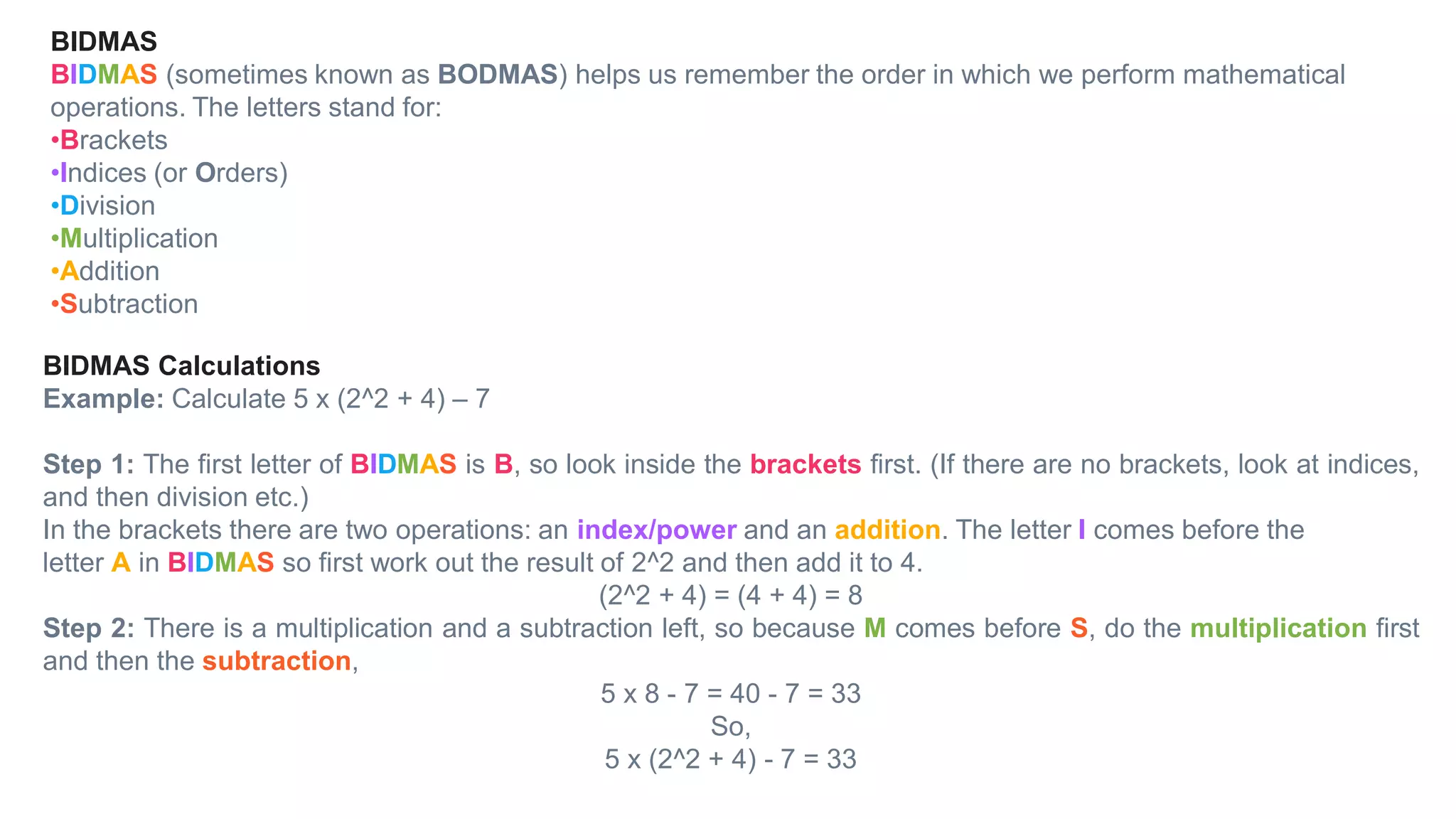
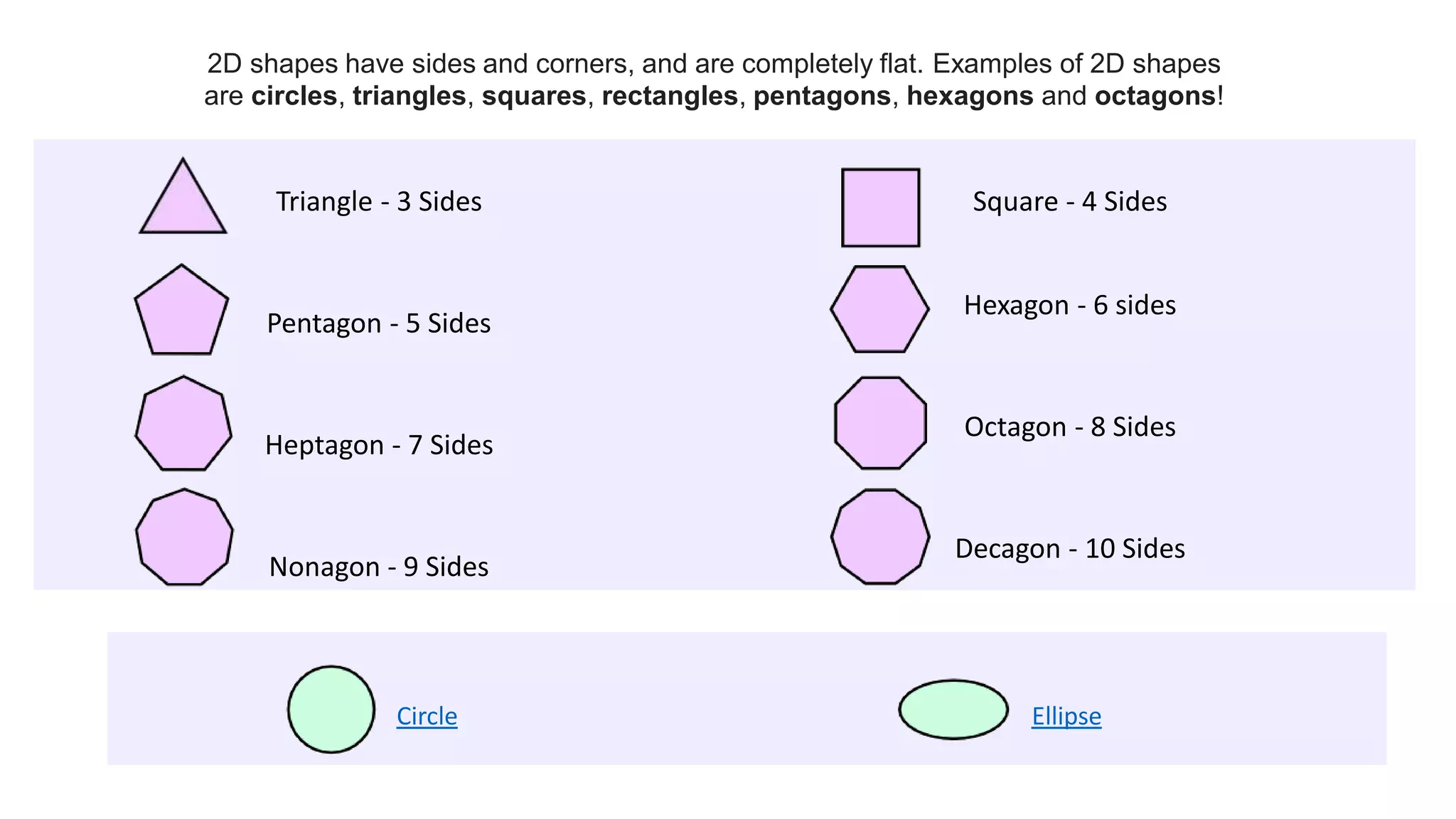
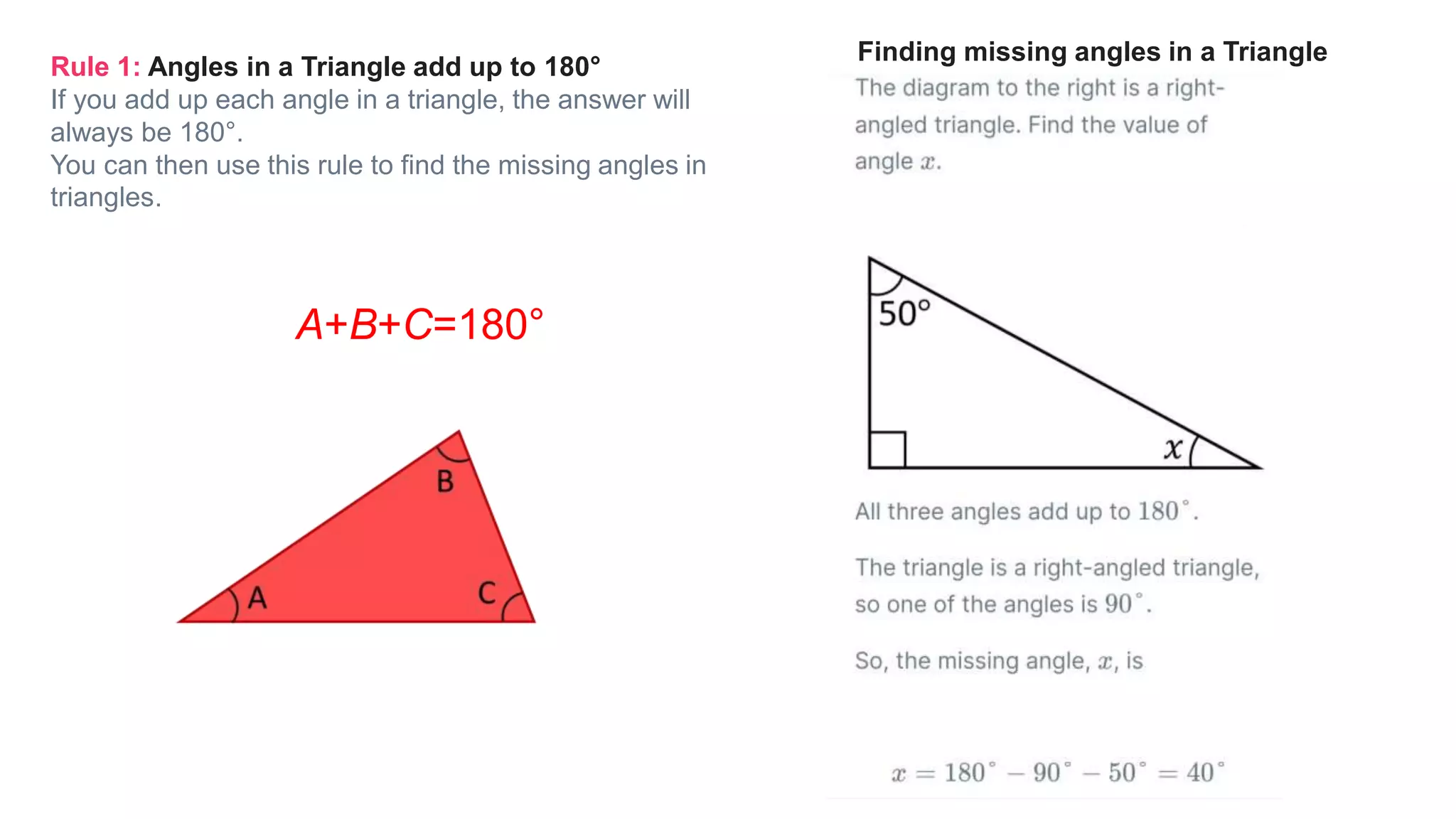
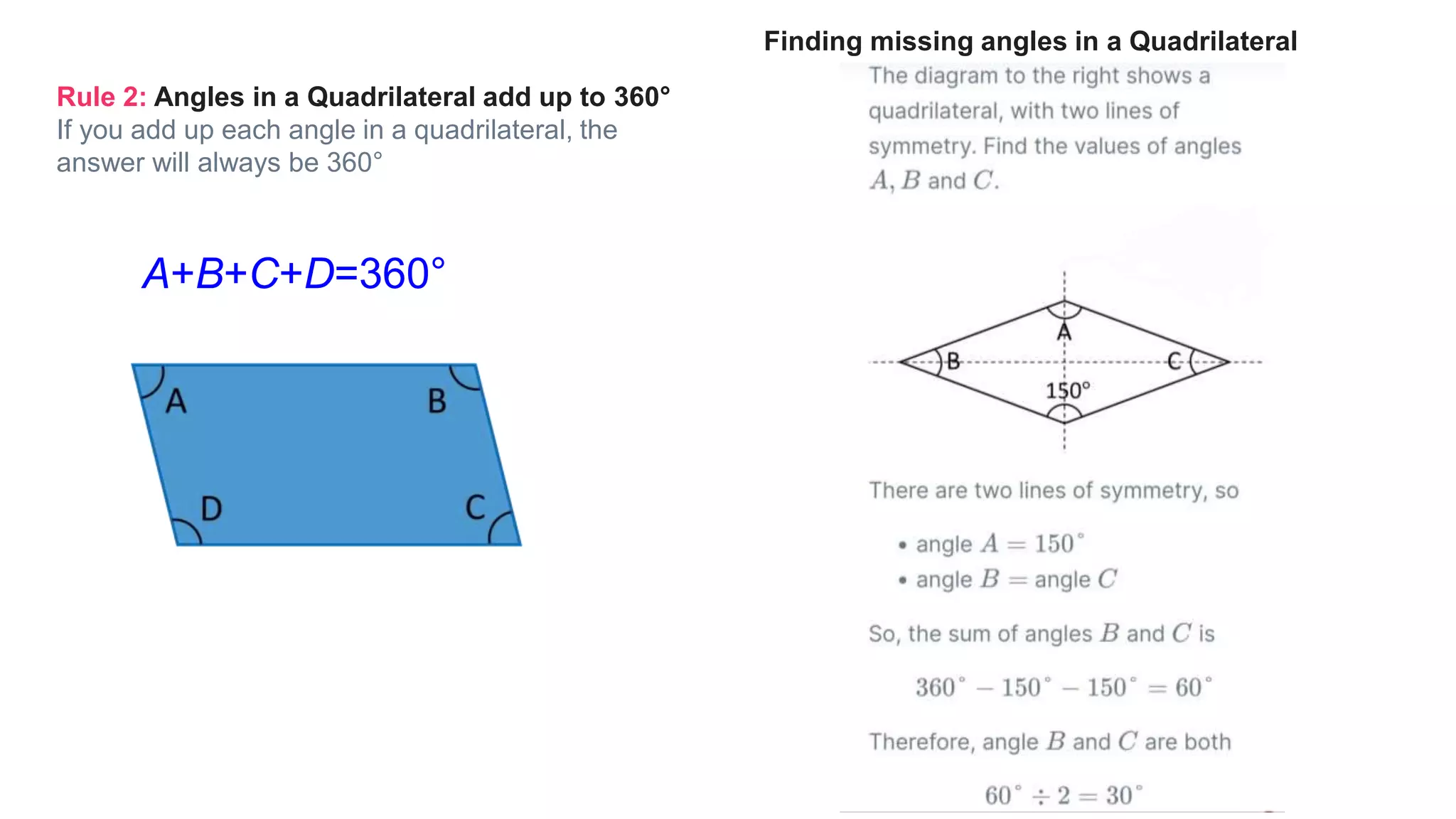
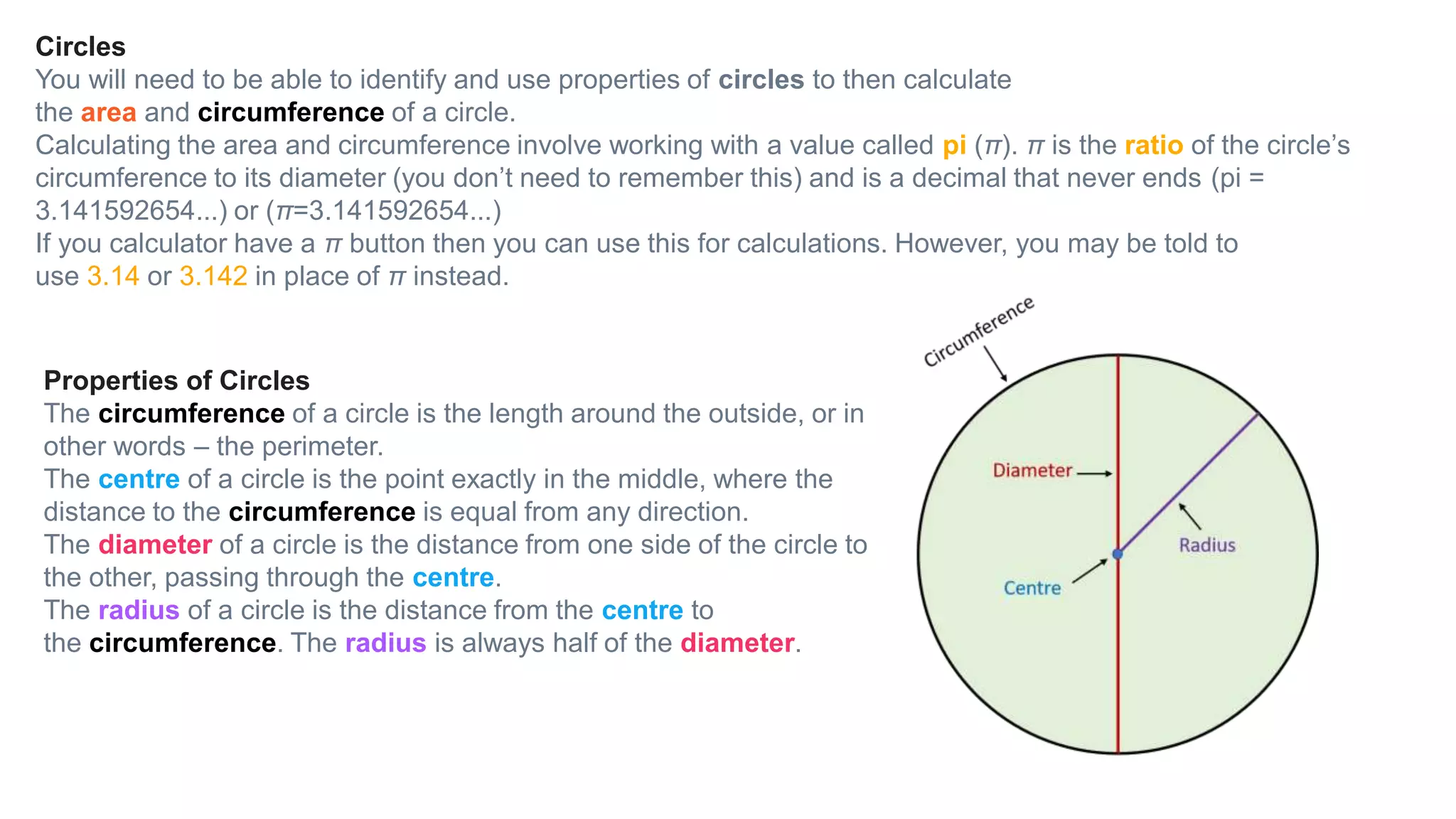
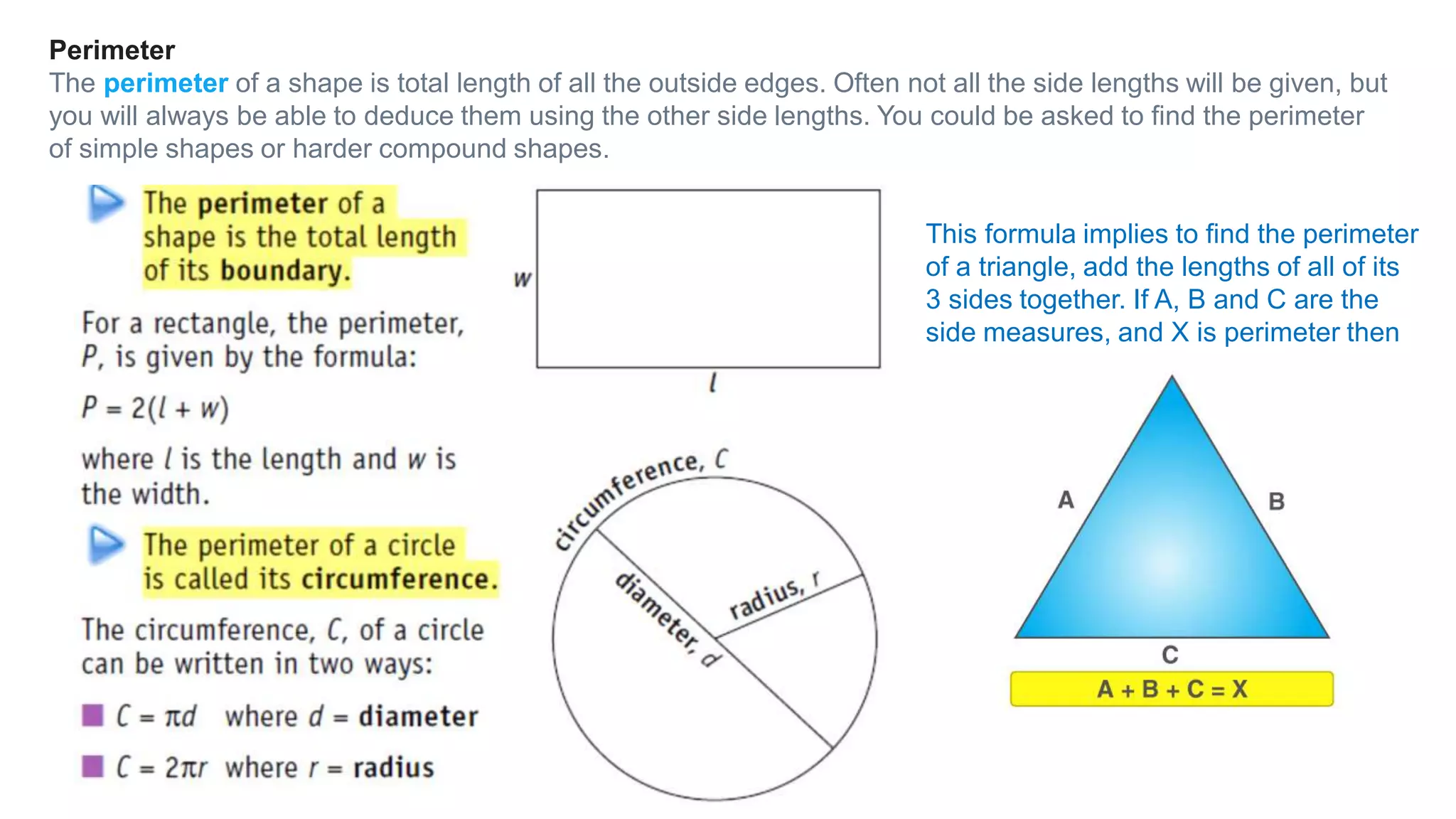
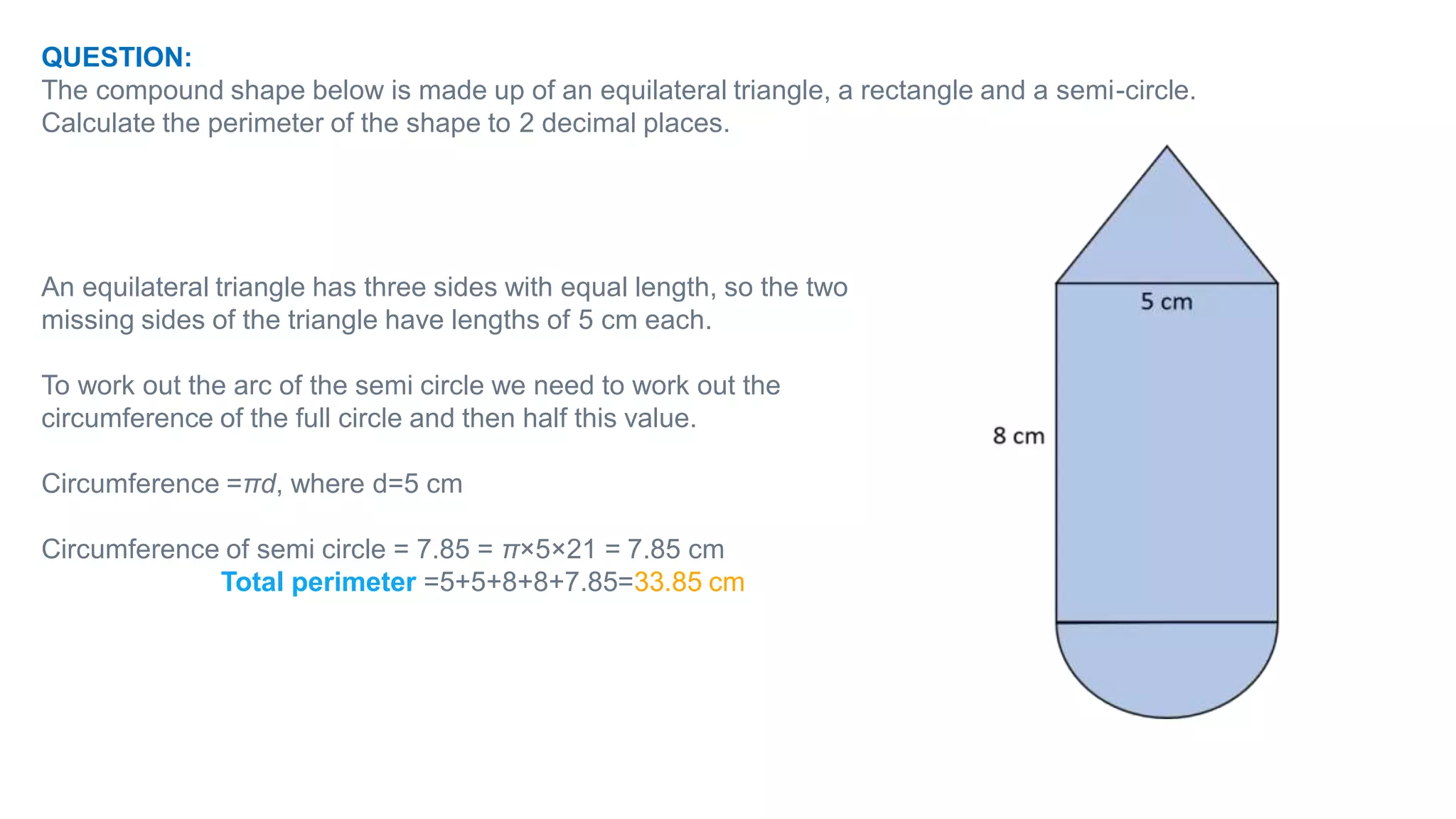
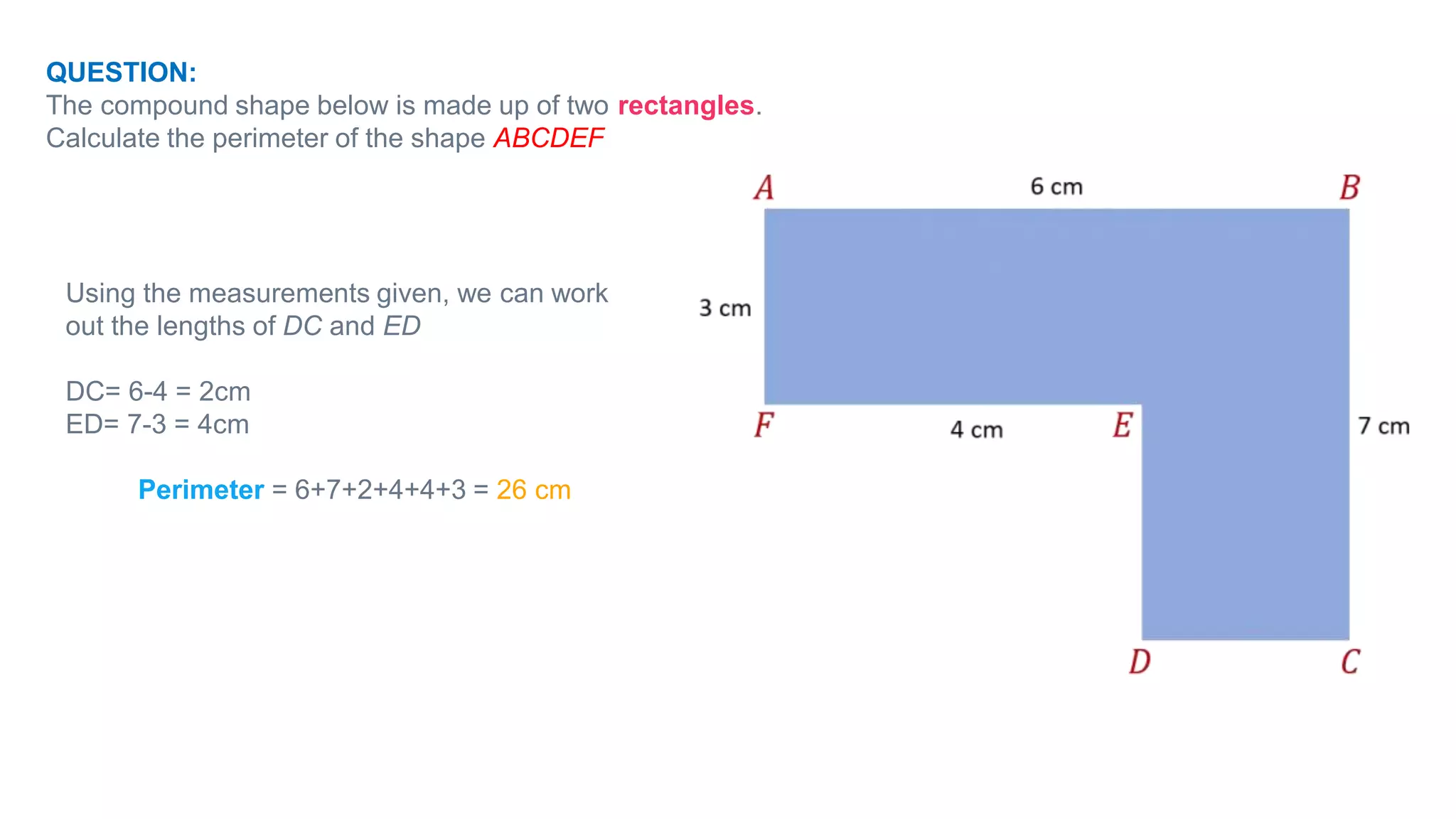
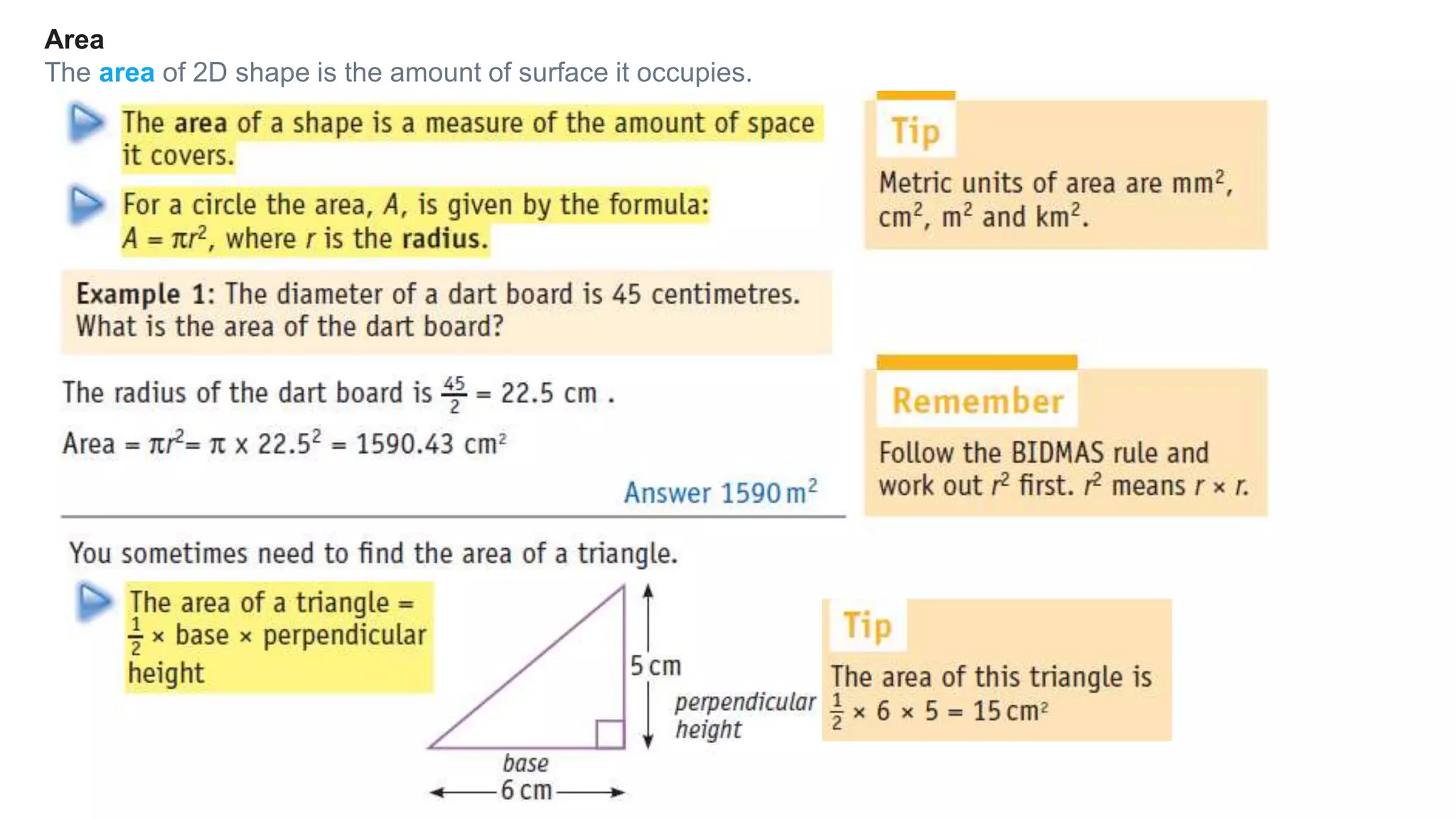
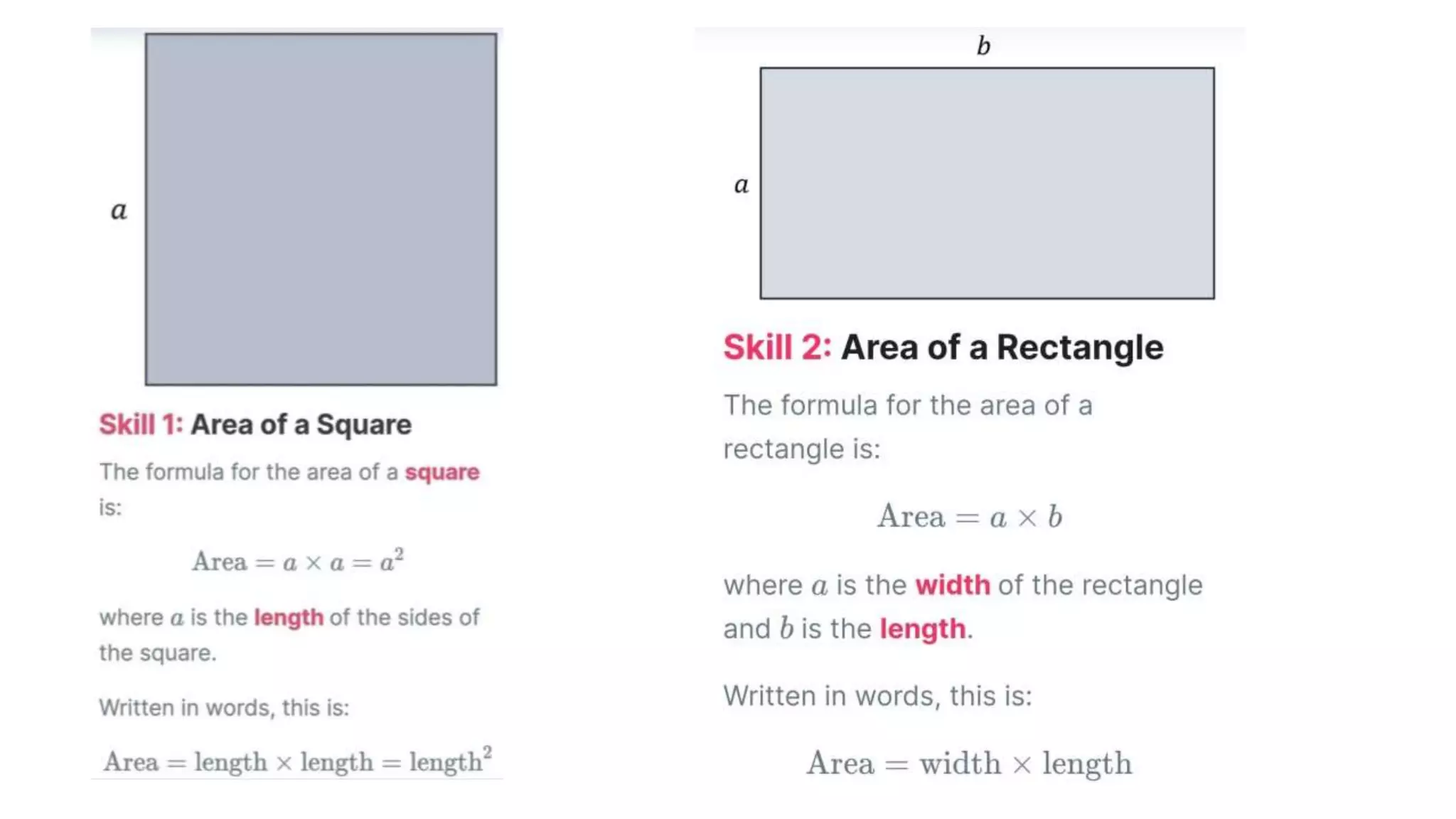
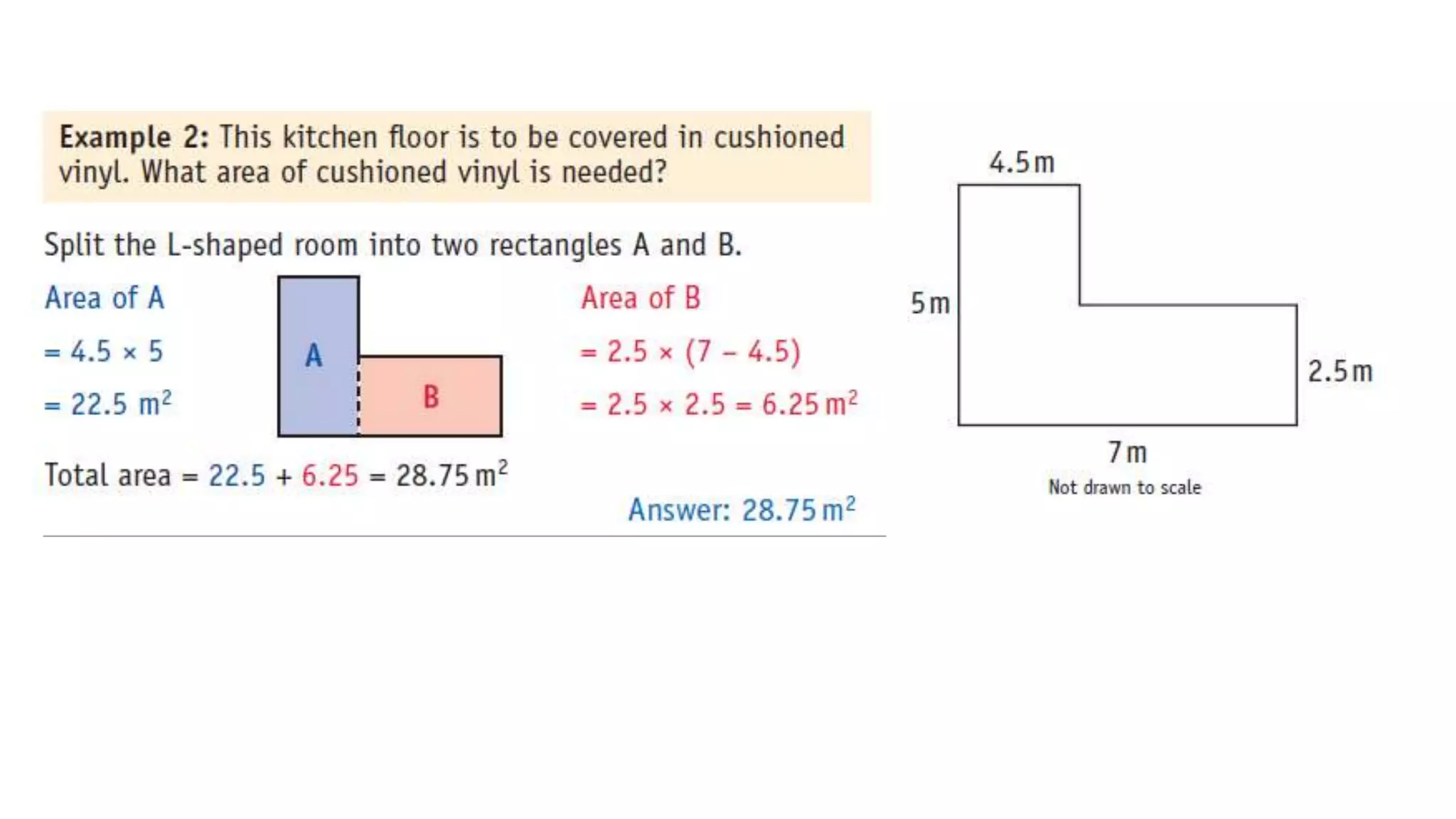
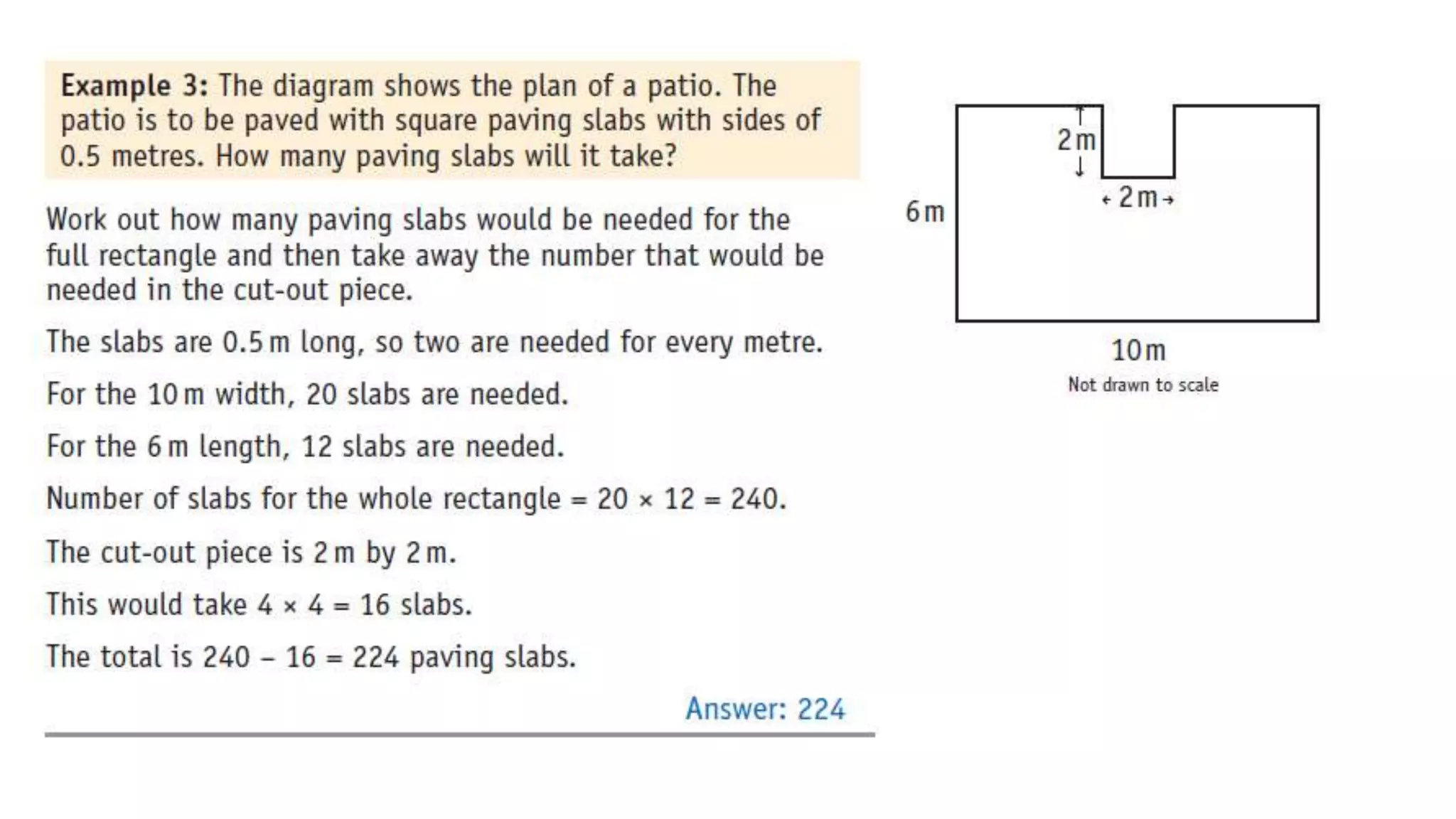
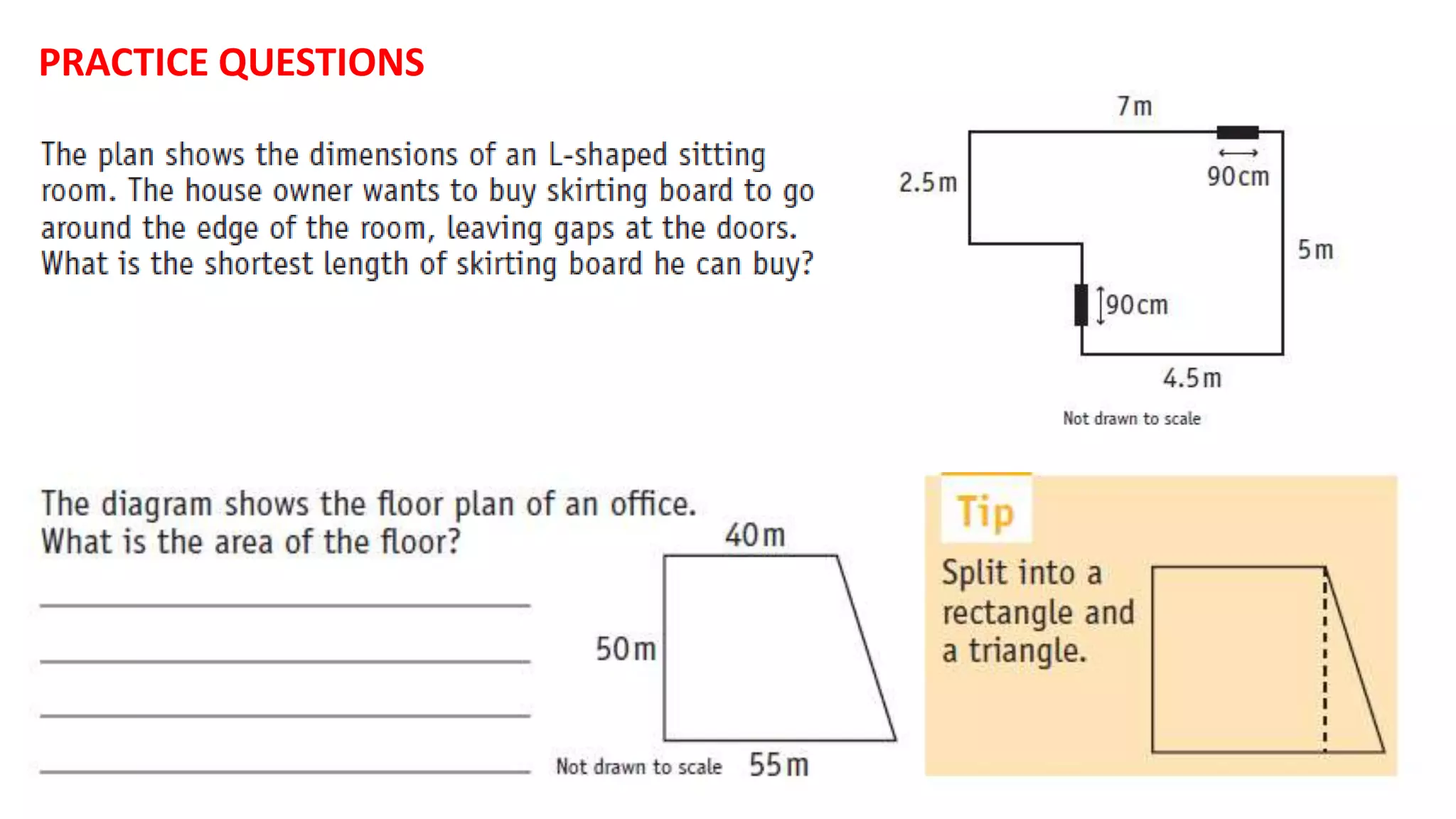
Topics covered in today's class include BIDMAS order of operations, 2D shapes, angles in 2D shapes, circles, and calculating area and perimeter. BIDMAS establishes the order for performing mathematical operations. 2D shapes were discussed along with properties of angles in triangles and quadrilaterals. Key circle properties like circumference, diameter, radius were defined. Calculating area involves using pi while perimeter finds the total length of edges. Practice questions provided calculations for perimeter of compound shapes and areas of rectangles.