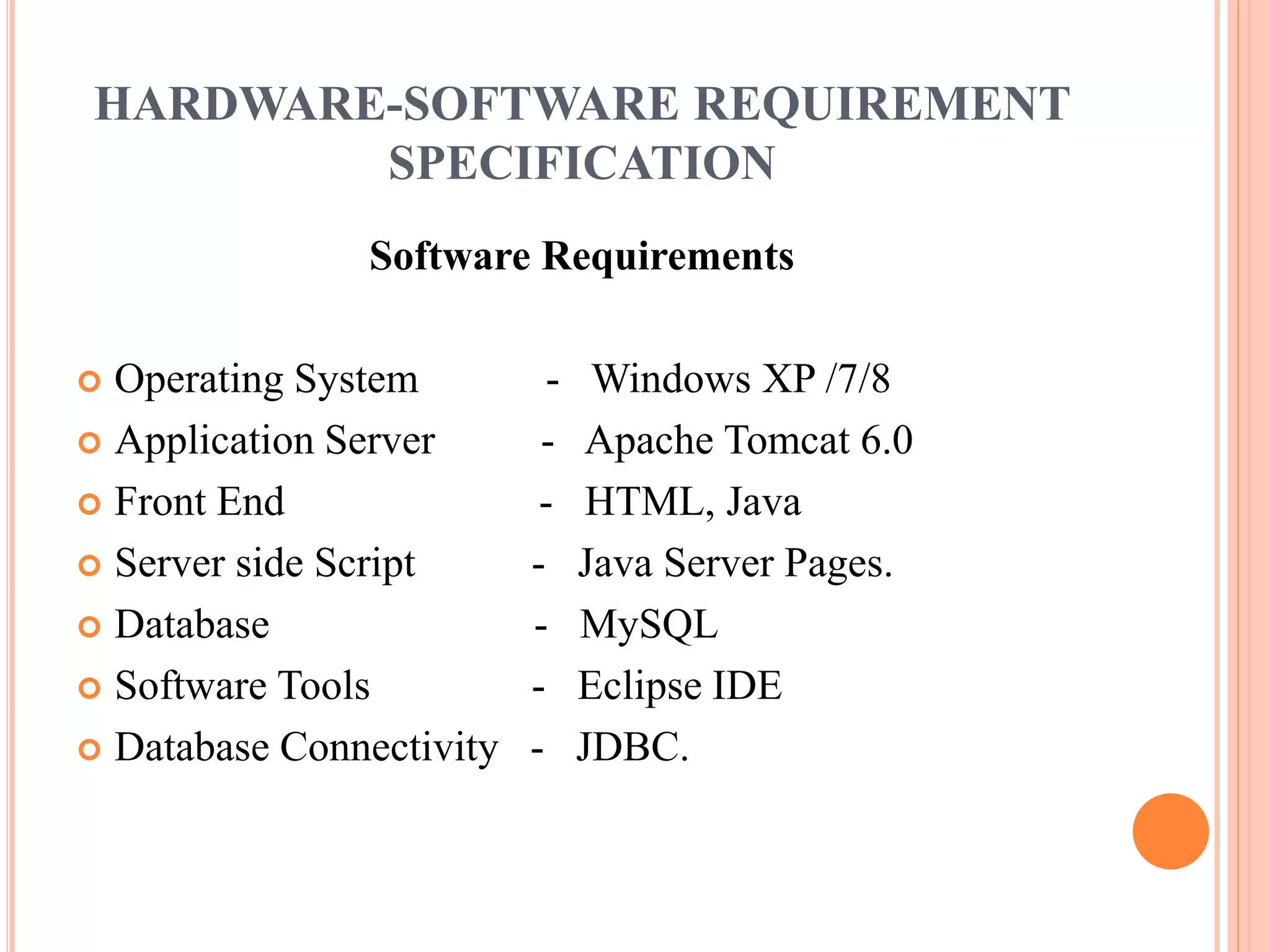
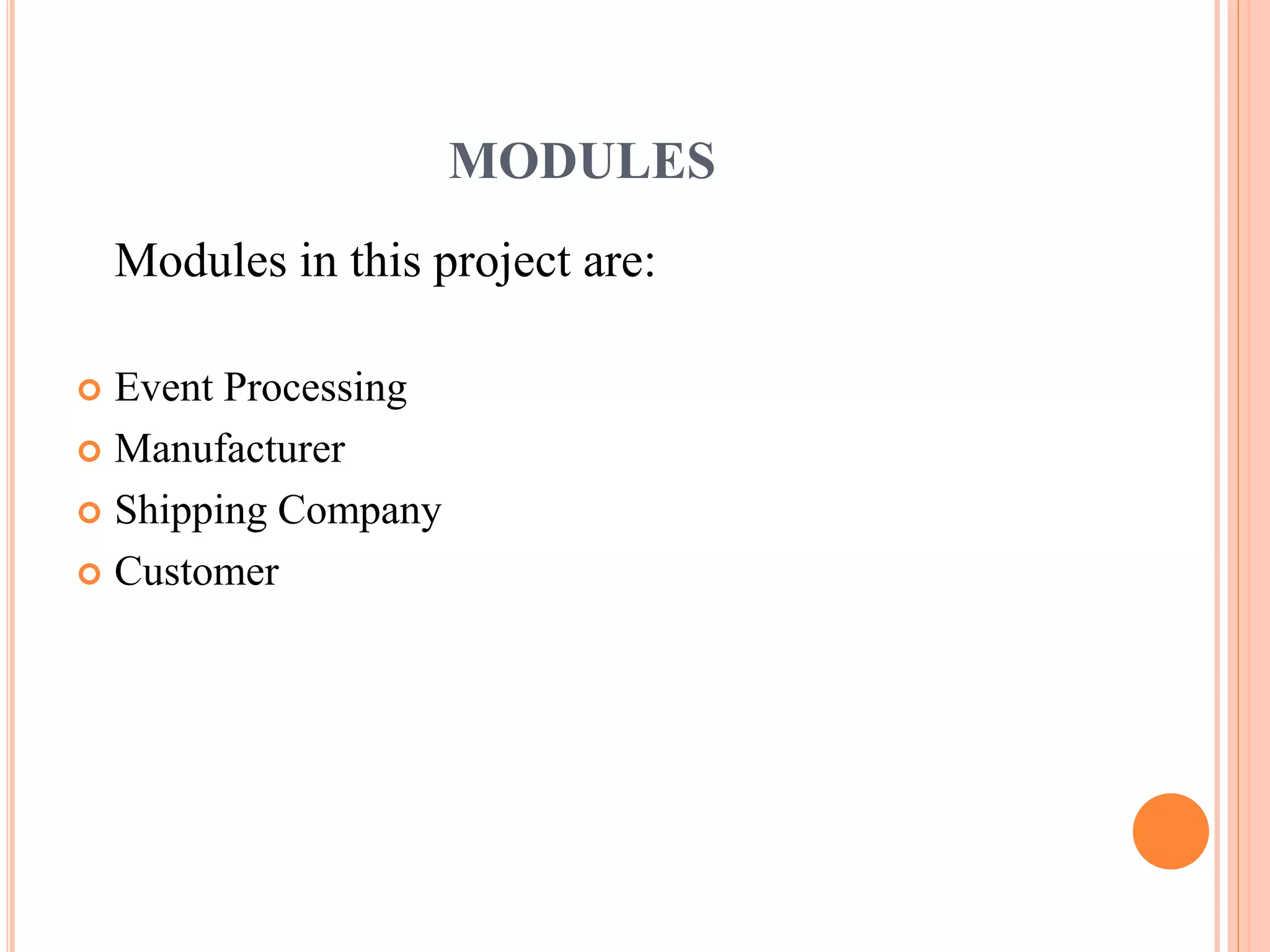
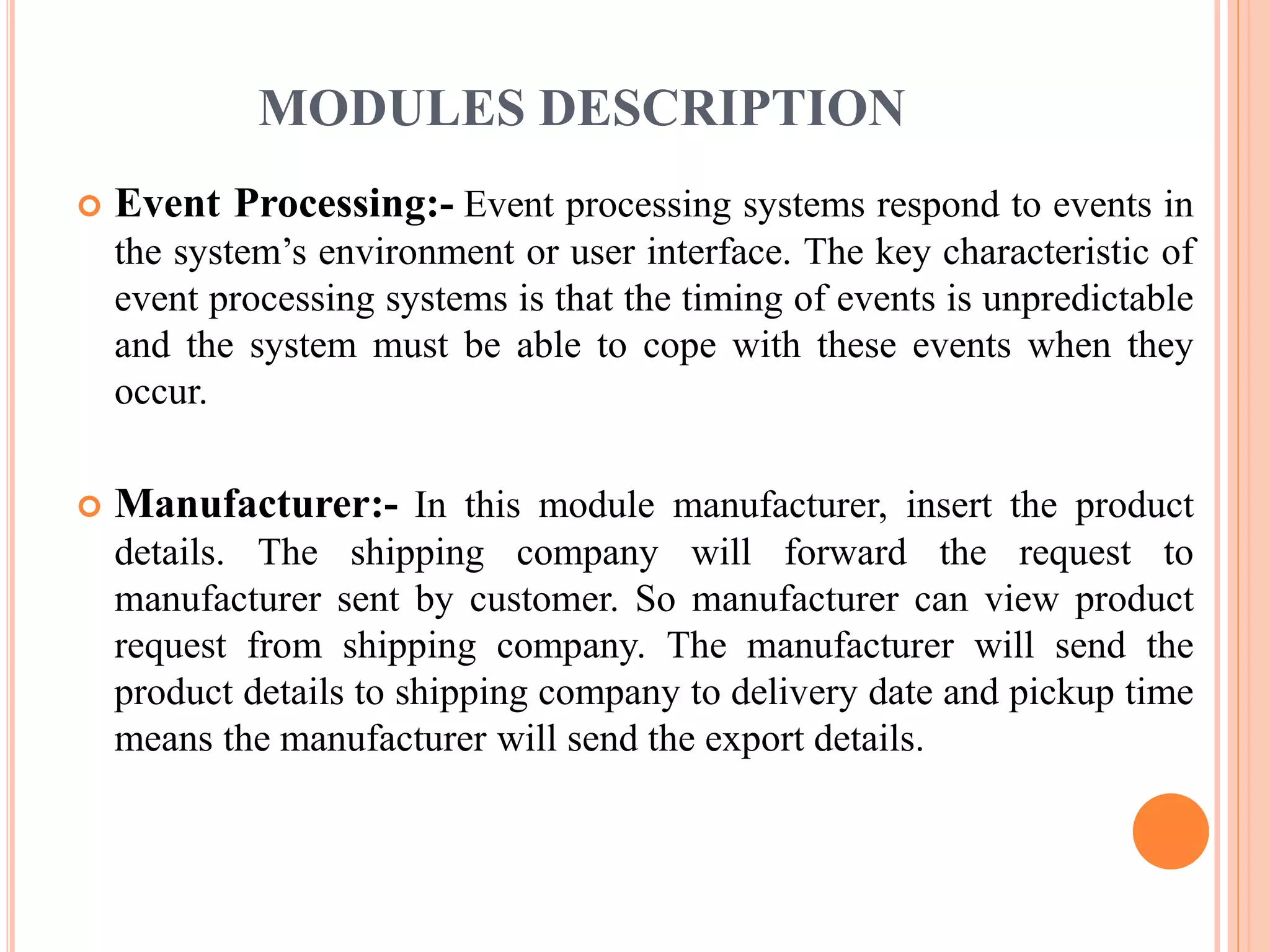
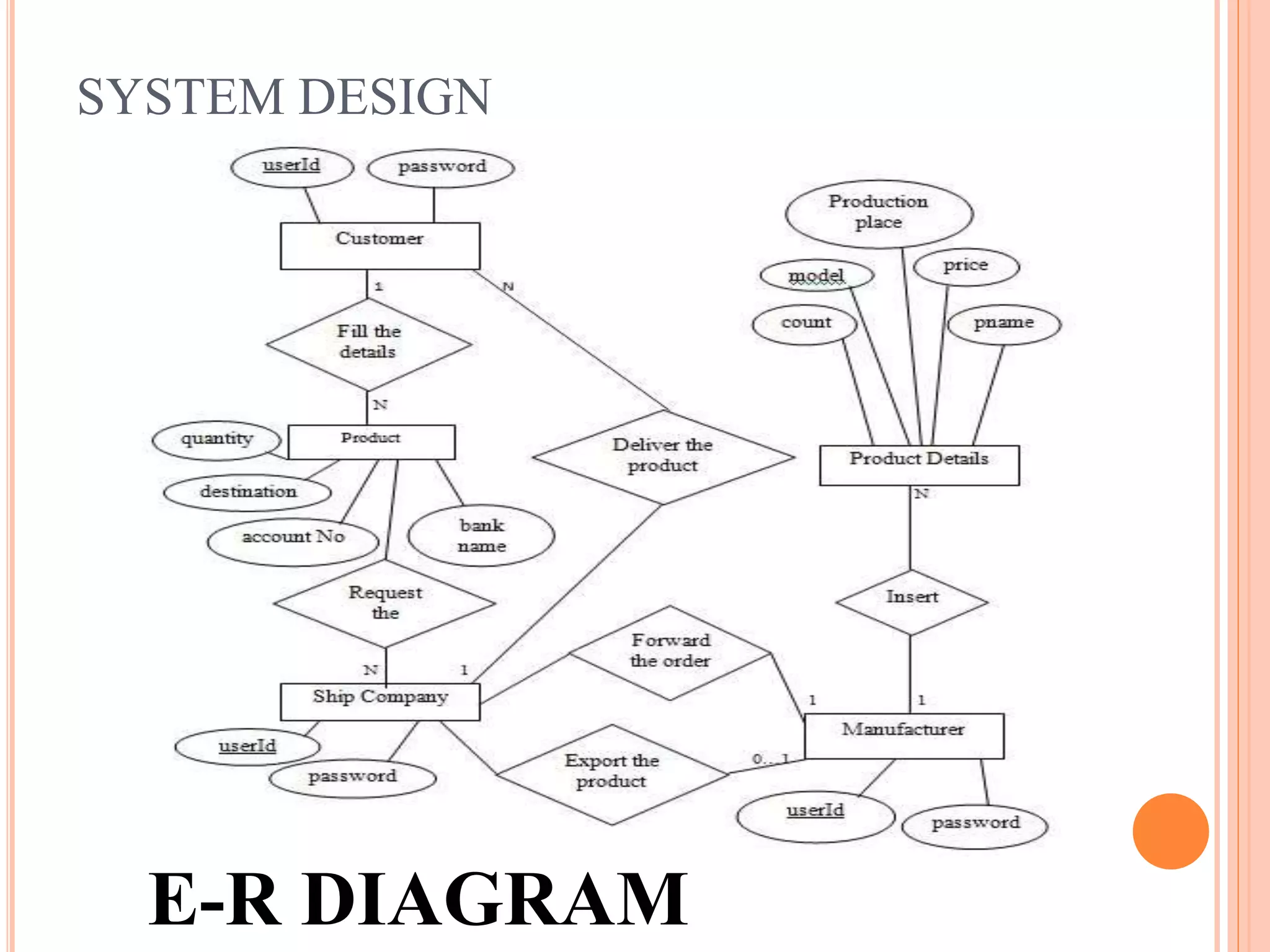
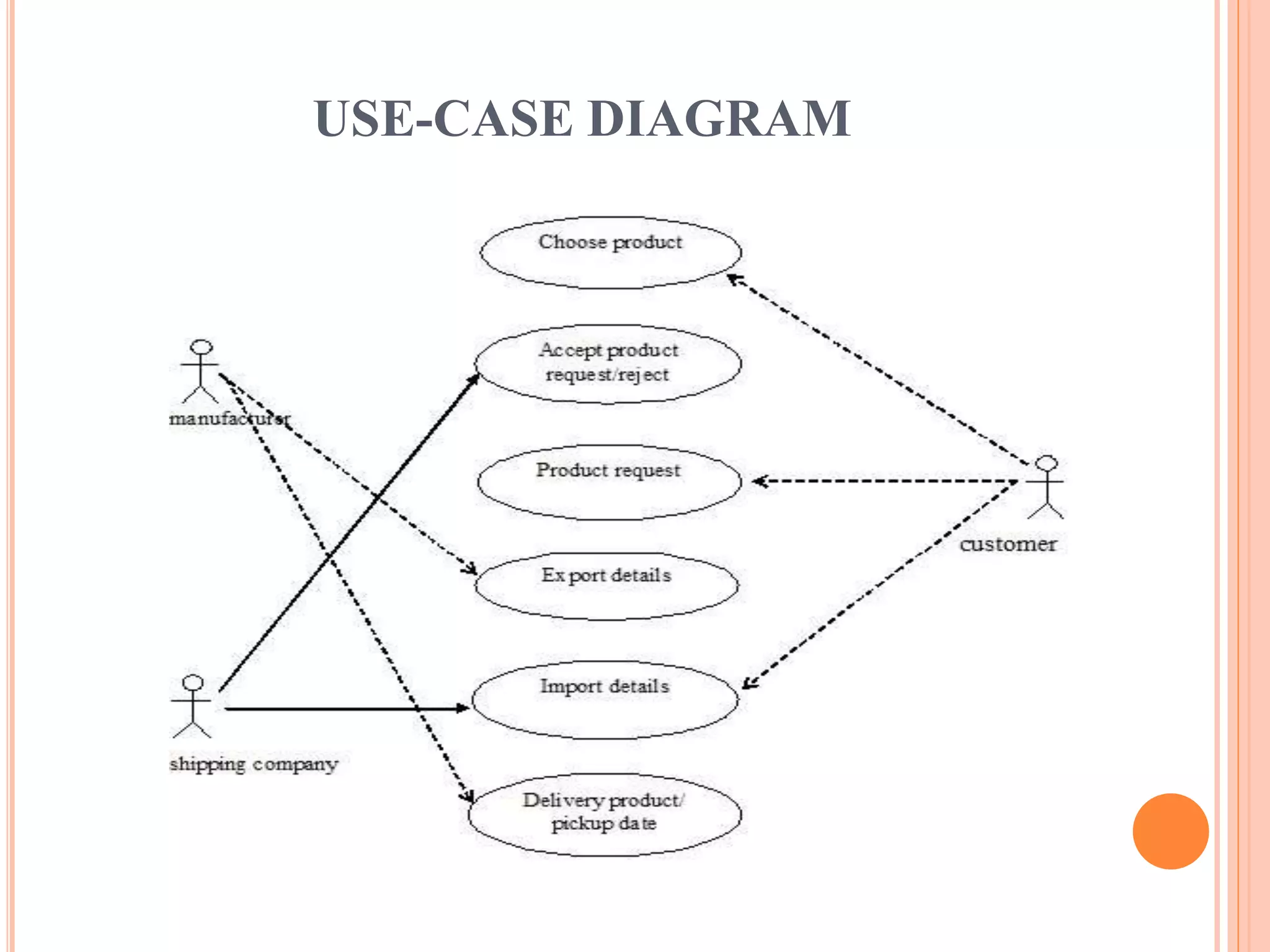
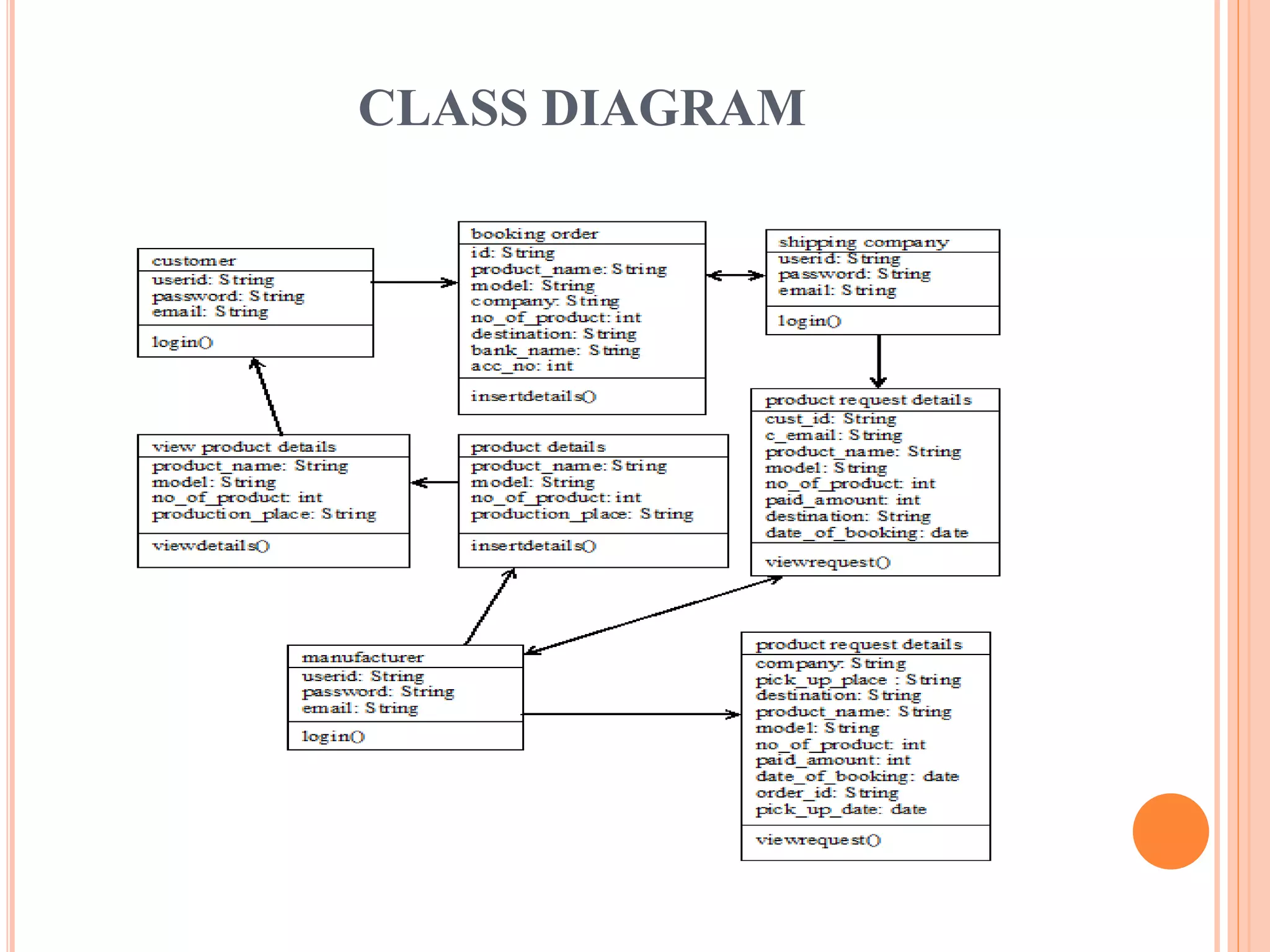
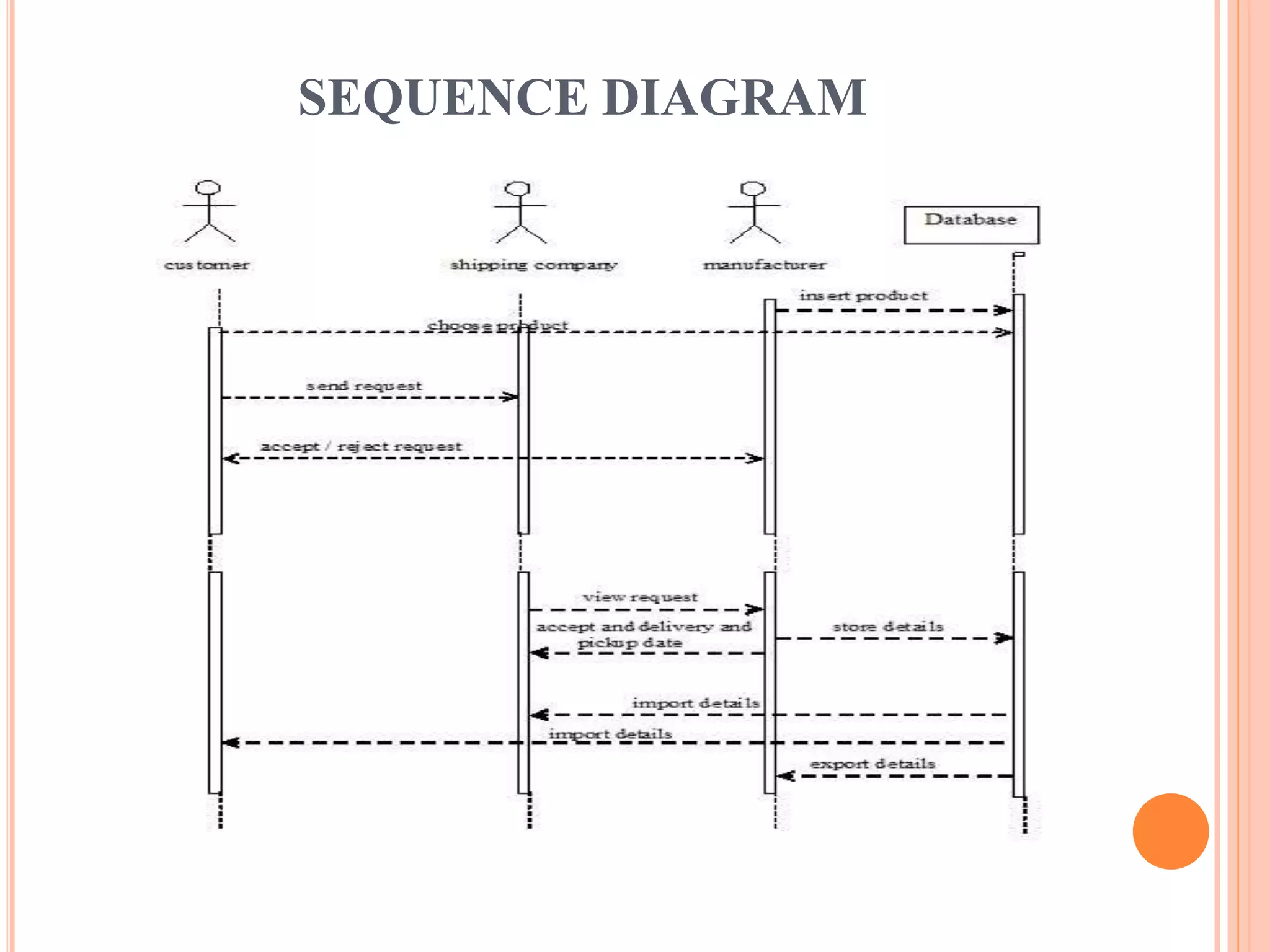
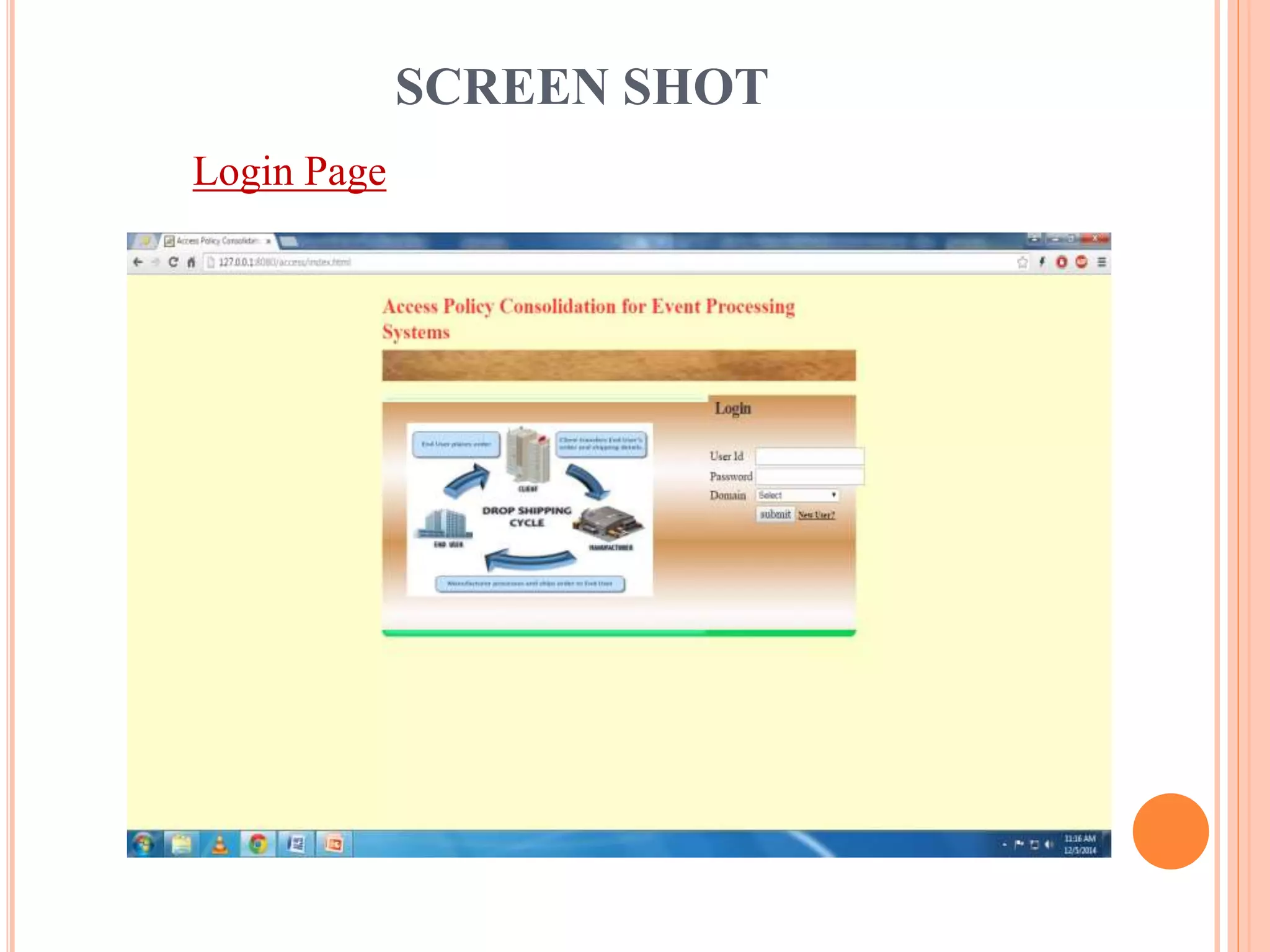
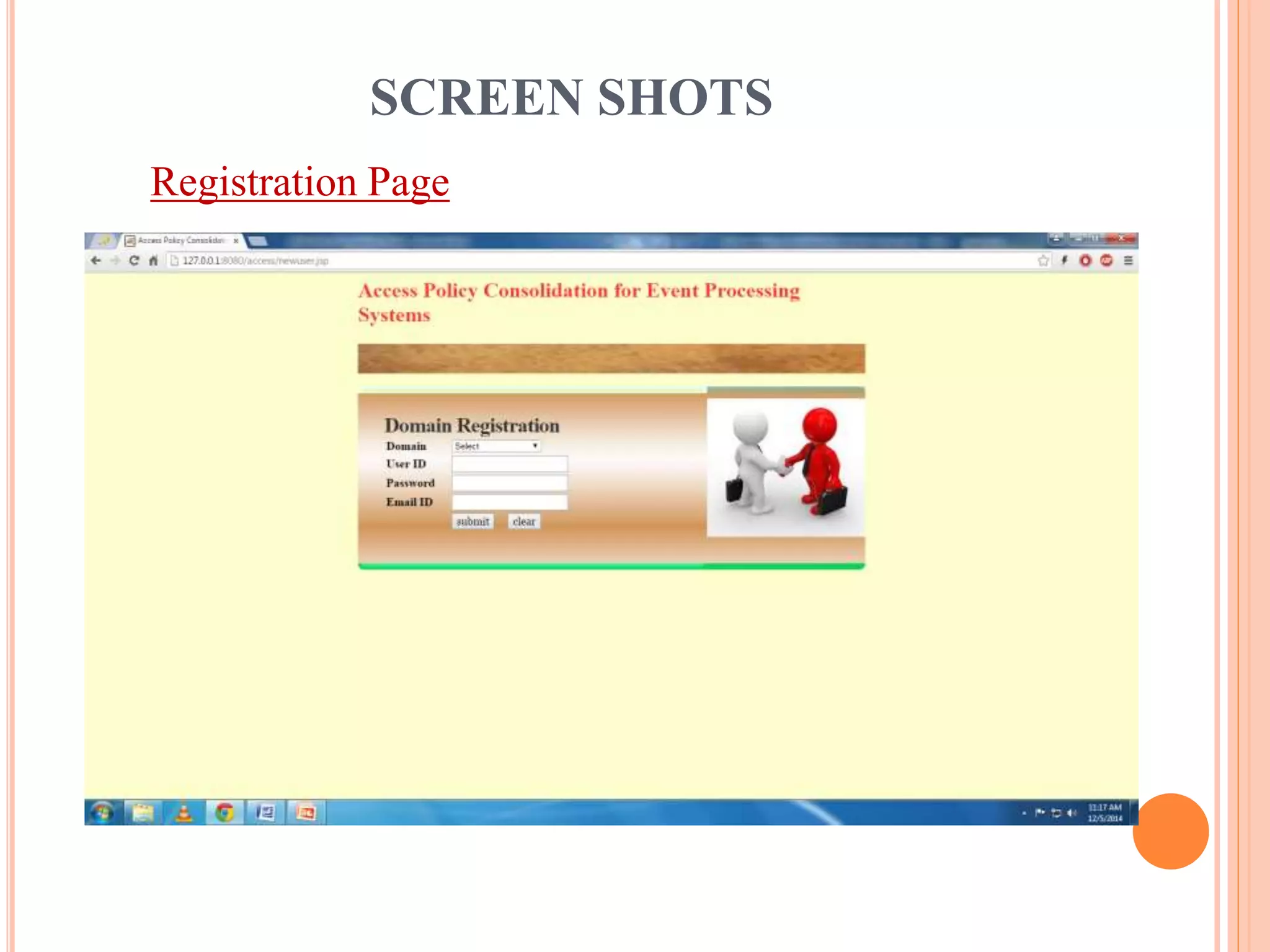
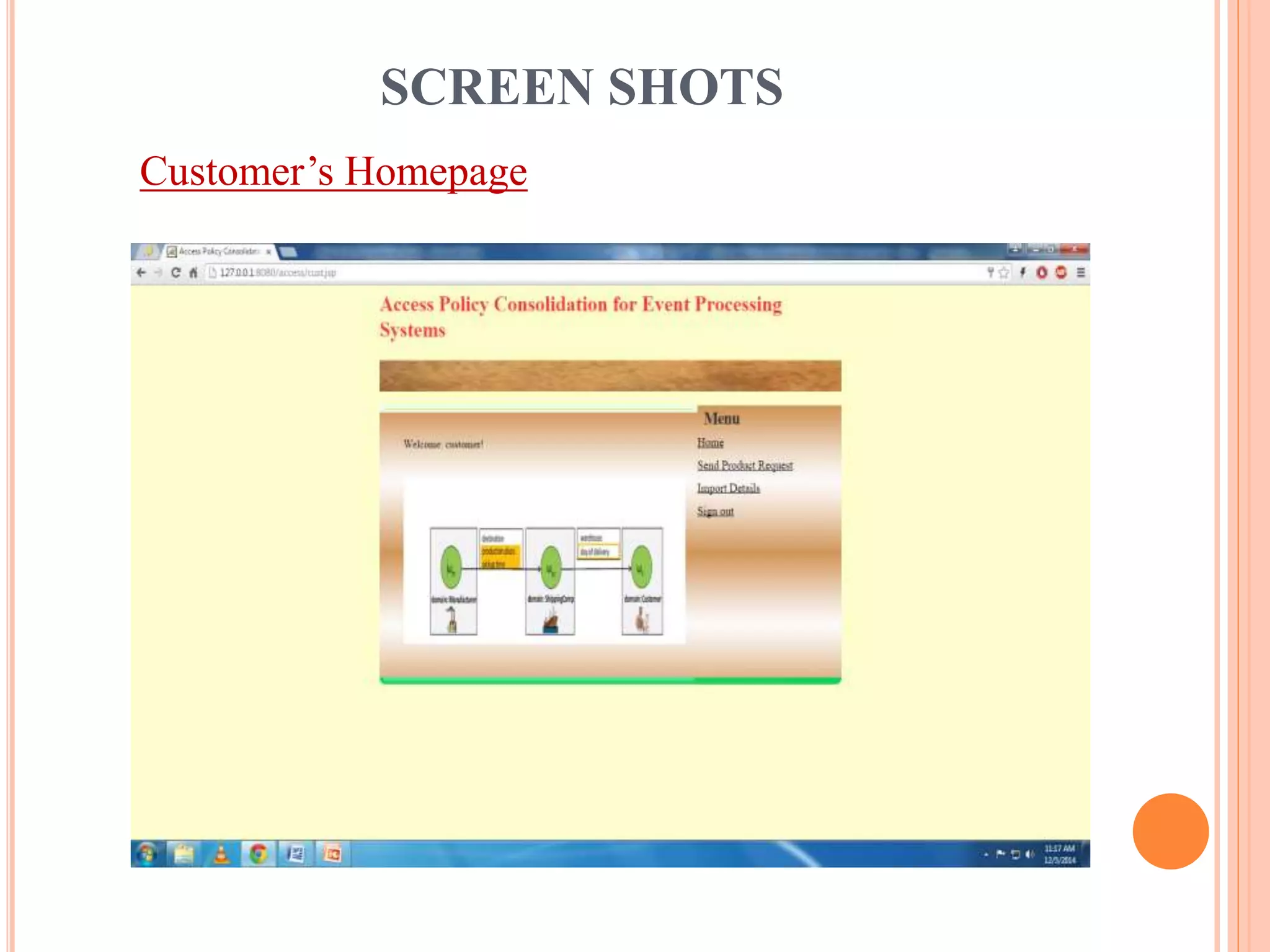
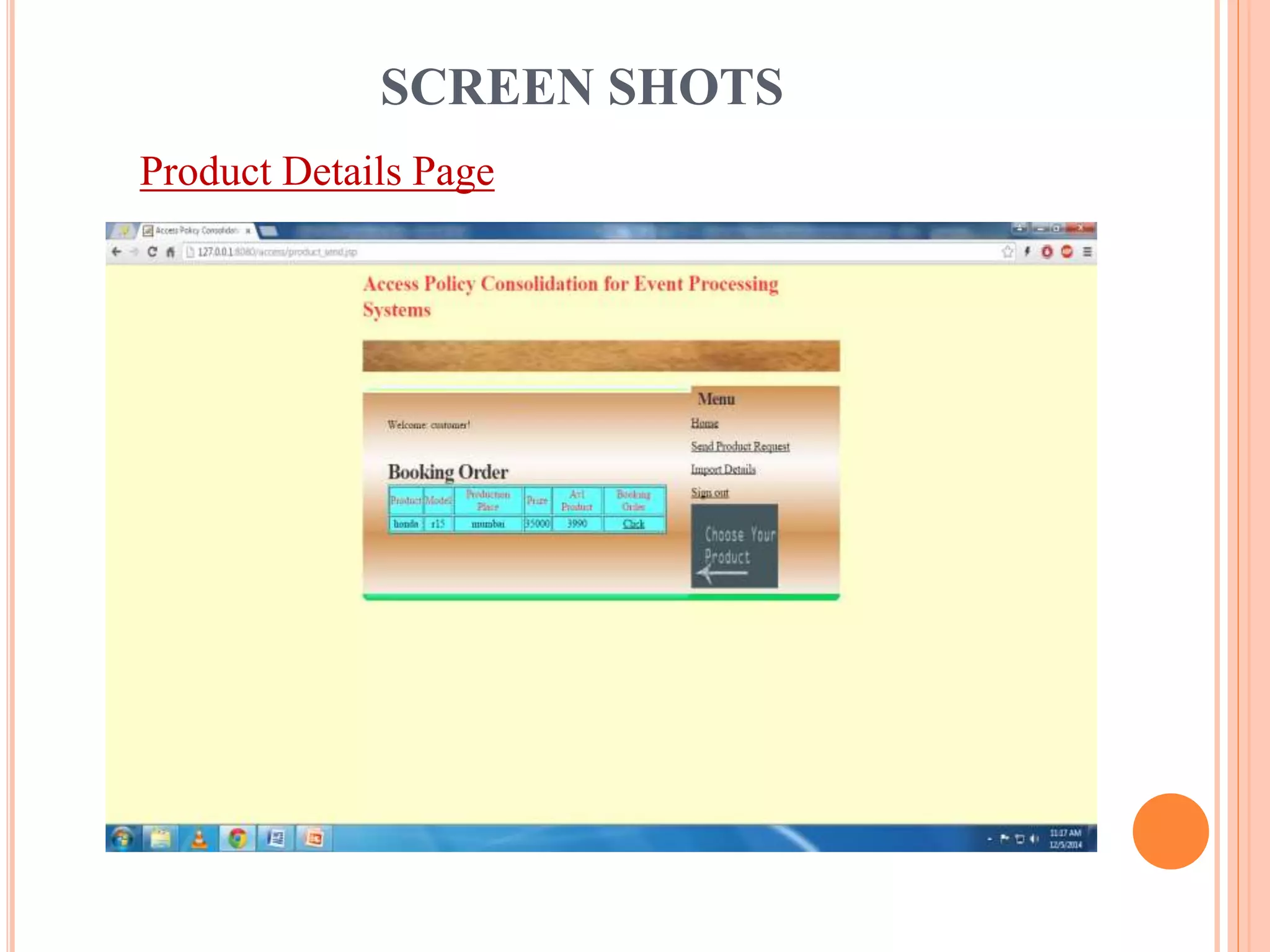
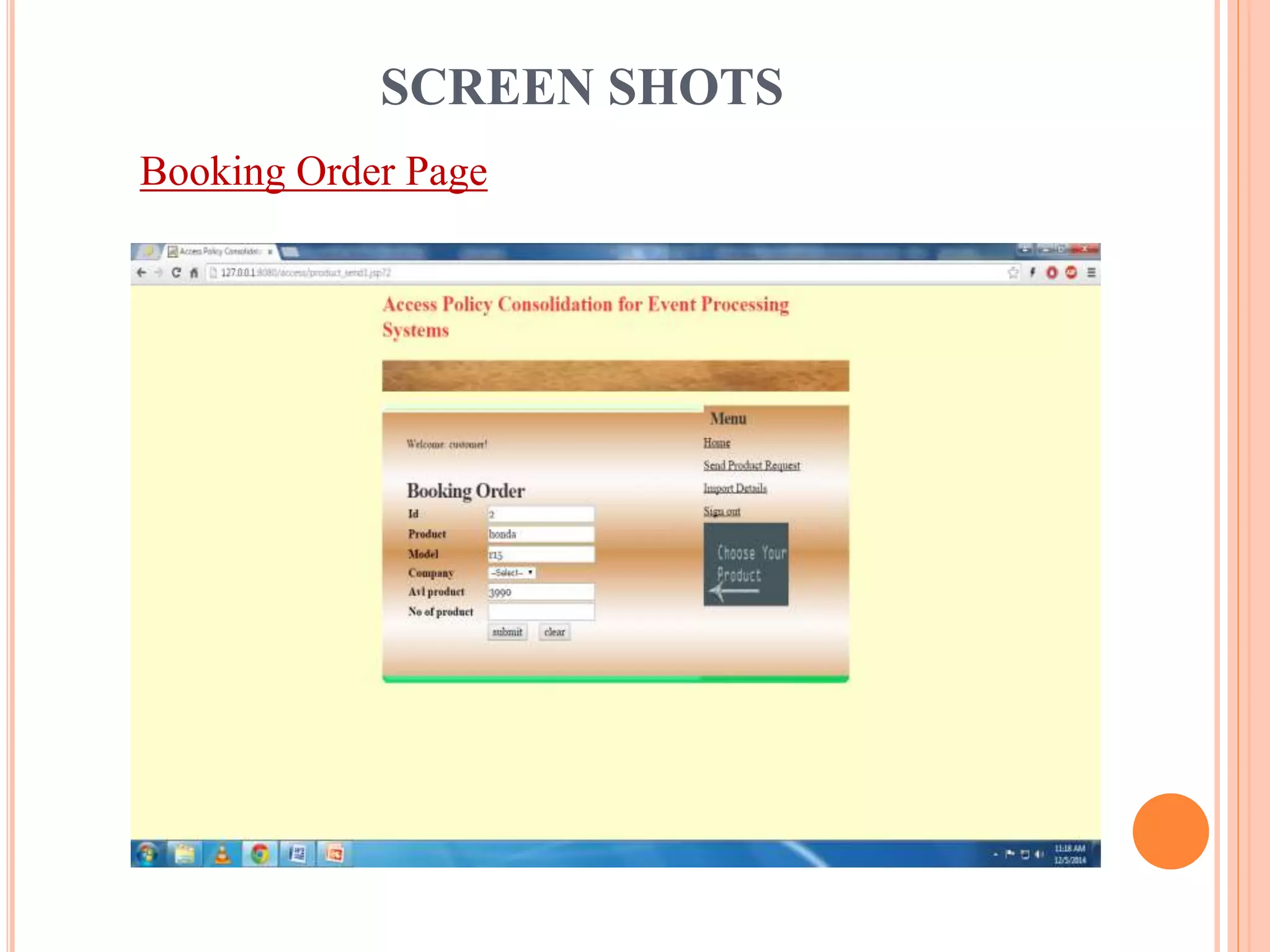
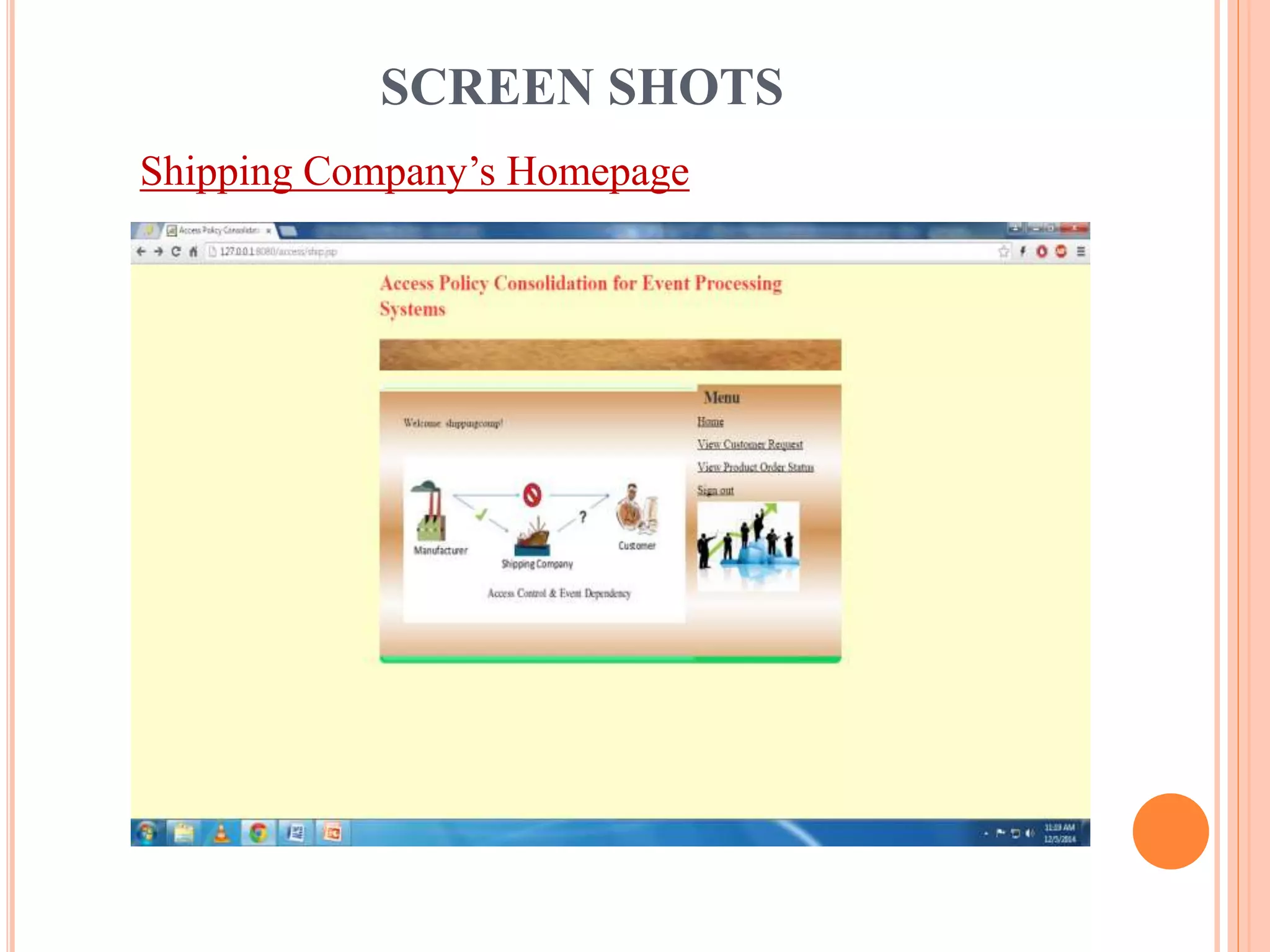
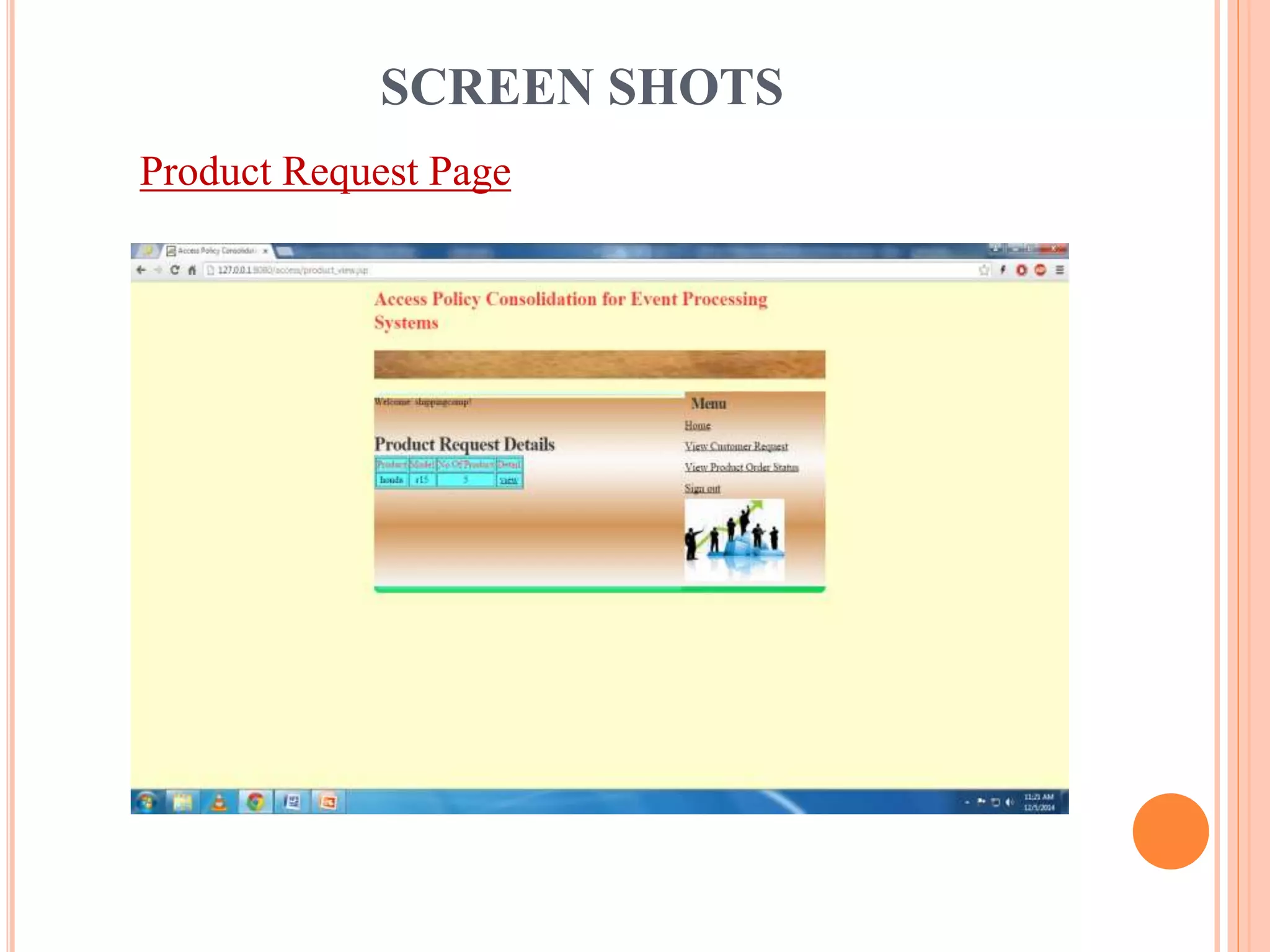
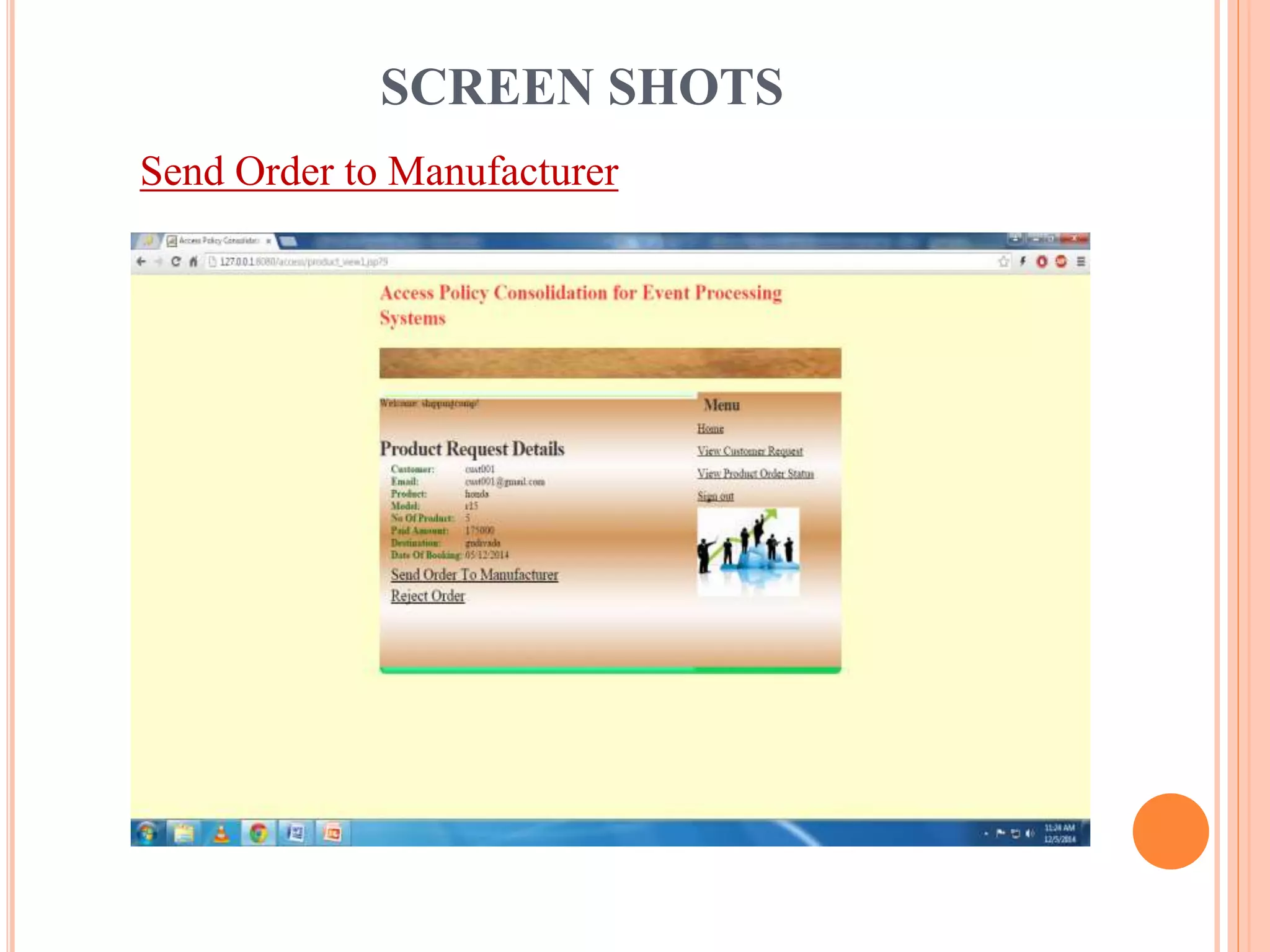
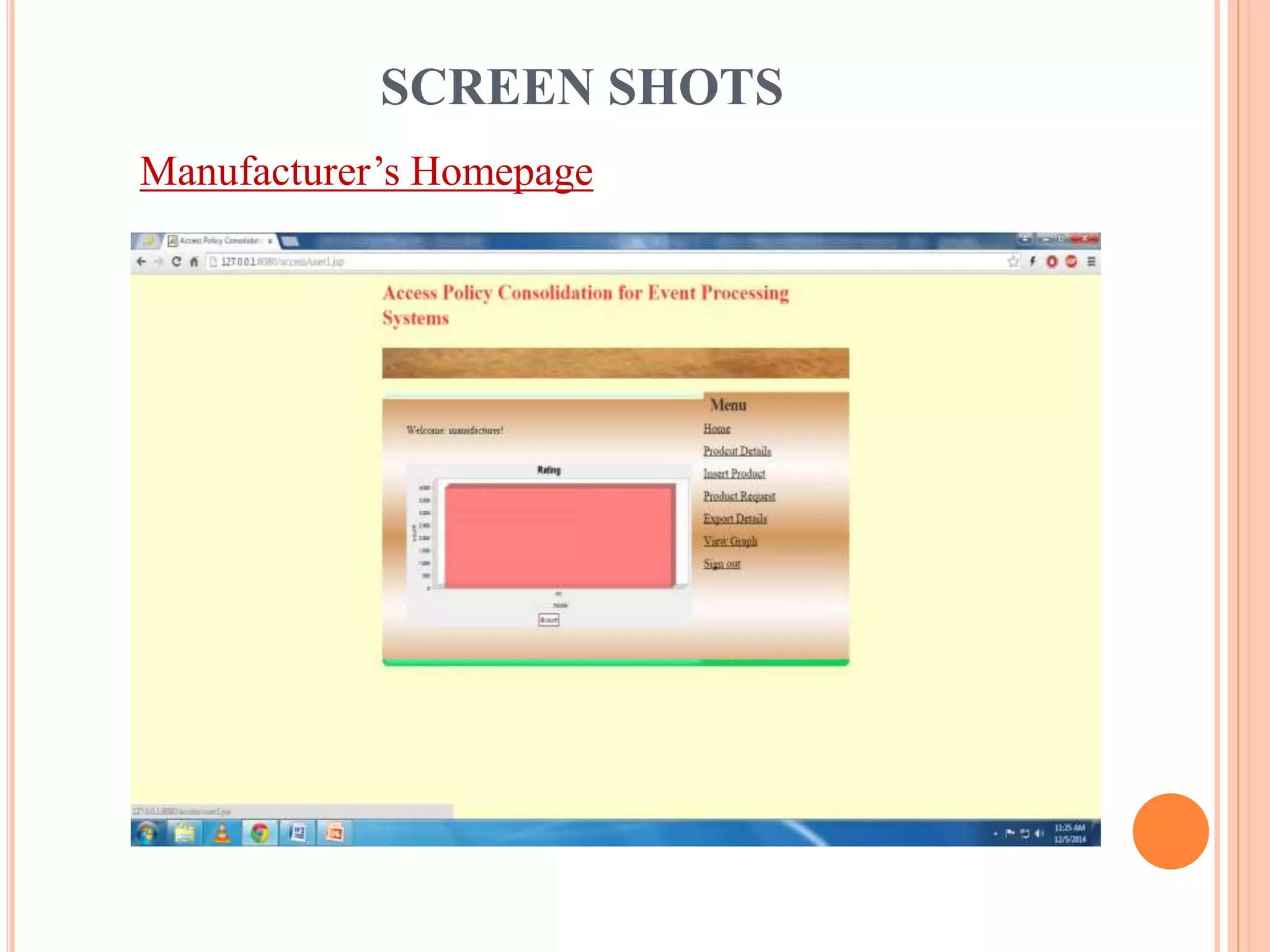
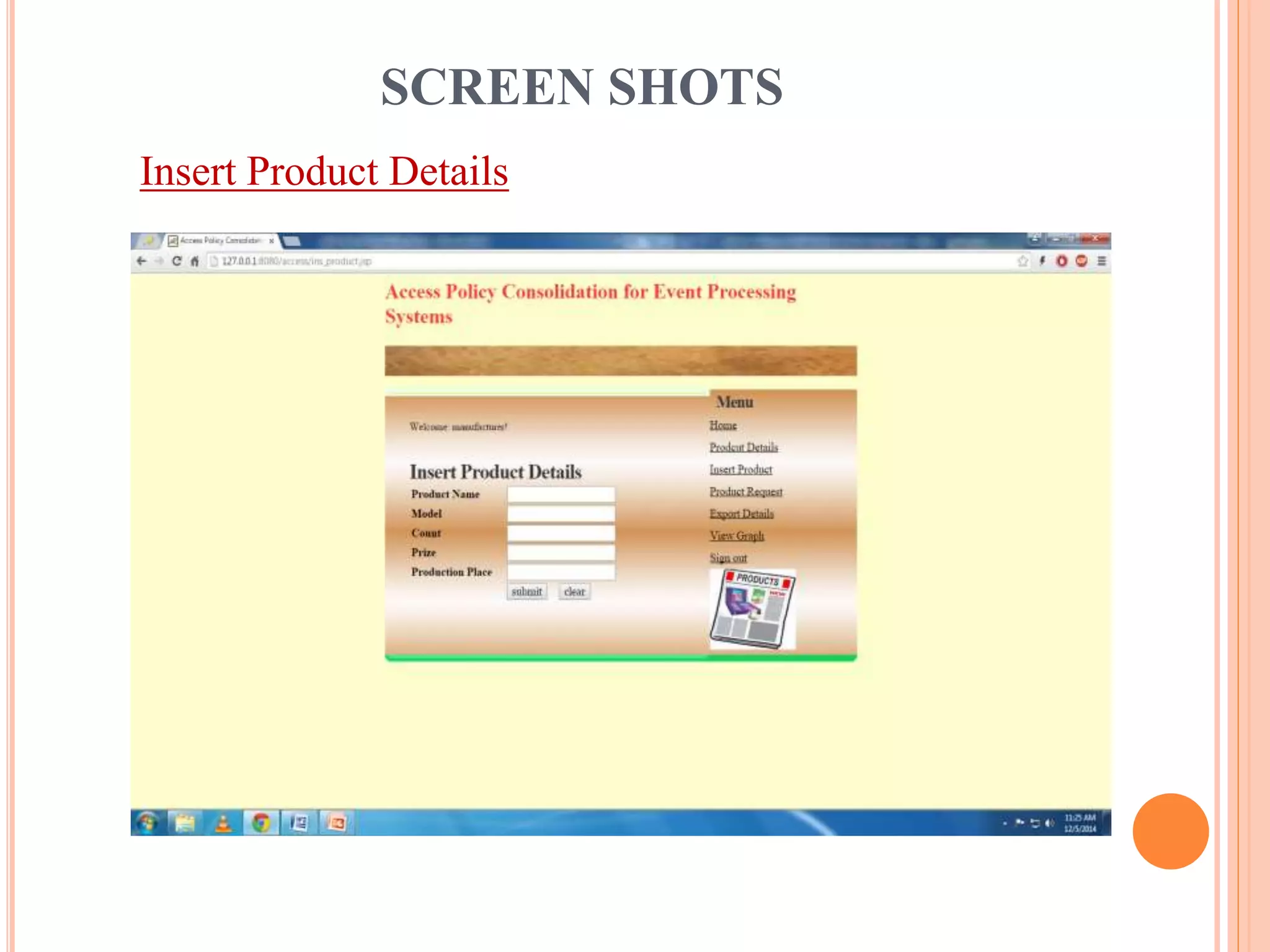
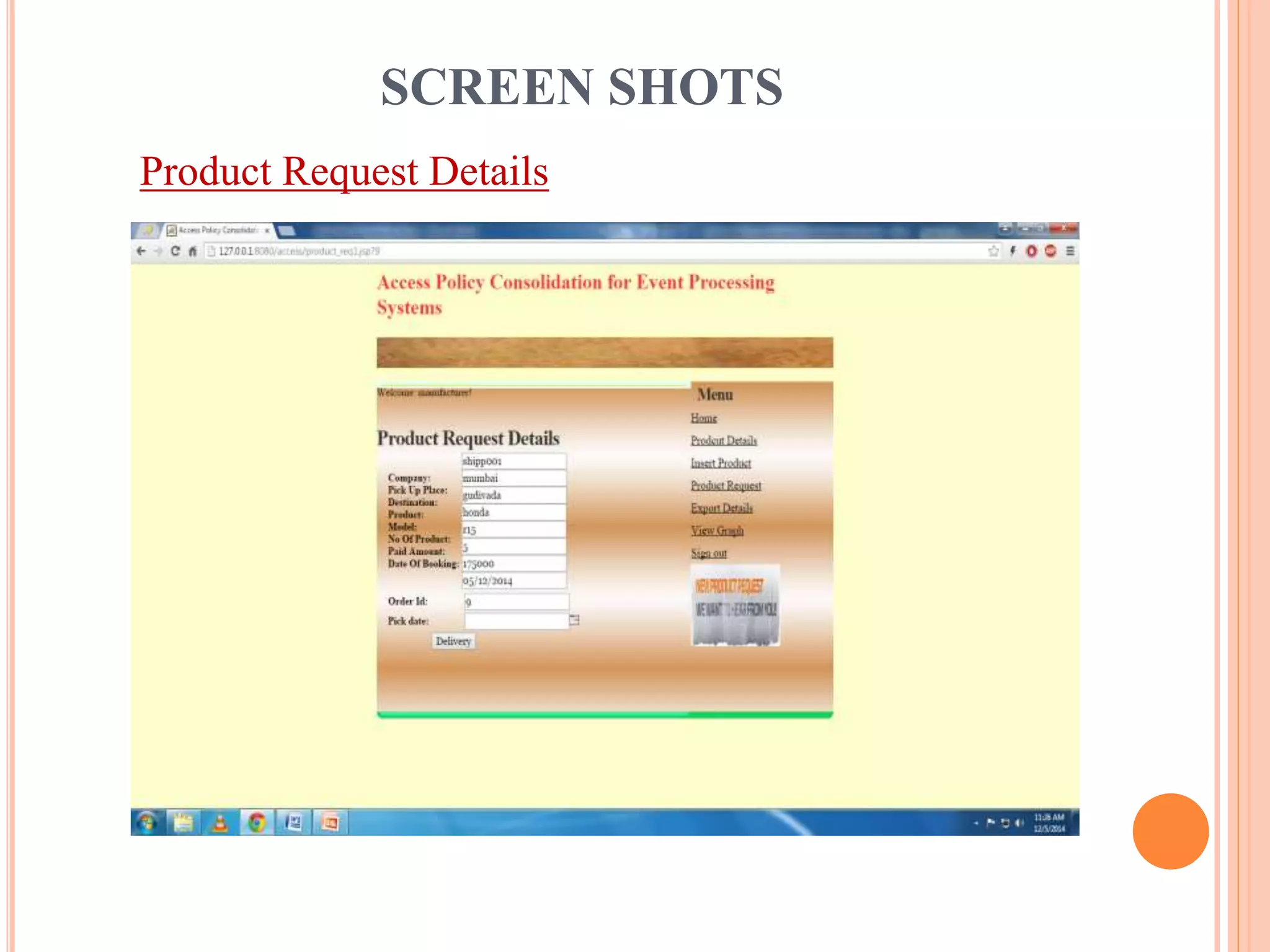
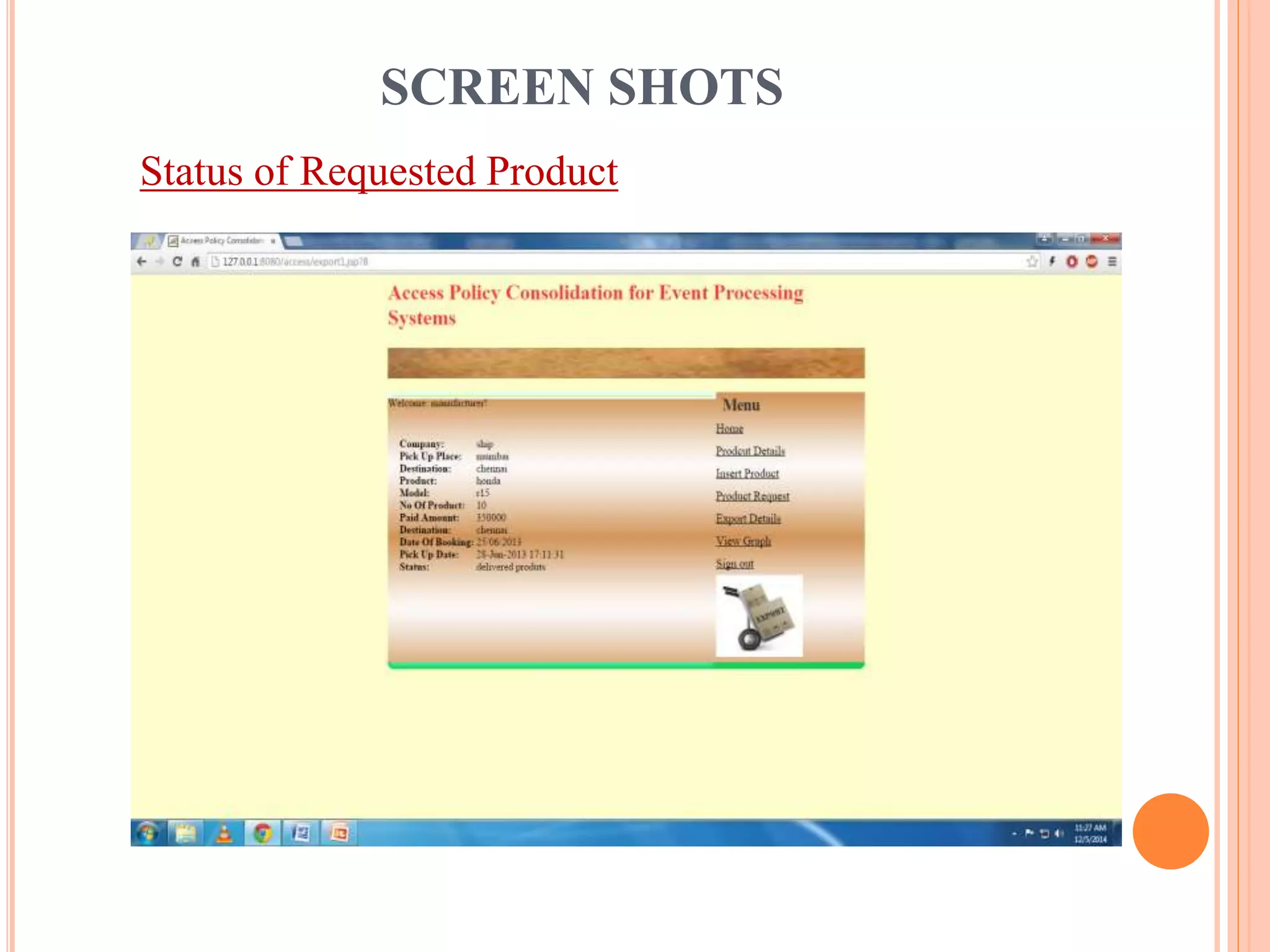
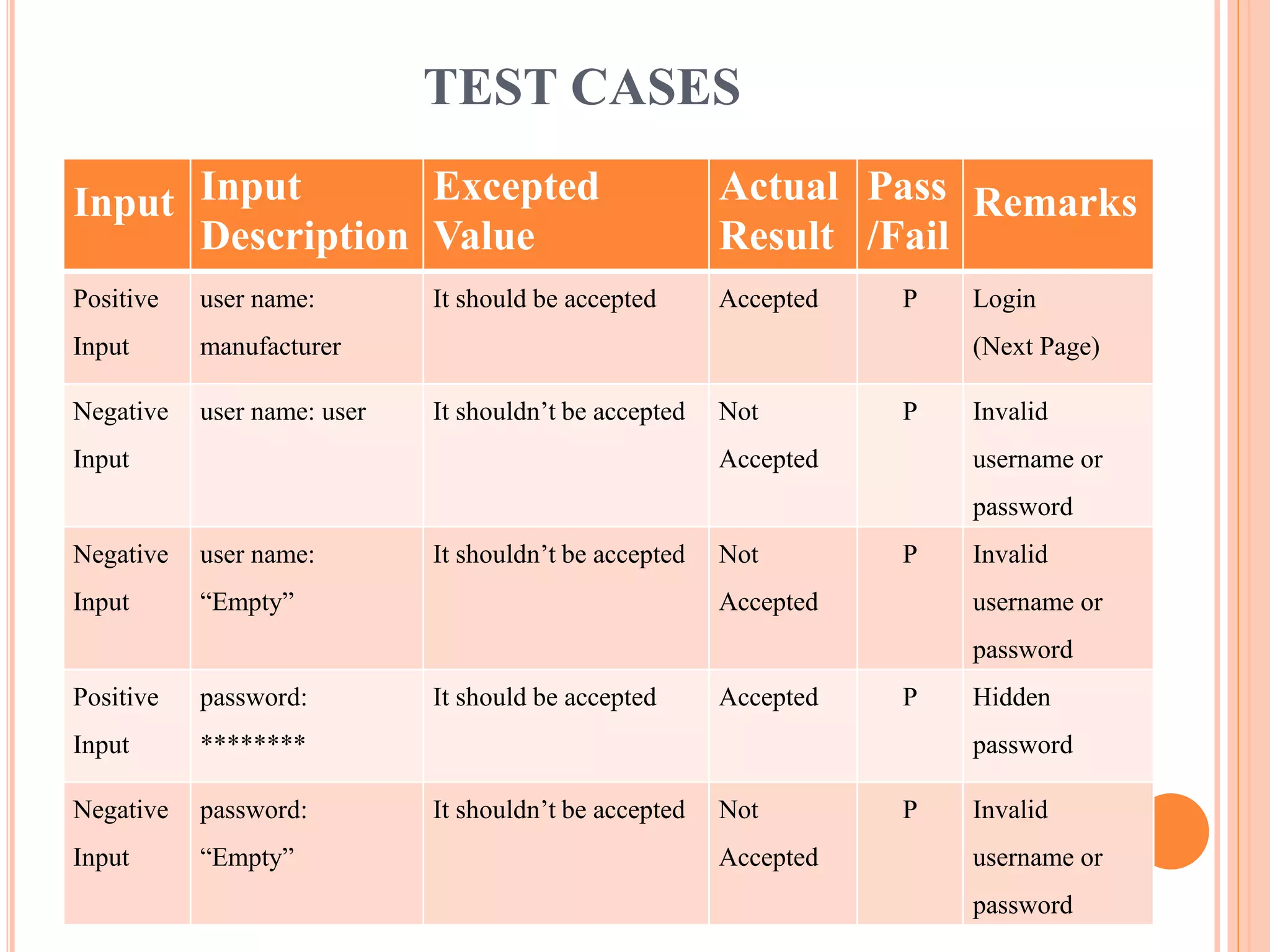
This document describes a project that aims to consolidate access policies for event processing systems. It discusses existing systems that lack privacy for event streams processed across multiple domains. The proposed system allows fine-grained access management through access policies specified for each incoming event stream. Key modules include event processing, manufacturer, shipping company, and customer, which interact via the consolidated access policies.