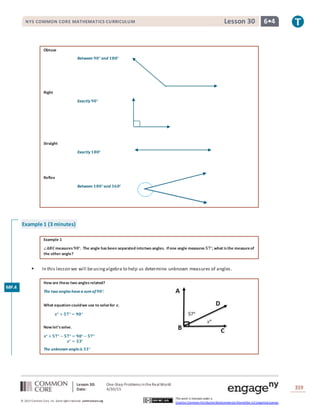
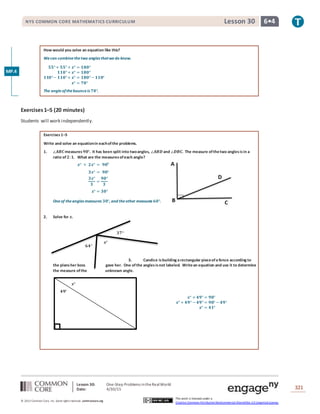
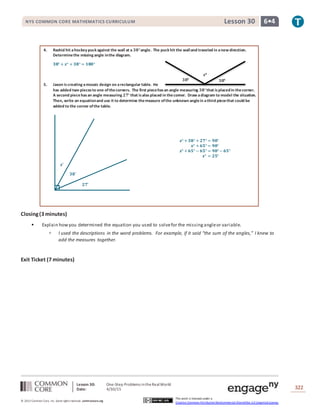
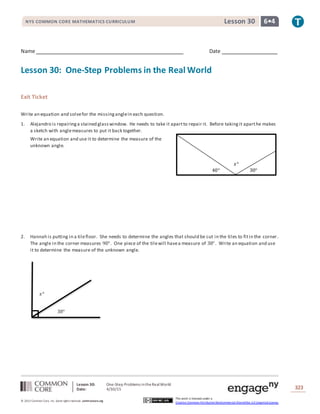
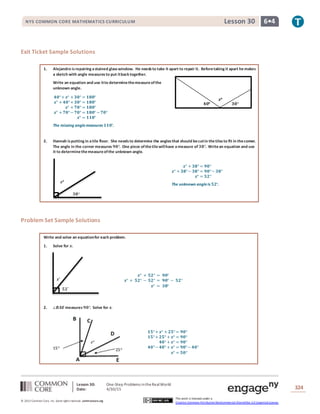
This lesson teaches students to calculate missing angle measures by writing and solving equations based on their understanding of angle properties developed in Grade 4. Students practice using equations to find unknown angles in one-step word problems involving angles that sum to straight lines, right angles, or other specified angle measures. Examples show setting up and solving equations like x° + 57° = 90° to find the measure of an unknown angle. Students then work independently on multi-step exercises and word problems, writing and solving their own equations to determine missing angle measures in diagrams.



![Lesson 30: One-Step Problems intheRealWorld
Date: 4/30/15 327
© 2013 Common Core, Inc. Some rightsreserved. commoncore.org
This work is licensed under a
Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License.
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM 6•4Lesson 30
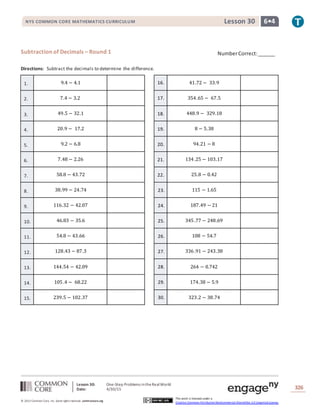
Subtraction of Decimals – Round 1 [KEY]
Directions: Subtract the decimals to determine the difference.
1. 9.4 − 4.1 𝟓. 𝟑 16. 41.72 − 33.9 𝟕. 𝟖𝟐
2. 7.4 − 3.2 𝟒. 𝟐 17. 354.65 − 67.5 𝟐𝟖𝟕. 𝟏𝟓
3. 49.5 − 32.1 𝟏𝟕. 𝟒 18. 448.9 − 329.18 𝟏𝟏𝟗. 𝟕𝟐
4. 20.9 − 17.2 𝟑. 𝟕 19. 8 − 5.38 𝟐. 𝟔𝟐
5. 9.2 − 6.8 𝟐. 𝟒 20. 94.21 − 8 𝟖𝟔. 𝟐𝟏
6. 7.48 − 2.26 𝟓. 𝟐𝟐 21. 134.25 − 103.17 𝟑𝟏. 𝟎𝟖
7. 58.8 − 43.72 𝟏𝟓. 𝟎𝟖 22. 25.8 − 0.42 𝟐𝟓. 𝟑𝟖
8. 38.99 − 24.74 𝟏𝟒. 𝟐𝟓 23. 115 − 1.65 𝟏𝟏𝟑. 𝟑𝟓
9. 116.32 − 42.07 𝟕𝟒. 𝟐𝟓 24. 187.49 − 21 𝟏𝟔𝟔. 𝟒𝟗
10. 46.83 − 35.6 𝟏𝟏. 𝟐𝟑 25. 345.77 − 248.69 𝟗𝟕. 𝟎𝟖
11. 54.8 − 43.66 𝟏𝟏. 𝟏𝟒 26. 108 − 54.7 𝟓𝟑. 𝟑
12. 128.43 − 87.3 𝟒𝟏. 𝟏𝟑 27. 336.91 − 243.38 𝟗𝟑. 𝟓𝟑
13. 144.54 − 42.09 𝟏𝟎𝟐. 𝟒𝟓 28. 264 − 0.742 𝟐𝟔𝟑. 𝟐𝟓𝟖
14. 105.4 − 68.22 𝟑𝟕. 𝟏𝟖 29. 174.38 − 5.9 𝟏𝟔𝟖. 𝟒𝟖
15. 239.5 − 102.37 𝟏𝟑𝟕. 𝟏𝟑 30. 323.2 − 38.74 𝟐𝟖𝟒. 𝟒𝟔](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/g6-m4-h-lesson30-t-150430115603-conversion-gate01/85/G6-m4-h-lesson-30-t-10-320.jpg)

![Lesson 30: One-Step Problems intheRealWorld
Date: 4/30/15 329
© 2013 Common Core, Inc. Some rightsreserved. commoncore.org
This work is licensed under a
Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License.
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM 6•4Lesson 30
Subtraction of Decimals – Round 2 [KEY]
Directions: Subtract the decimals to determine the difference.
1. 8.4 − 5.4 𝟑. 𝟎 16. 14 − 10.32 𝟑. 𝟔𝟖
2. 5.6 − 3.1 𝟐. 𝟓 17. 43.37 − 28 𝟏𝟓. 𝟑𝟕
3. 9.7 − 7.2 𝟐. 𝟓 18. 24.56 − 18.88 𝟓. 𝟔𝟖
4. 14.3 − 12.1 𝟐. 𝟐 19. 33.55 − 11.66 𝟐𝟏. 𝟖𝟗
5. 34.5 − 13.2 𝟐𝟏. 𝟑 20. 329.56 − 284.49 𝟒𝟓. 𝟎𝟕
6. 14.86 − 13.85 𝟏. 𝟎𝟏 21. 574.3 − 342.18 𝟐𝟑𝟐. 𝟏𝟐
7. 43.27 − 32.14 𝟏𝟏. 𝟏𝟑 22. 154 − 128.63 𝟐𝟓. 𝟑𝟕
8. 48.48 − 27.27 𝟐𝟏. 𝟐𝟏 23. 247.1 − 138.57 𝟏𝟎𝟖. 𝟓𝟑
9. 64.74 − 31.03 𝟑𝟑. 𝟕𝟏 24. 12 − 3.547 𝟖. 𝟒𝟓𝟑
10. 98.36 − 24.09 𝟕𝟒. 𝟐𝟕 25. 1.415 − 0.877 𝟎. 𝟓𝟑𝟖
11. 33.54 − 24.4 𝟗. 𝟏𝟒 26. 185.774 − 154.86 𝟑𝟎. 𝟗𝟏𝟒
12. 114.7 − 73.42 𝟒𝟏. 𝟐𝟖 27. 65.251 − 36.9 𝟐𝟖. 𝟑𝟓𝟏
13. 45.2 − 32.7 𝟏𝟐. 𝟓 28. 144.2 − 95.471 𝟒𝟖. 𝟕𝟐𝟗
14. 74.8 − 53.9 𝟐𝟎. 𝟗 29. 2.11 − 1.949 𝟎. 𝟏𝟔𝟏
15. 238.4 − 114.36 𝟏𝟐𝟒. 𝟎𝟒 30. 100 − 34.746 𝟔𝟓. 𝟐𝟓𝟒](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/g6-m4-h-lesson30-t-150430115603-conversion-gate01/85/G6-m4-h-lesson-30-t-12-320.jpg)