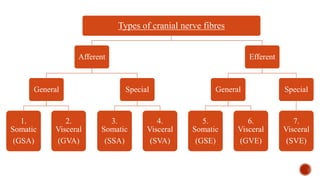
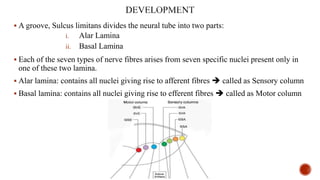
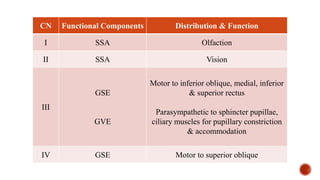
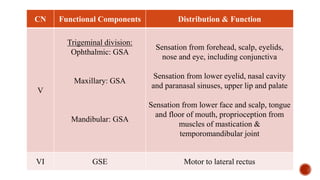
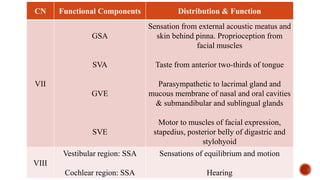
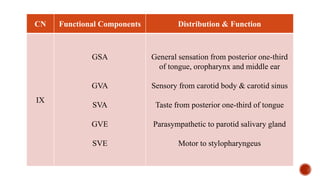
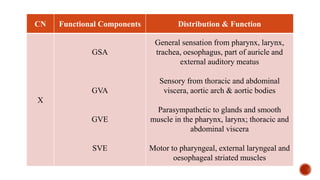
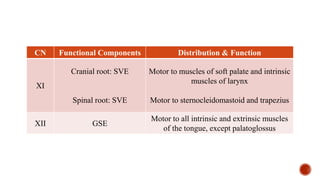
The document outlines the types, functions, and classifications of cranial nerve fibres, categorizing them as sensory, motor, or mixed. It describes how nerve fibres are classified by signal direction, structure supplied, and sensory functions, detailing the specific cranial nerves associated with each type. Additionally, it explains the structural division of the neural tube and the origin of nerve fibre nuclei within the alar and basal laminae.