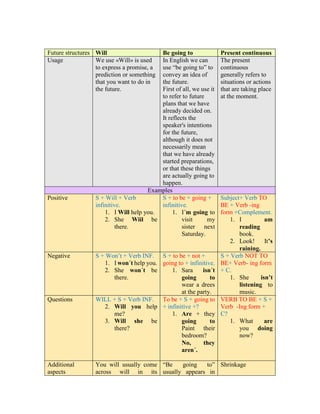
This document provides an overview of how to use will, be going to, and the present continuous tense to express future meaning in English. It explains that will is used to express promises, predictions, or planned actions. Be going to conveys intentions or plans that have already been decided. The present continuous generally refers to ongoing situations or actions happening now. Examples of positive, negative, and question forms are provided for each structure. Additional aspects note that will is usually contracted and be going to appears in informal contexts, also often contracted.