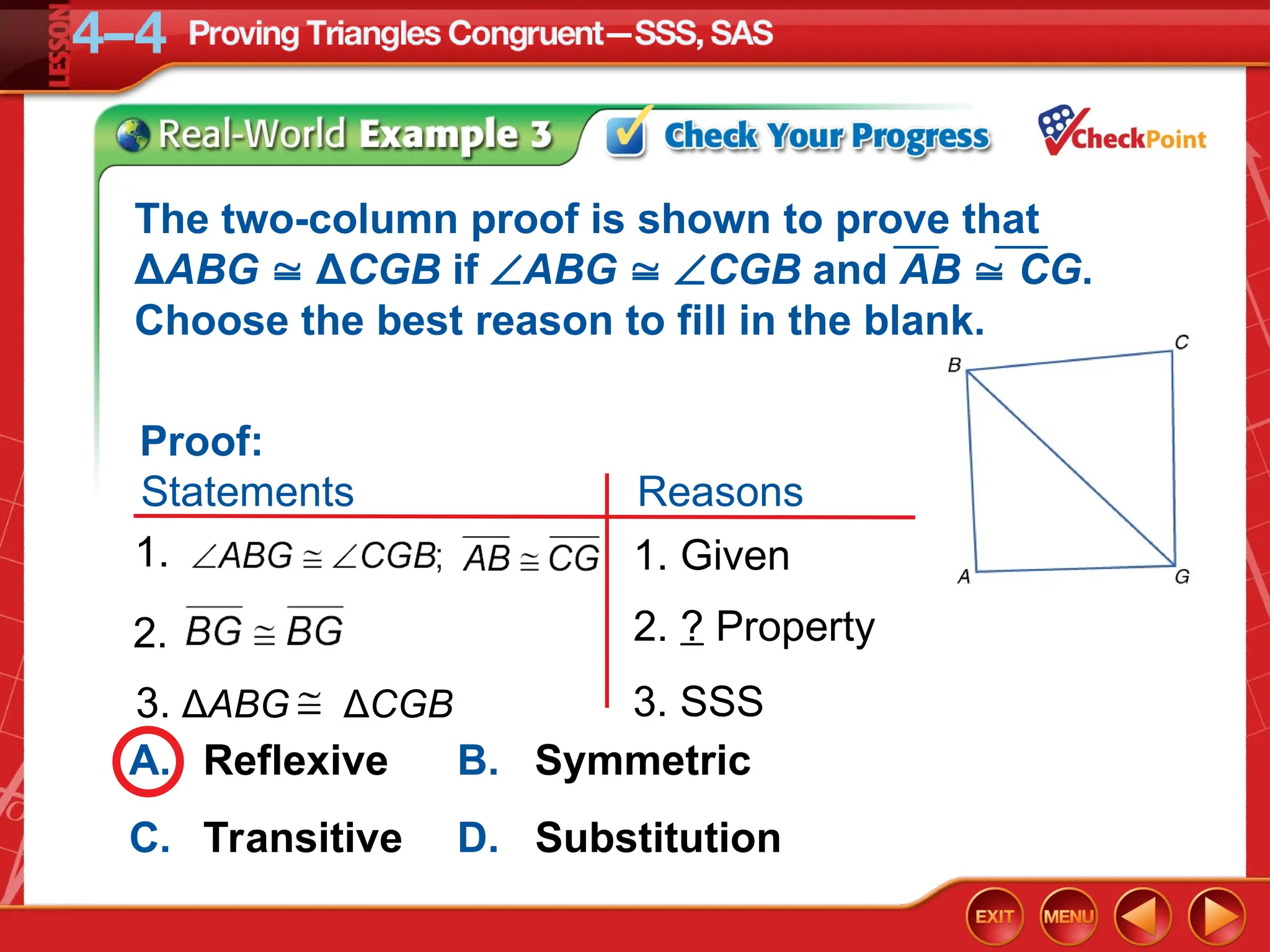
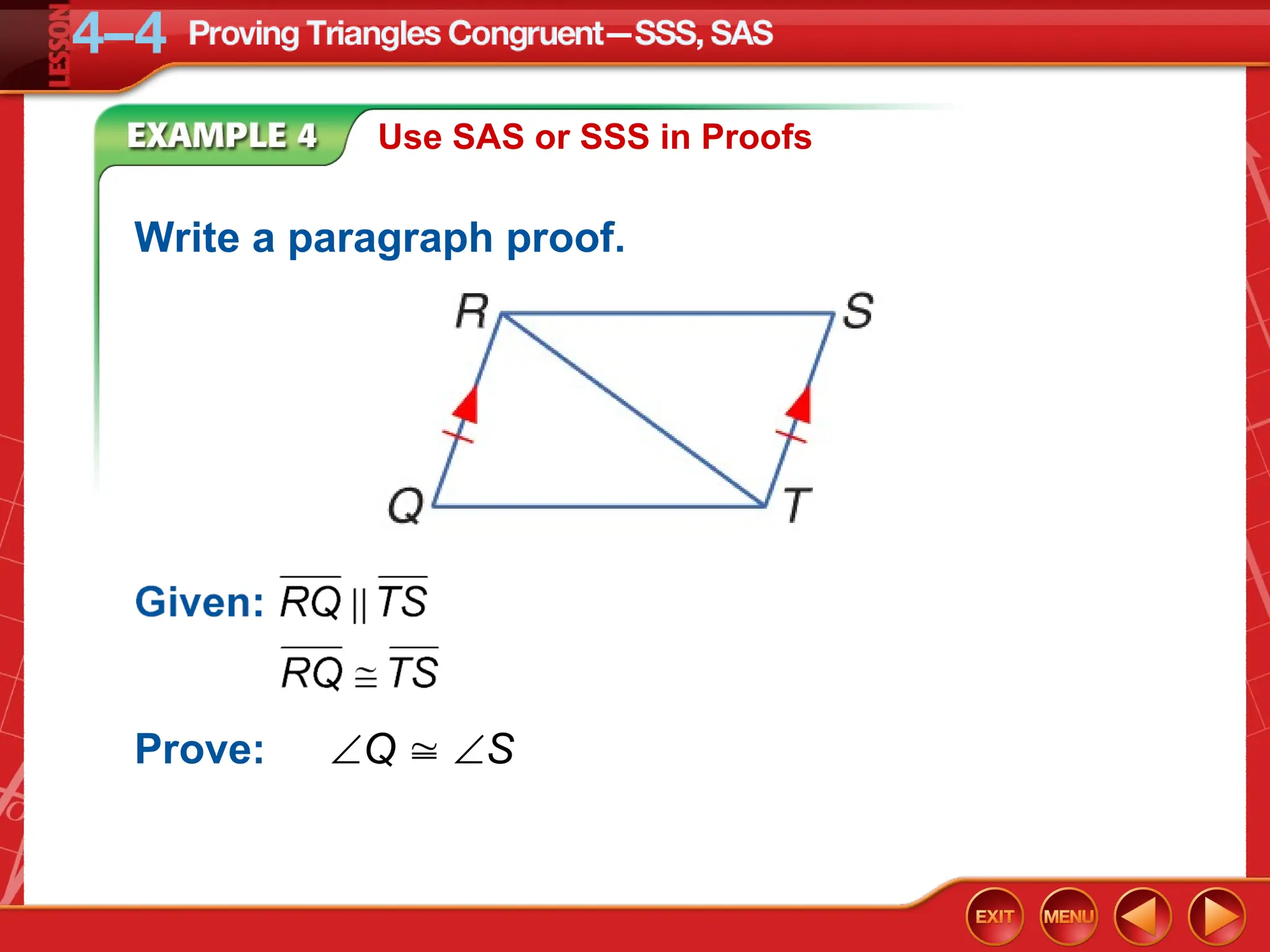
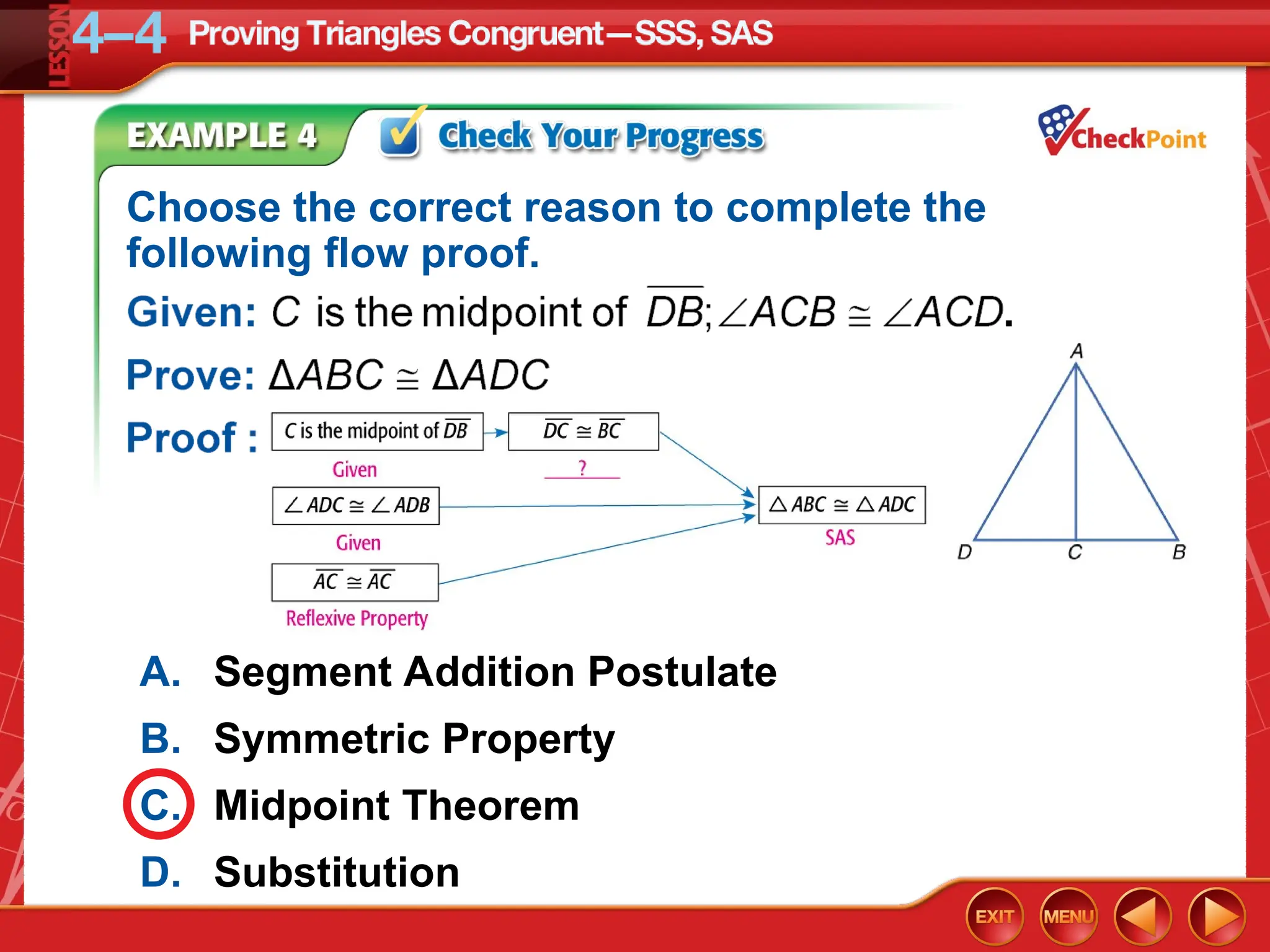
The document focuses on triangle congruence and presents various exercises related to congruence statements, corresponding angles and sides, and proofs using SSS and SAS postulates. It includes instructions to graph triangles, make conjectures, and construct logical arguments to support findings about triangle congruence. The content aligns with geometry standards and incorporates coordinate geometry approaches for solving problems related to triangle relationships.