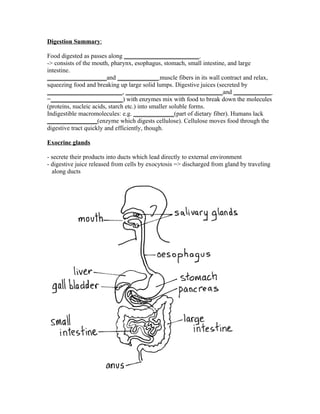
The digestive system consists of the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine and large intestine. Food passes through these organs where muscles squeeze and break up food while digestive juices containing enzymes break down molecules. Cellulose, a type of dietary fiber, is not broken down as humans lack the enzyme to digest it. Hormones and nerves control the secretion of digestive juices from exocrine glands like the stomach and pancreas in response to food. Digestive enzymes remain attached to cells lining the small intestine so products of digestion can be immediately absorbed. Pepsinogen and trypsinogen are secreted as inactive enzymes and activated once in the stomach and small intestine, respectively.