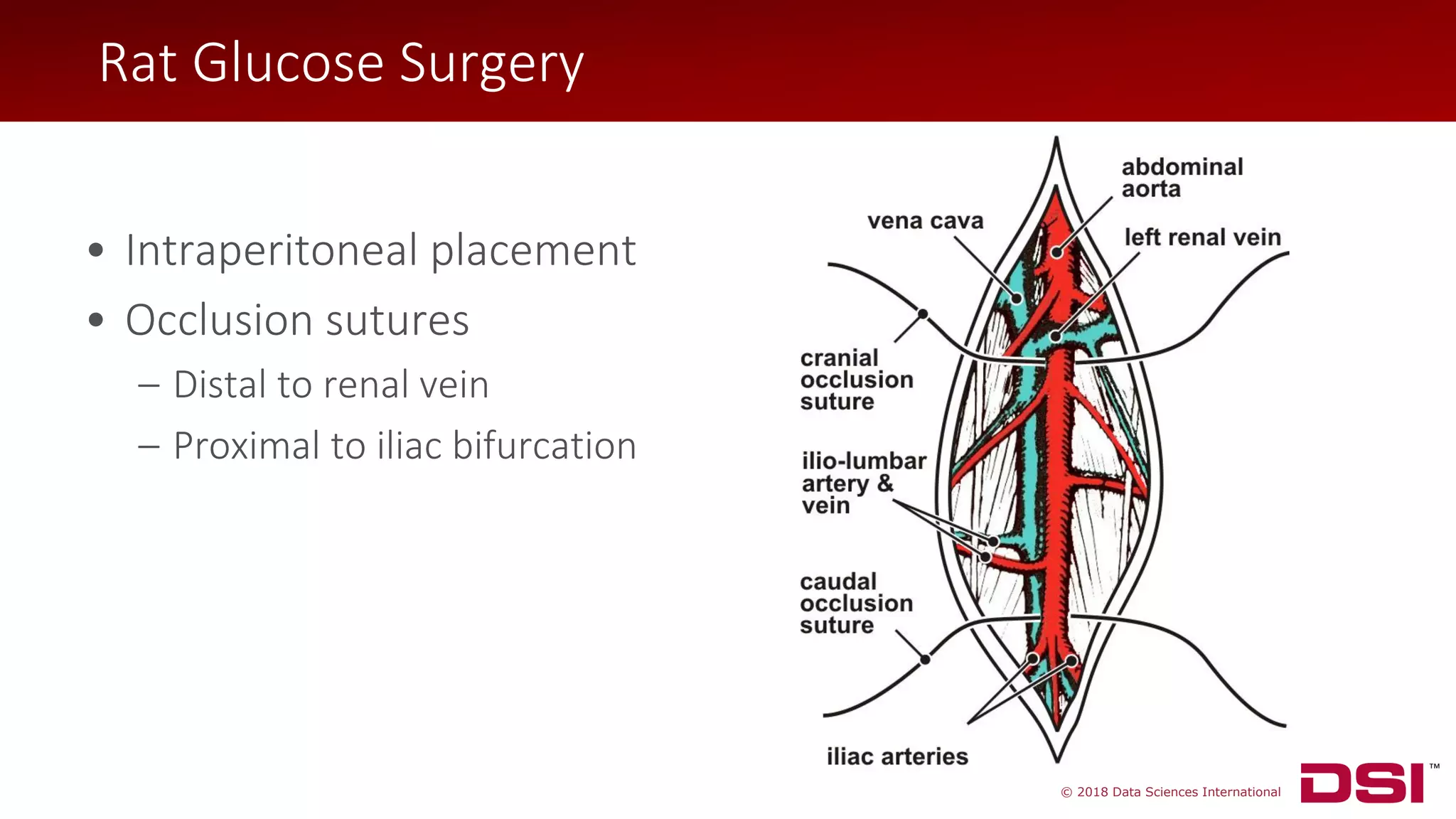
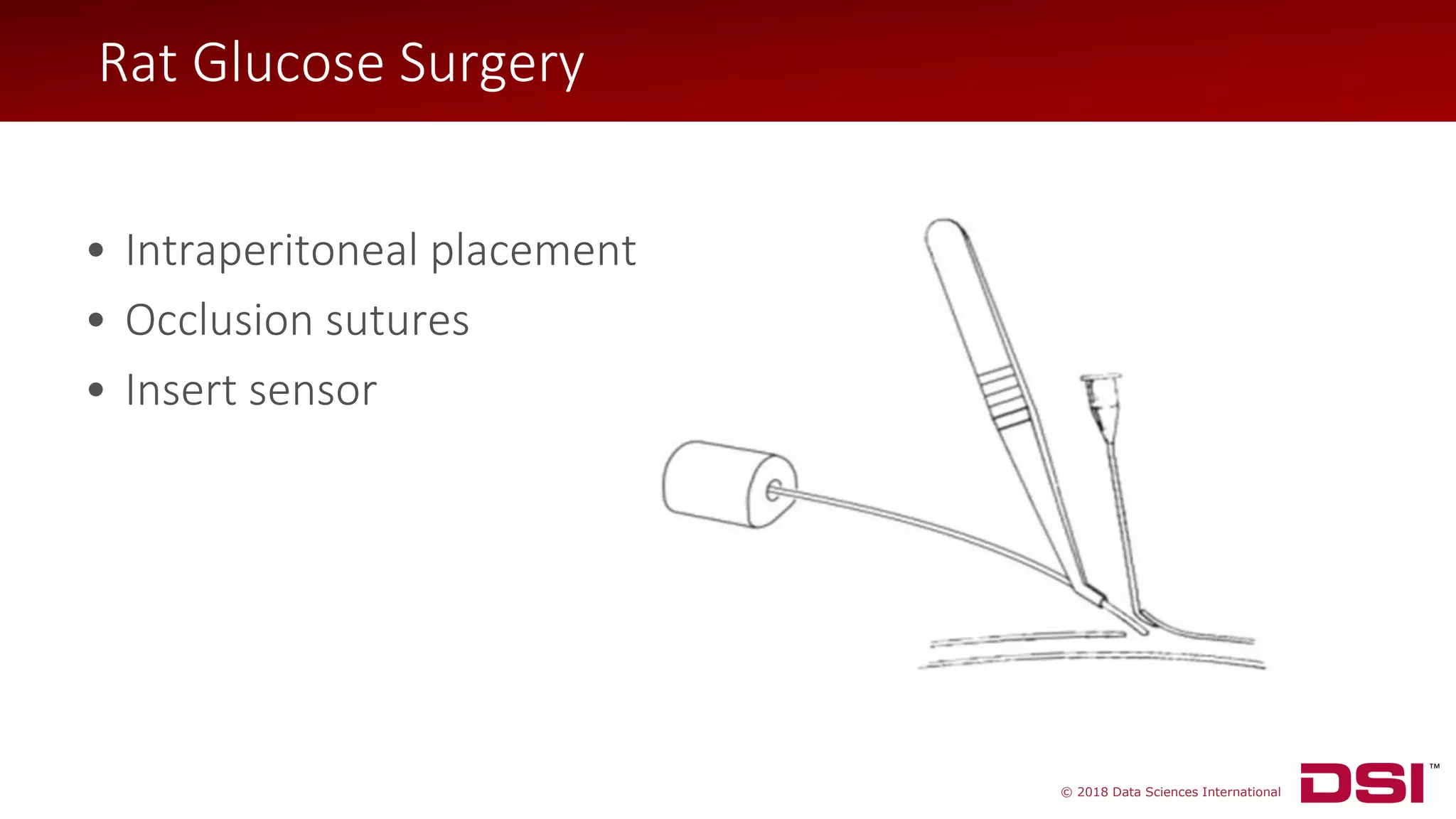
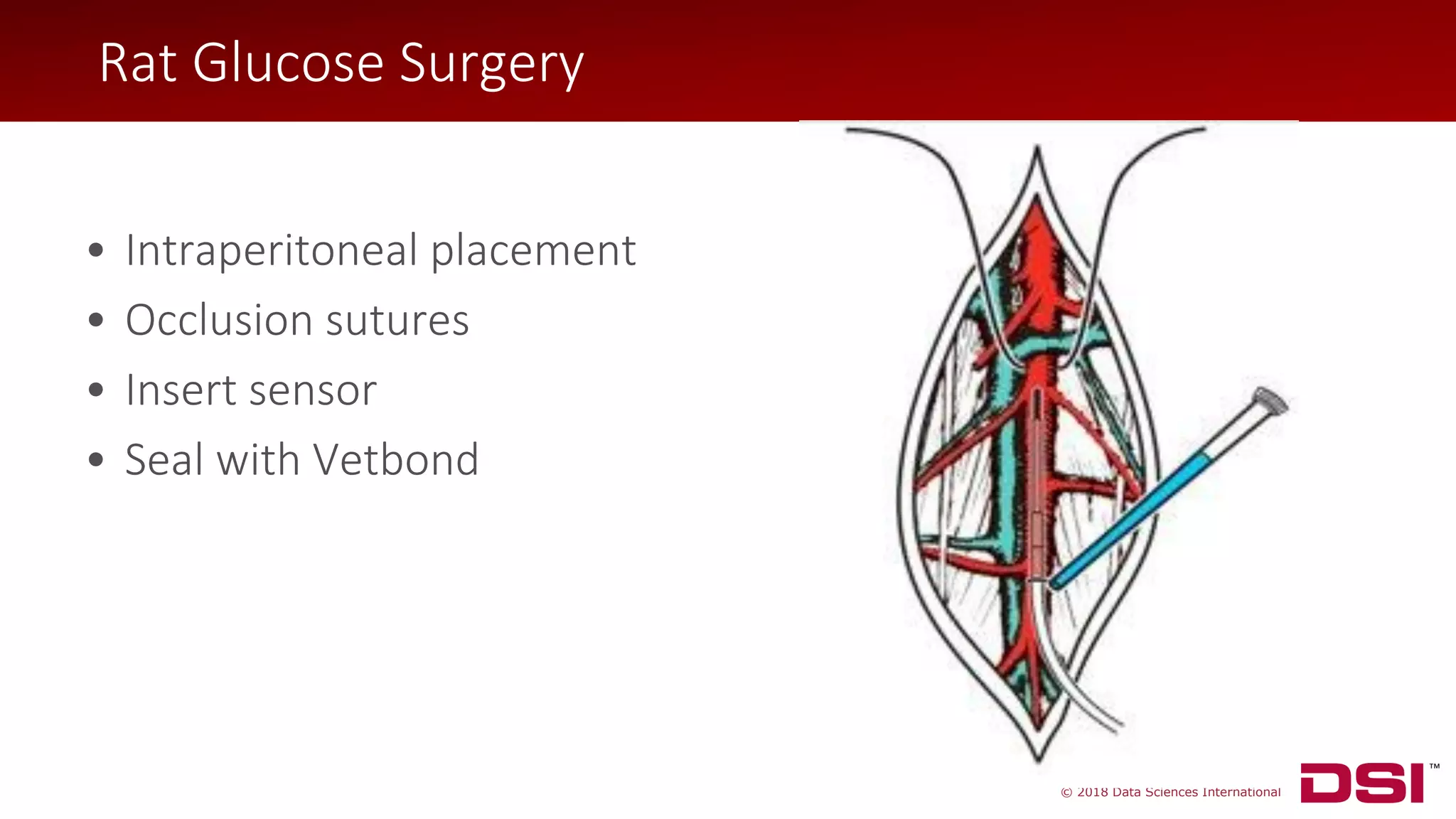
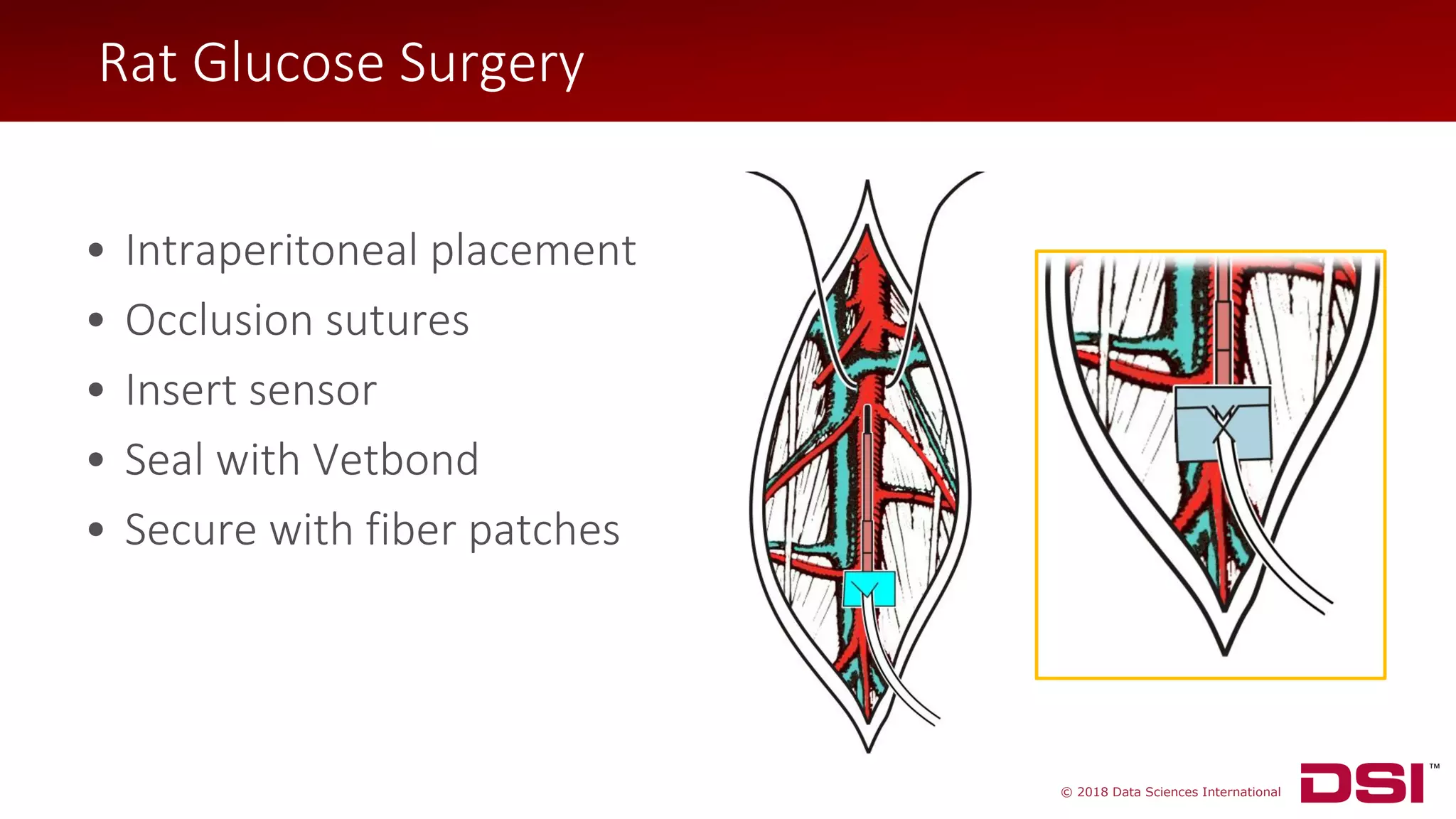
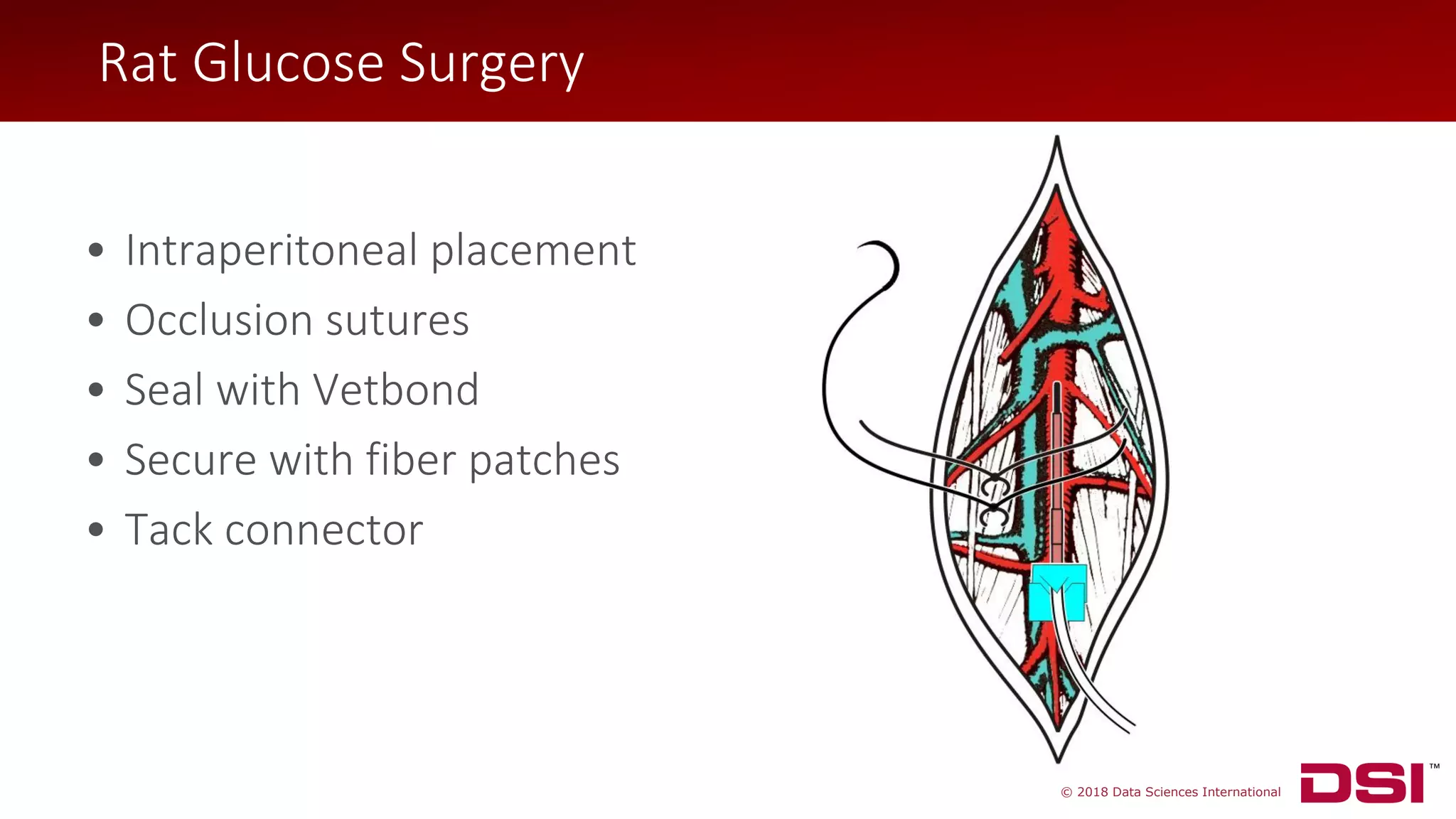
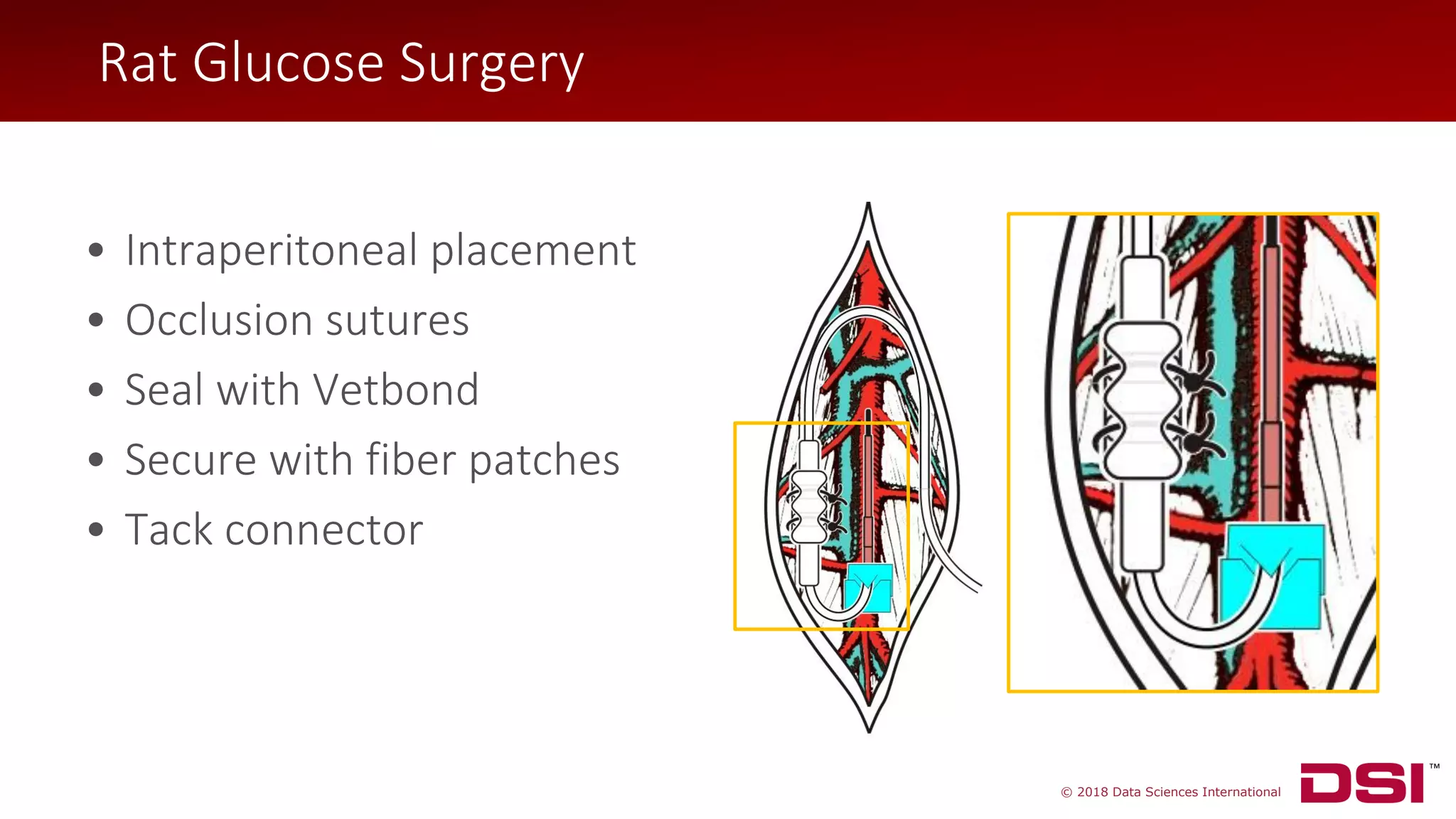
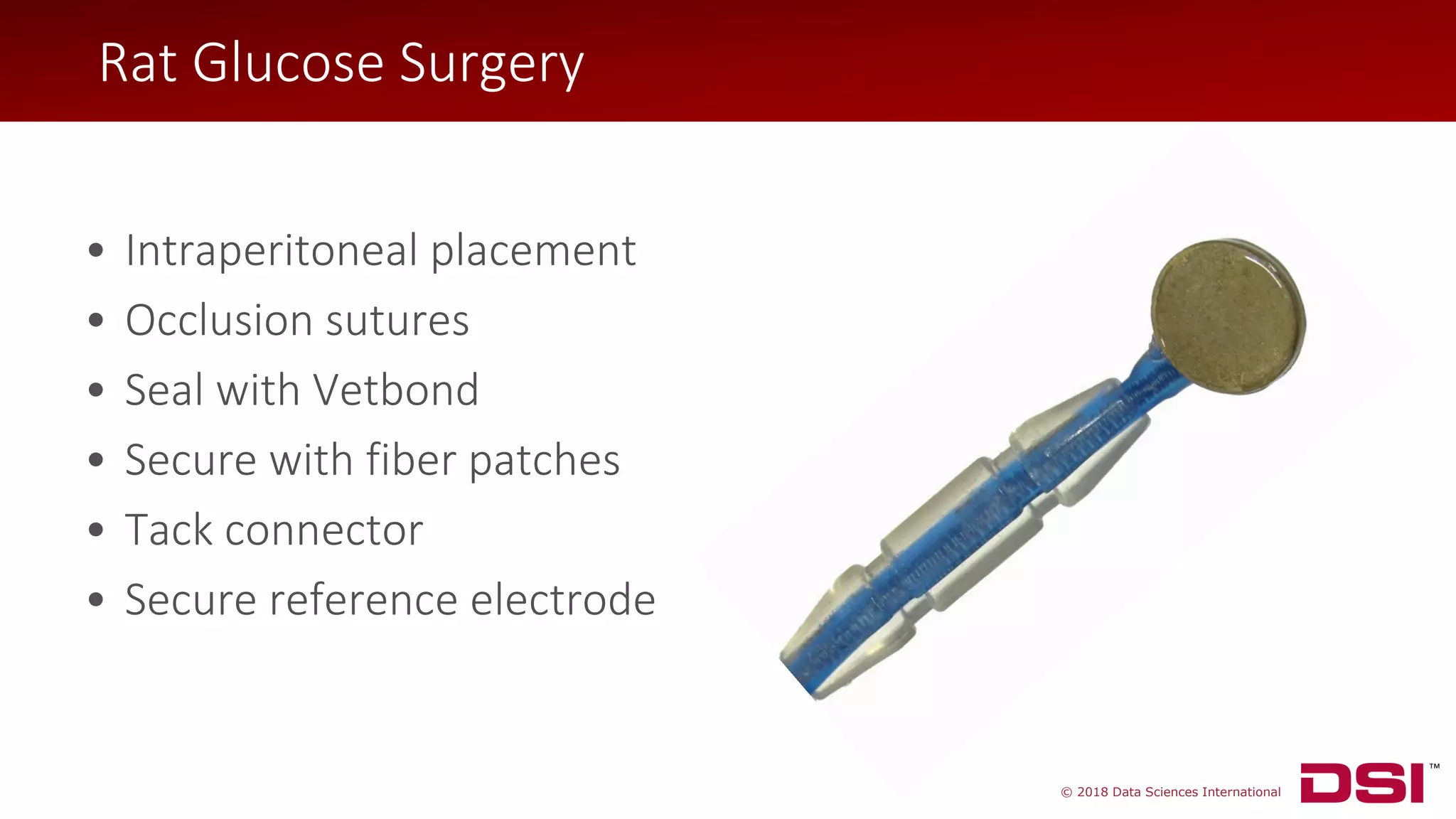
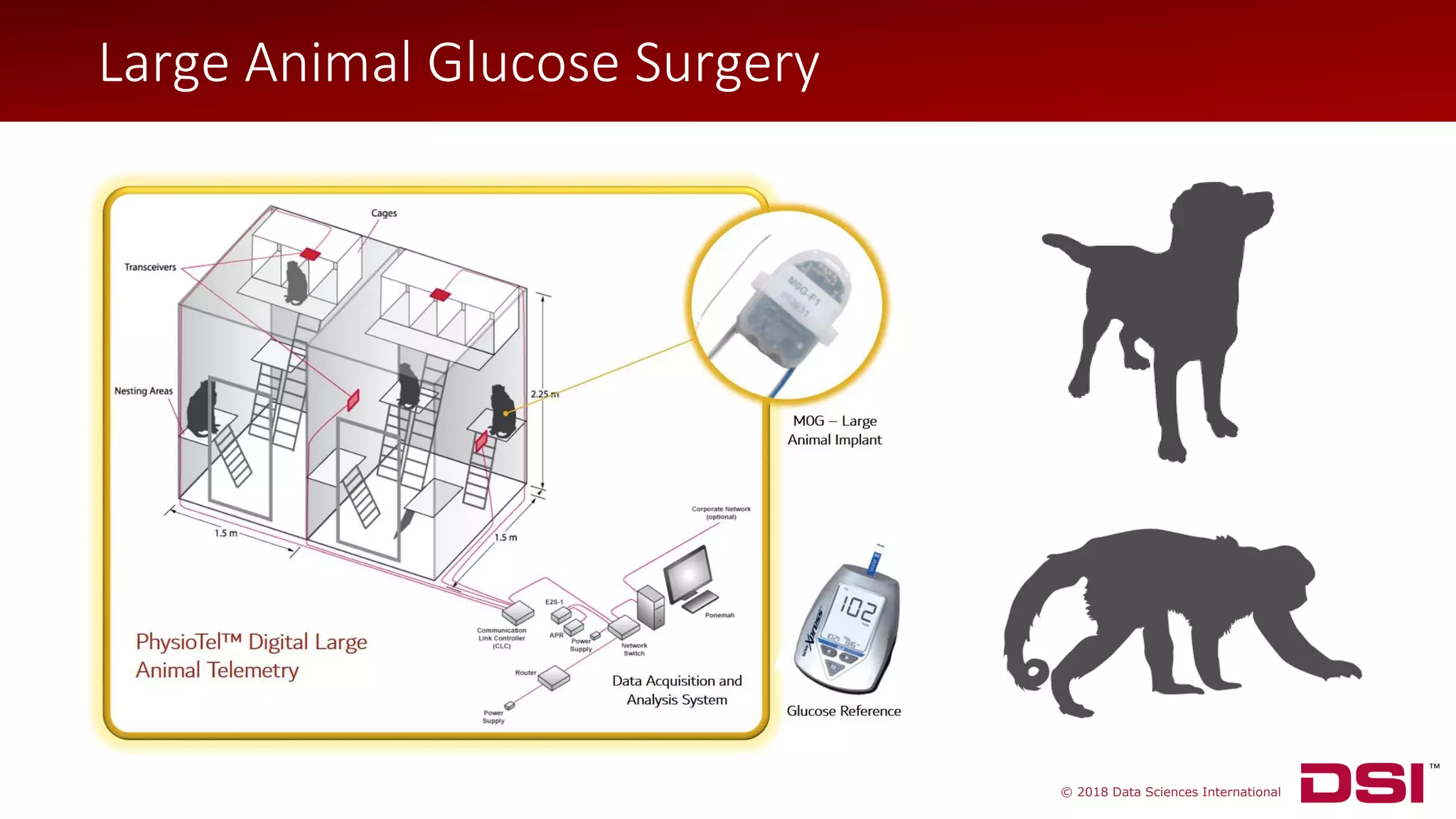
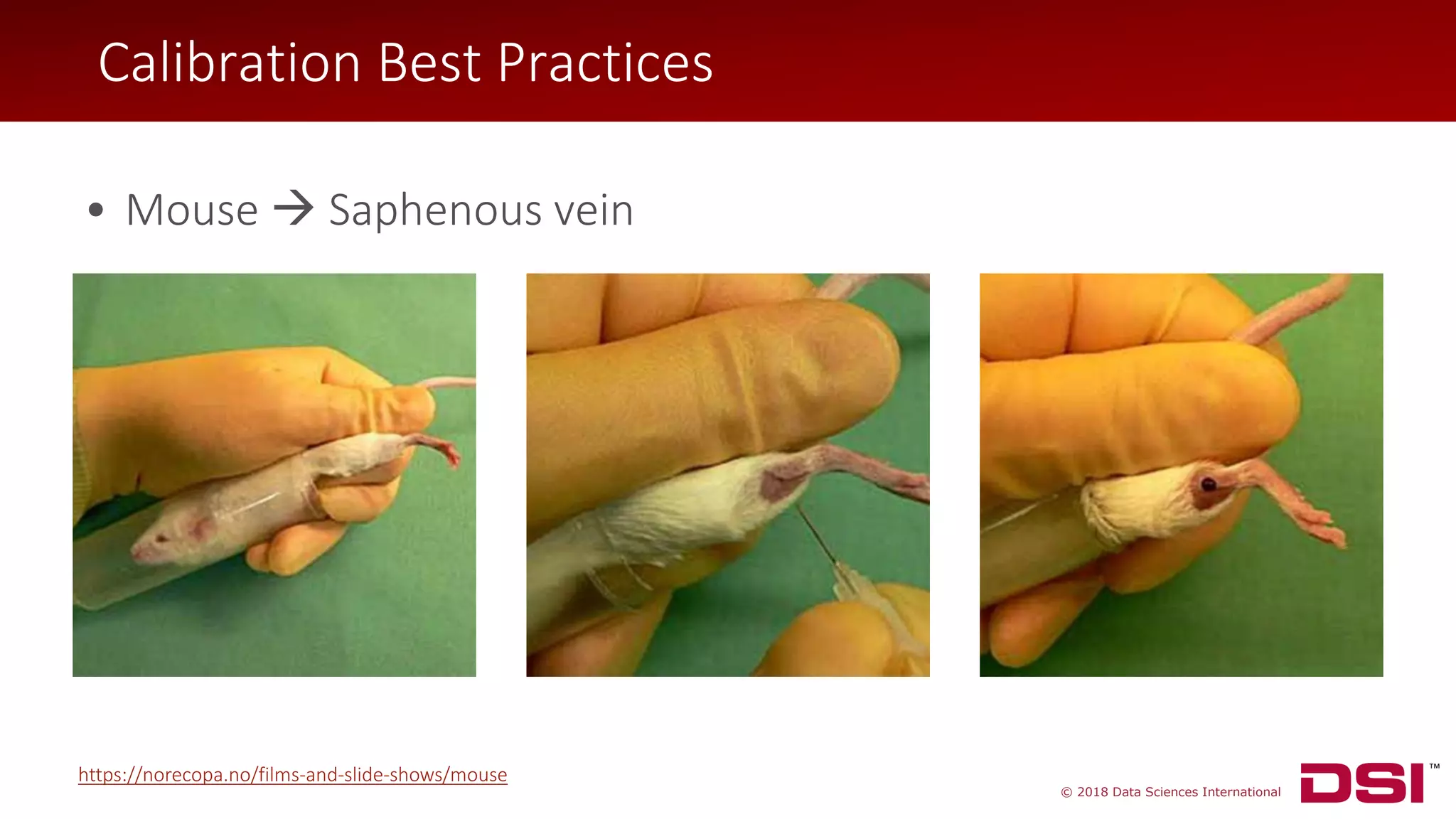
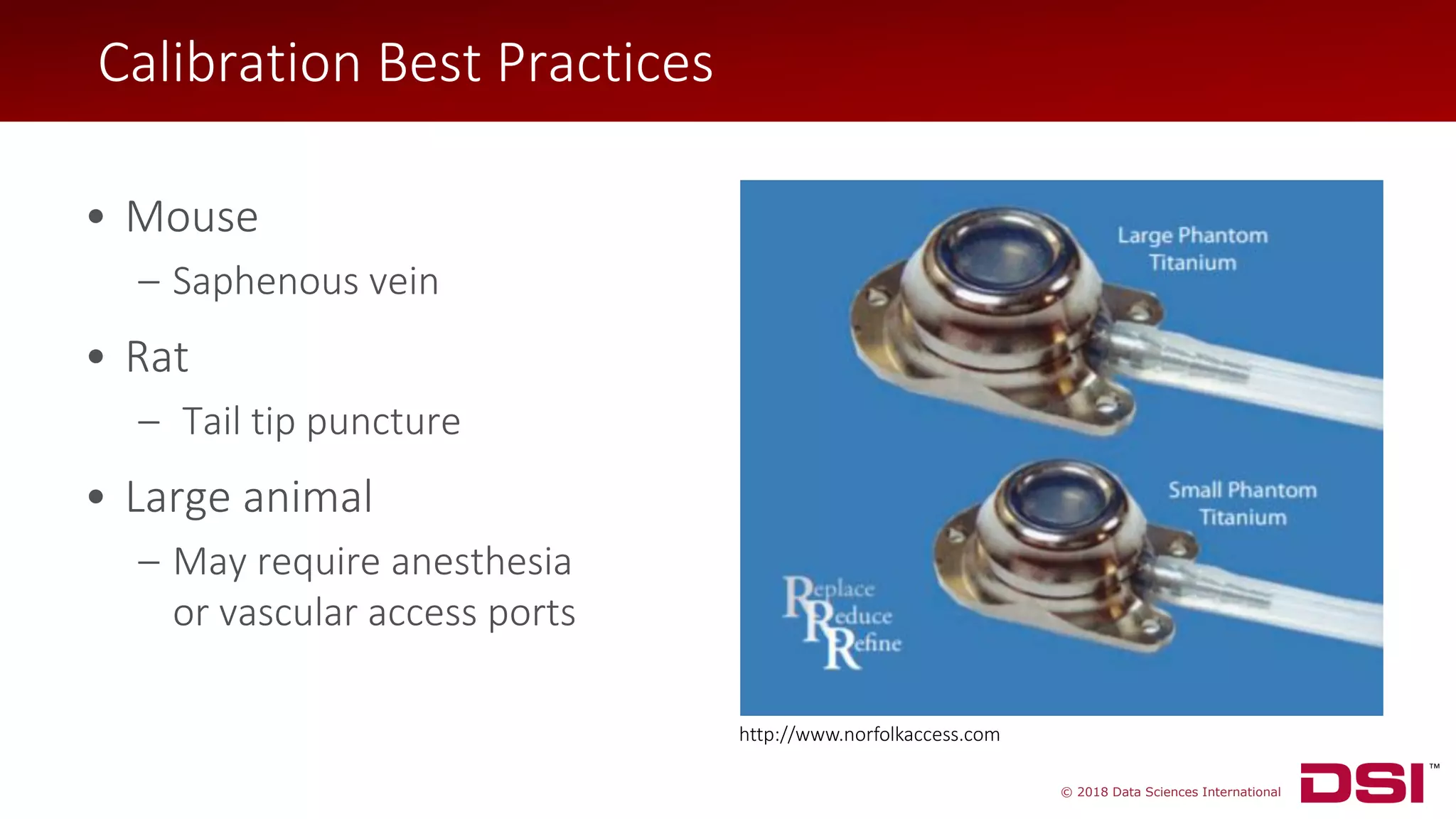
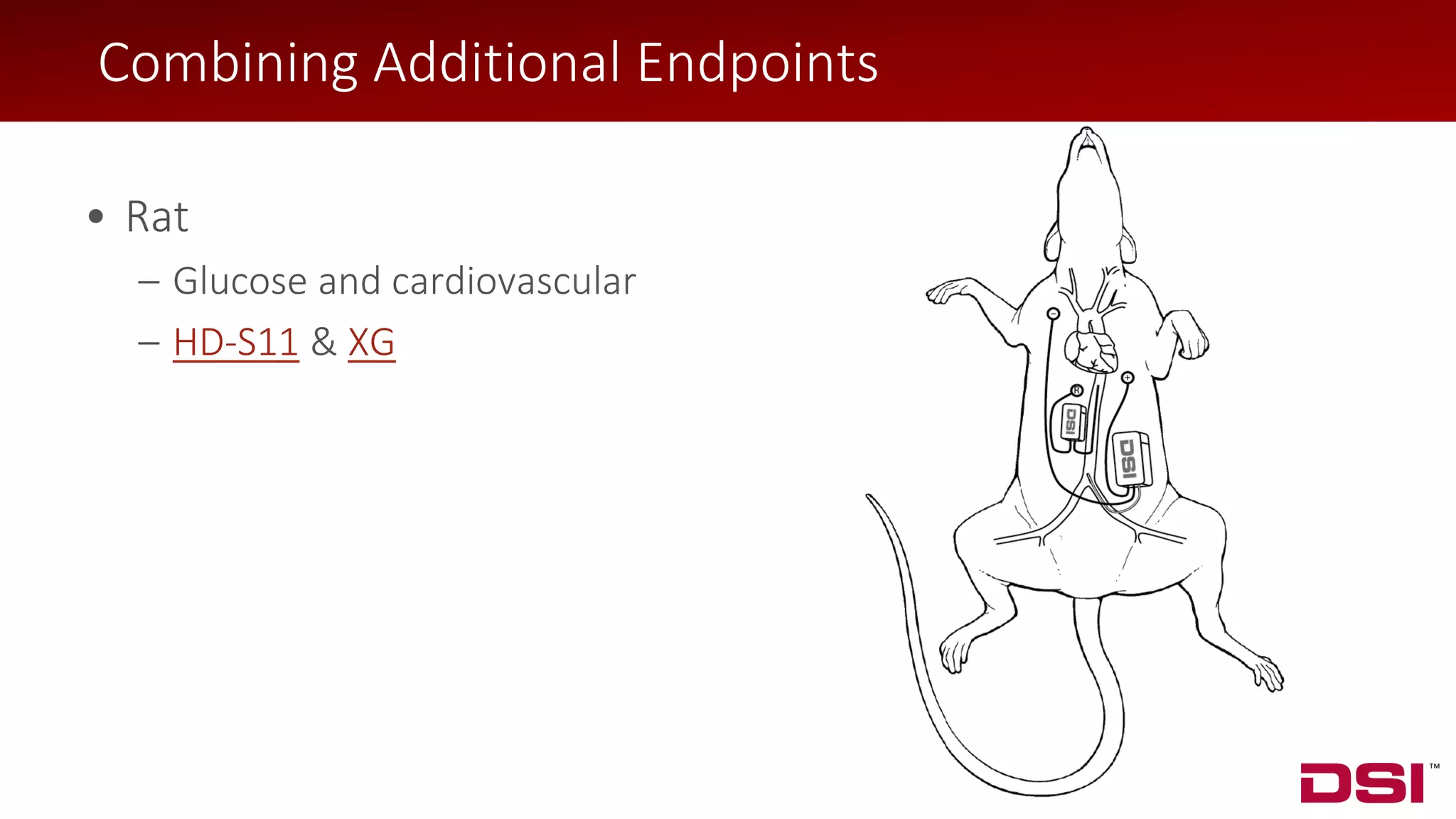
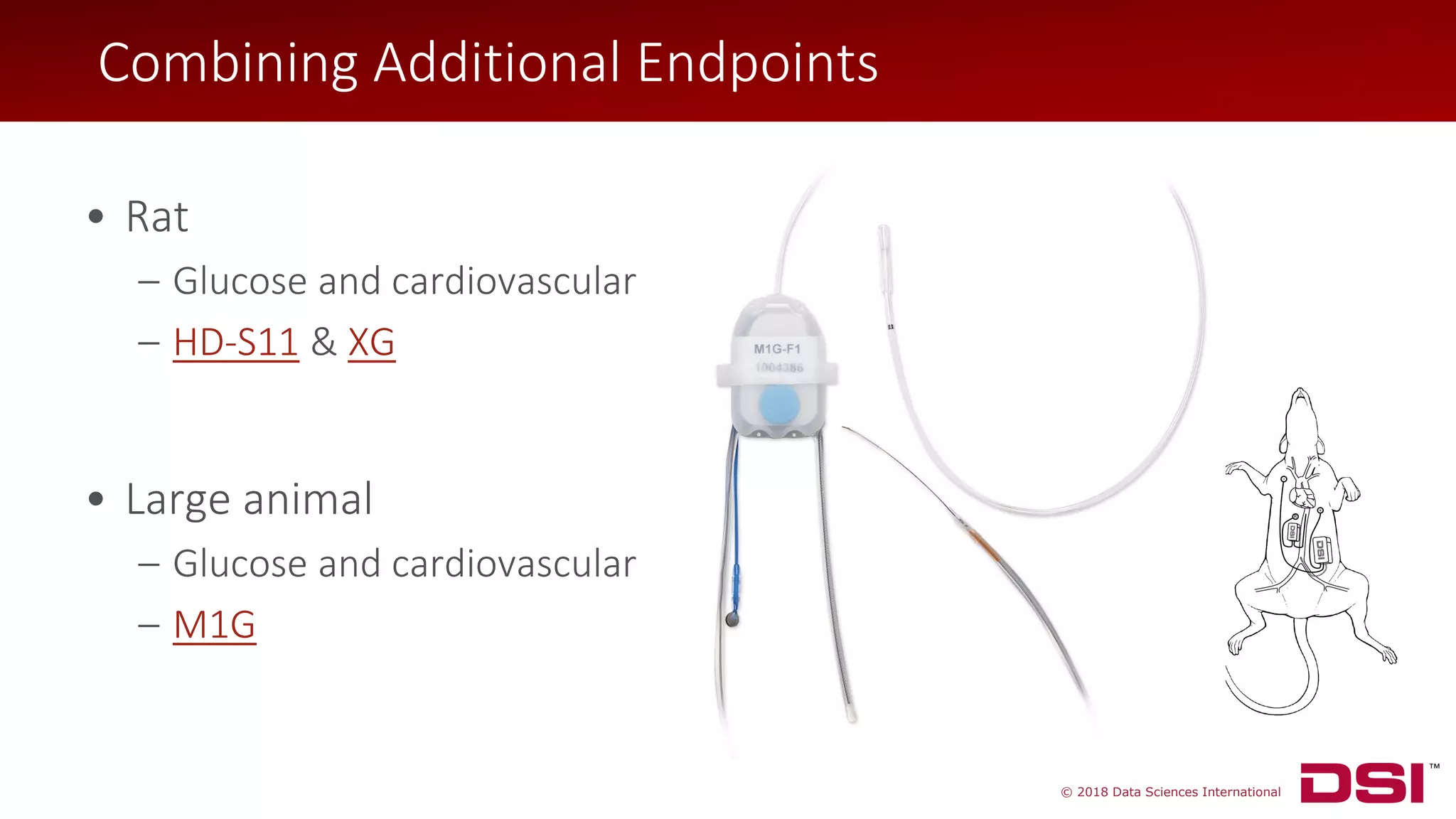
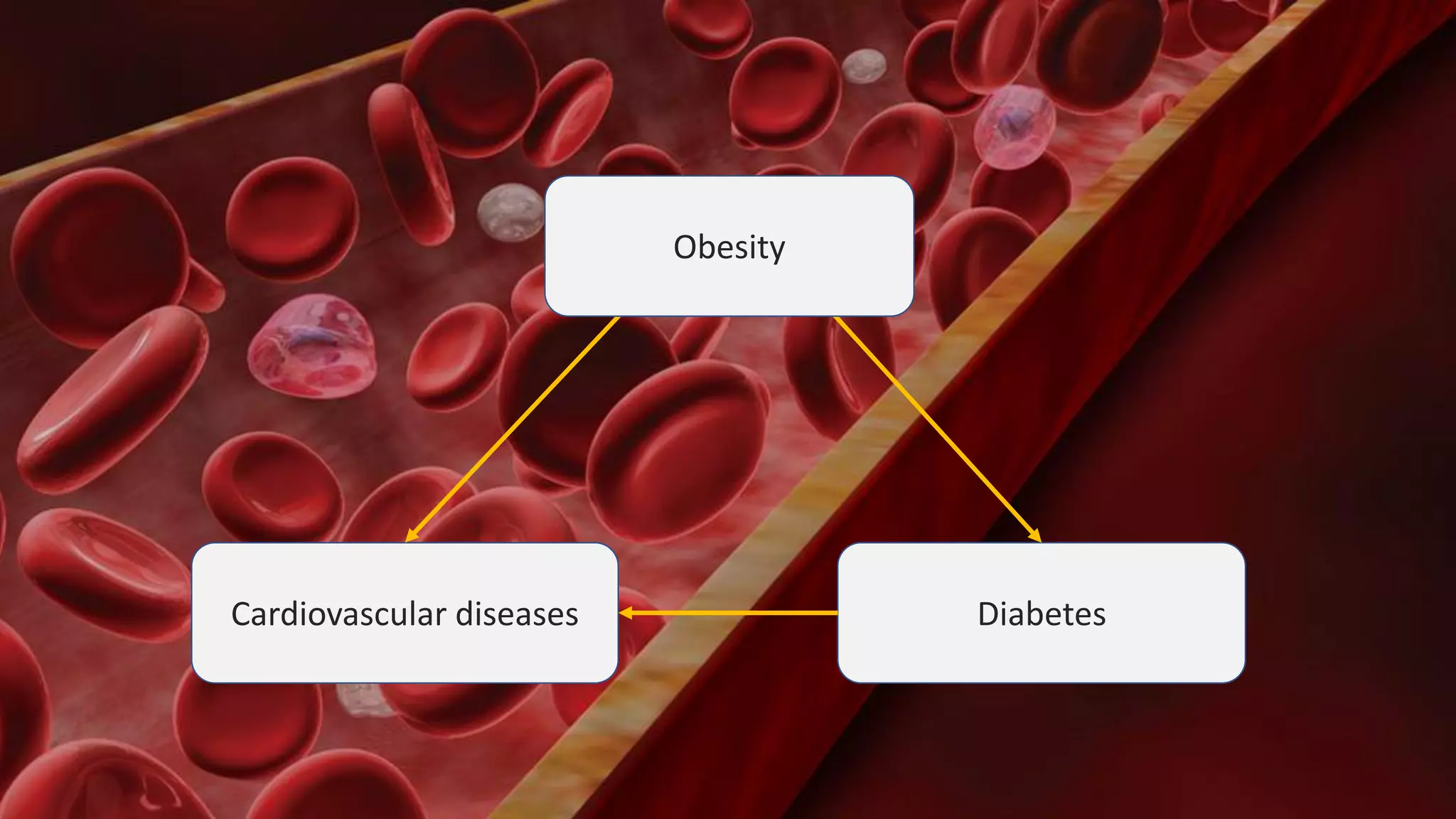
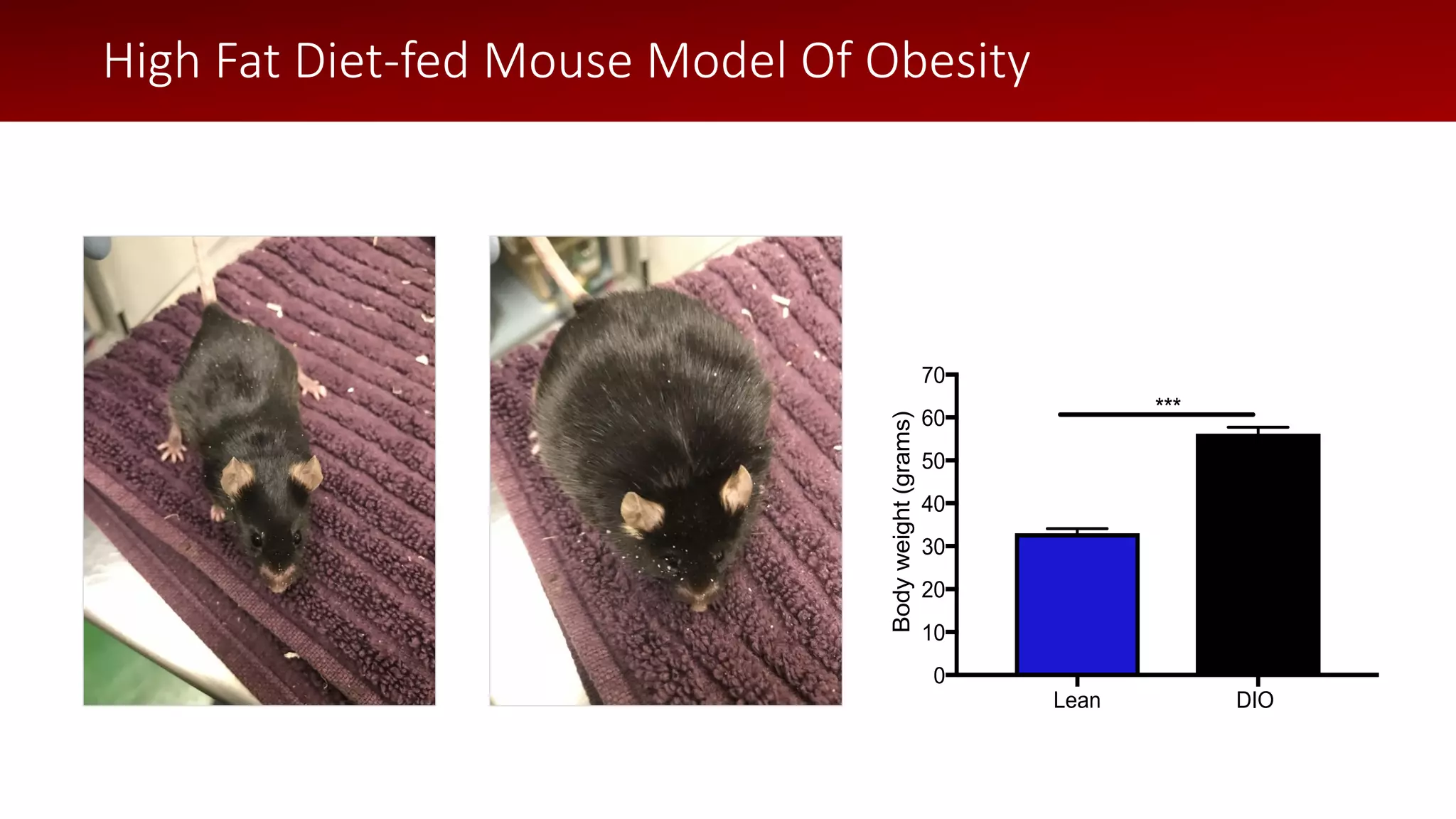
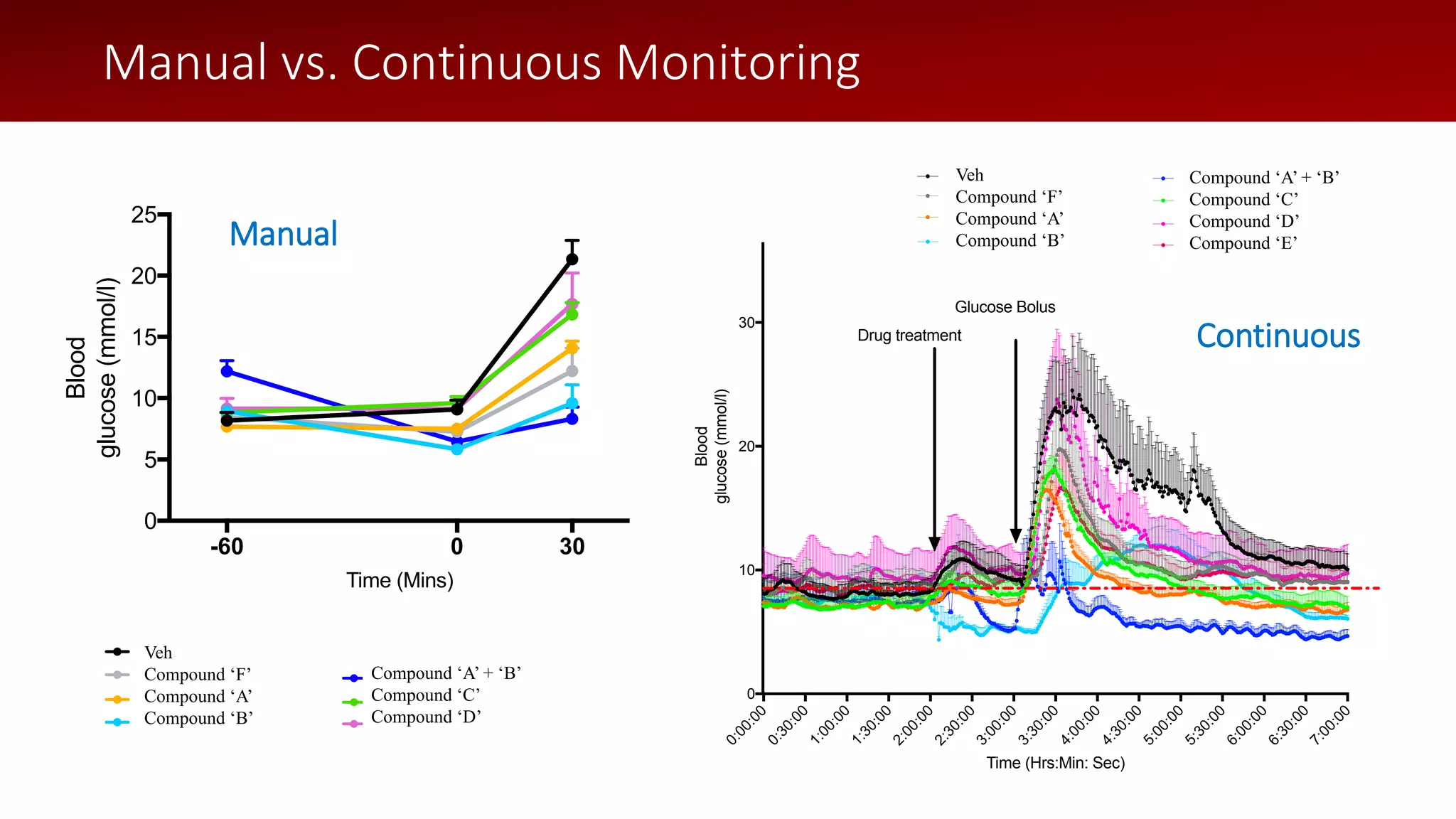
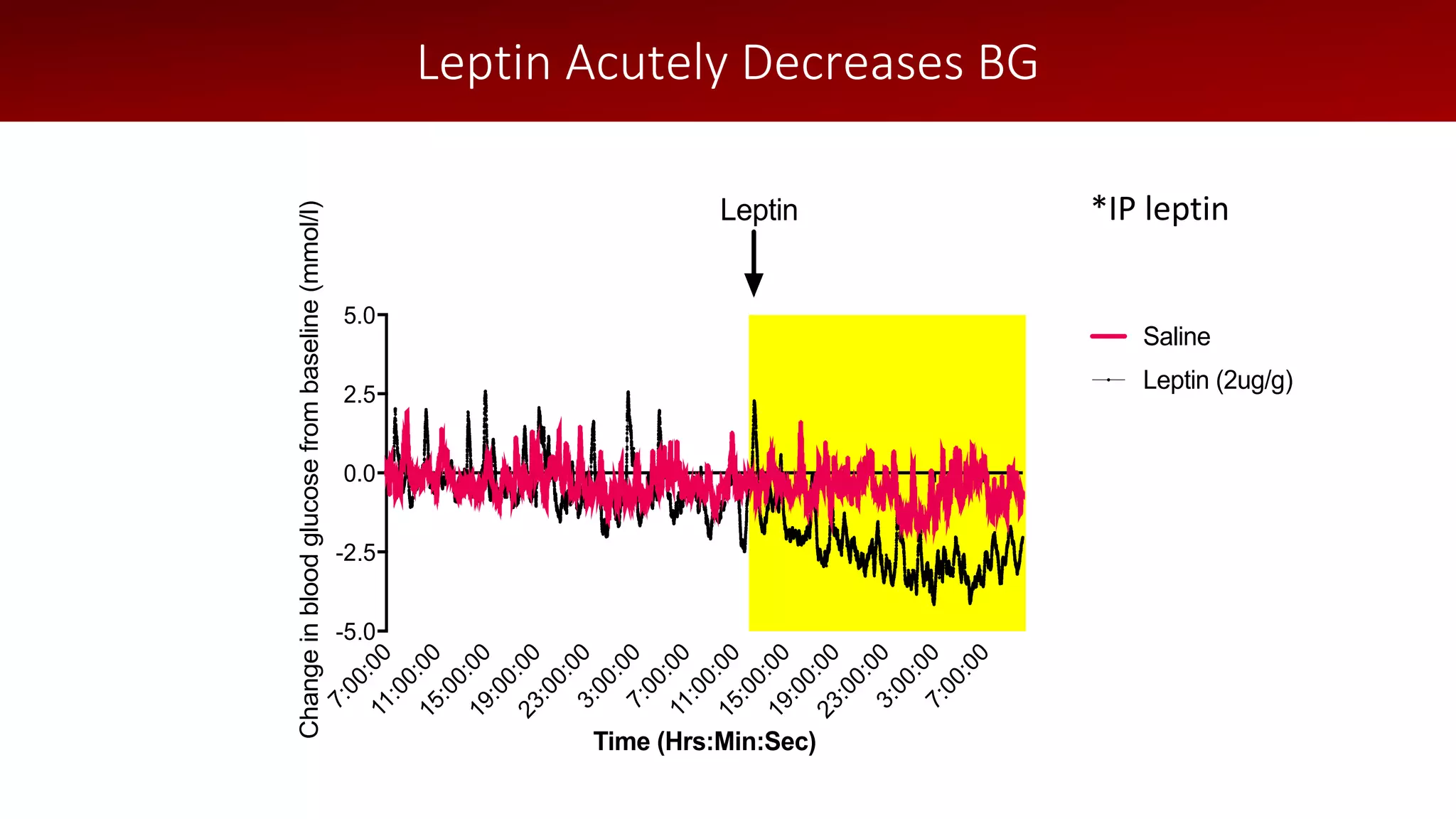
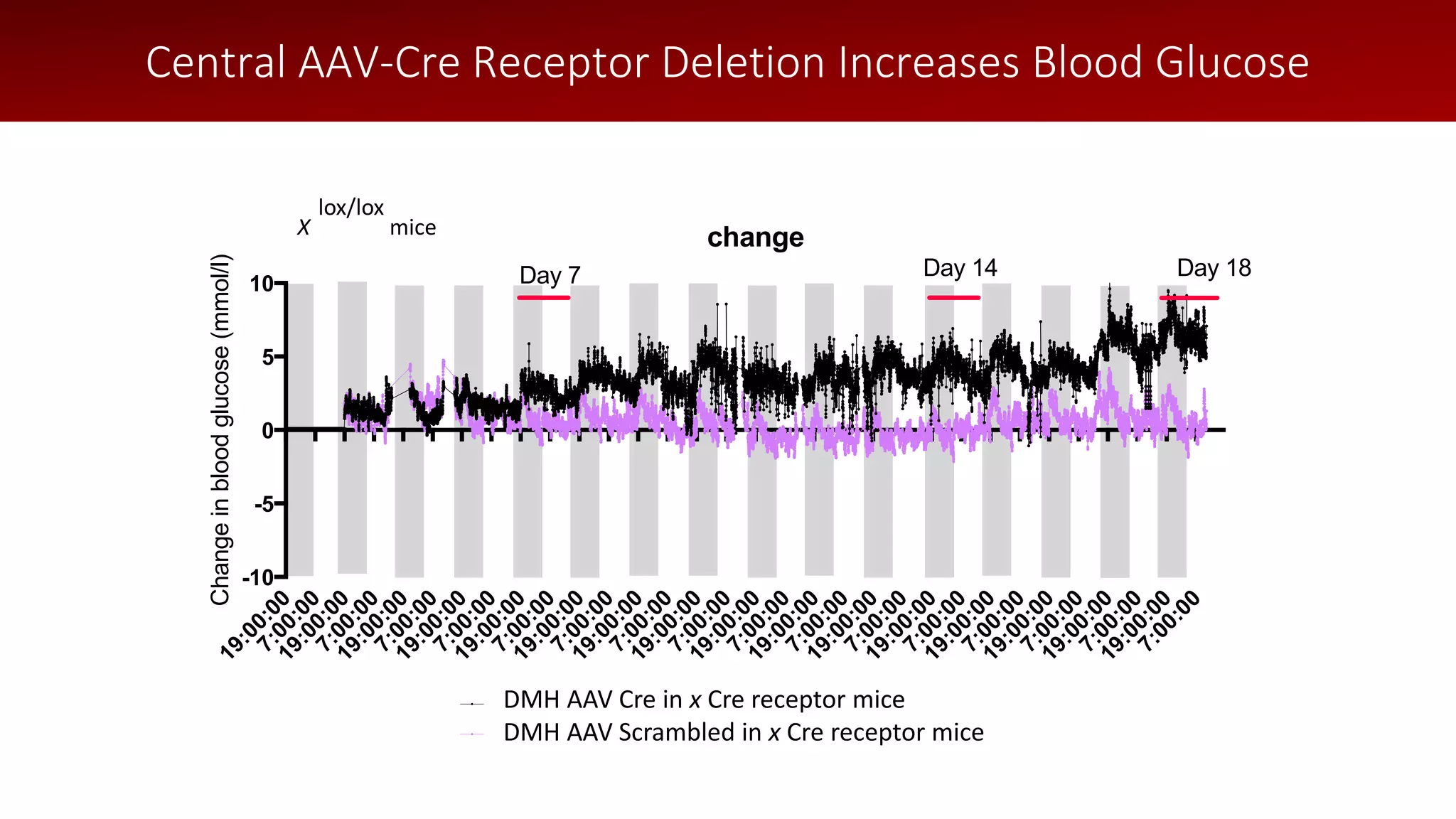
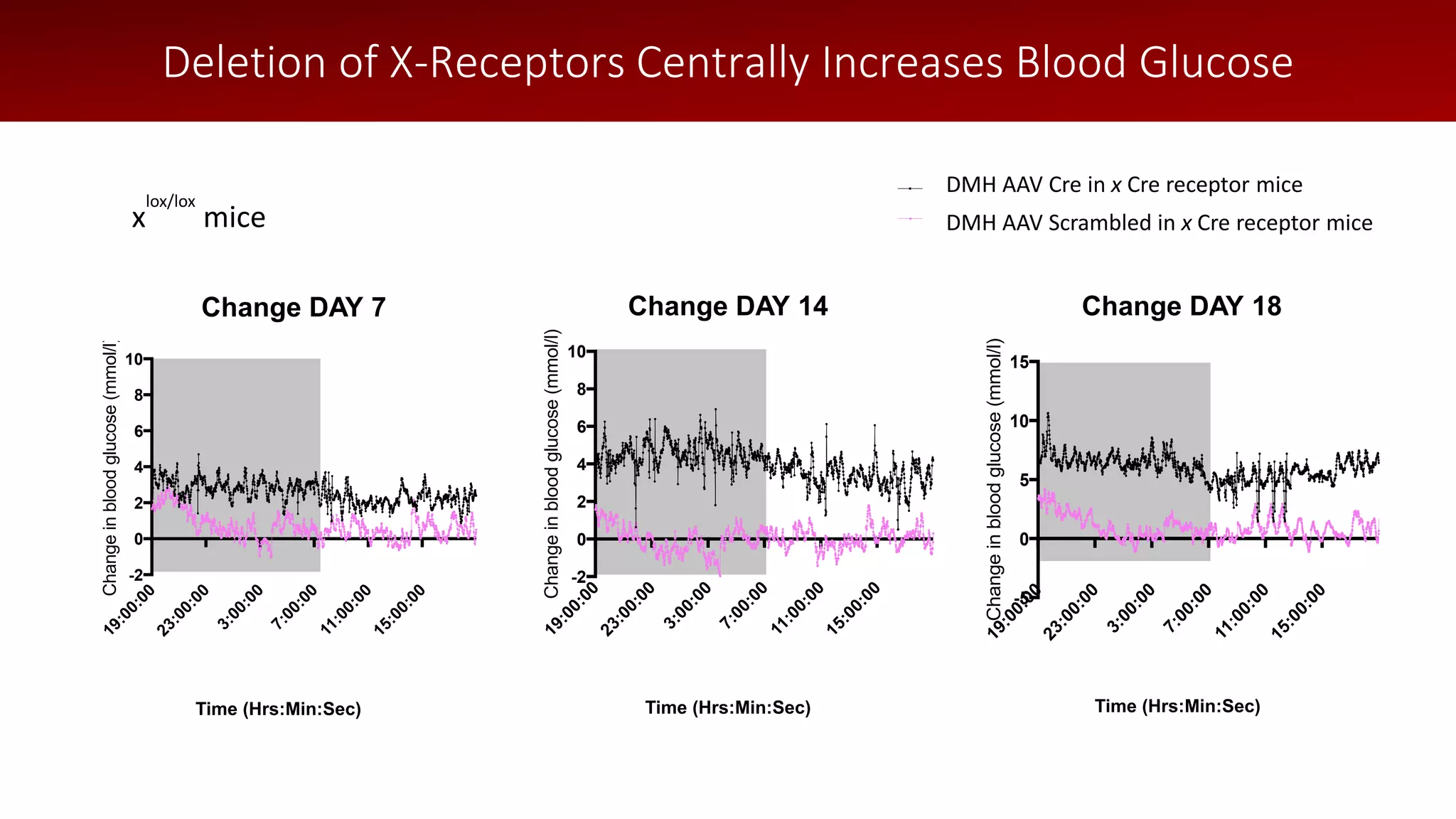
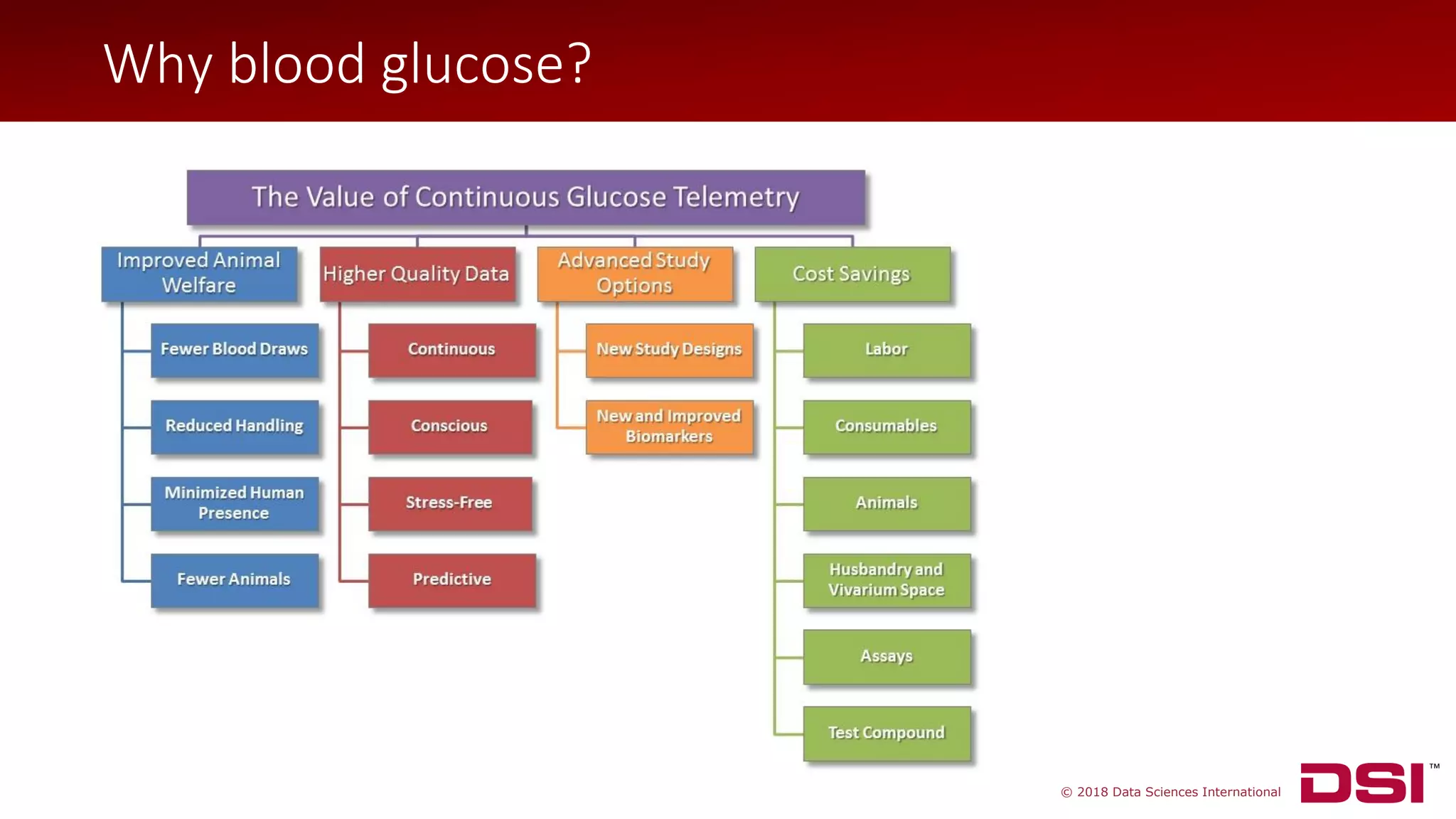
The document discusses a wireless glucose monitoring methodology utilized by researchers to revolutionize preclinical research, particularly in studying obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases. It summarizes findings from continuous glucose telemetry in animal models, including experiments on high-fat diet effects and drug therapy efficacy. The use of advanced monitoring techniques over the past nine years has significantly enhanced the understanding of metabolic responses and hormone actions in these disease processes.





![https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8603777
More than 20 years ago…
Zymogenetics Corporation is a wholly owned subsidiary of Novo
Nordisk A/S, a manufacturer of therapeutics for the treatment of
diabetes.
BBB, blood-brain barrier; CRH, corticotropin-releasing hormone;
MES, 2-[Nmorpholino]ethanesulfonic acid; NPY, neuropeptide Y;
PVN, paraventricular nucleus.
DIABETES, VOL. 45, APRIL 1996
(A) Serum glucose in ob/ob and db/db mice after 5 daily intraperitoneal
injections of 150 µg of recombinant murine leptin or saline
genotype: ob/ob db/db
treatment:
Specificity of Leptin Action on
Elevated Blood Glucose Levels and
Hypothalamic Neuropeptide Y Gene
Expression in ob/ob Mice
Michael W. Schwartz, Denis G. Baskin, Thomas R. Bukowski,
Joseph L. Kuijper, Donald Foster, Gerry Lasser, Donna E.
Prunkard, Daniel Porte, Jr., Stephen C. Woods, Randy J. Seeley,
and David S. Weigle](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dsiglucose-2018masterslidesharefinal-180712135928/75/From-Mouse-to-Monkey-Revolutionizing-Research-via-Preclinical-Continuous-Glucose-Telemetry-15-2048.jpg)






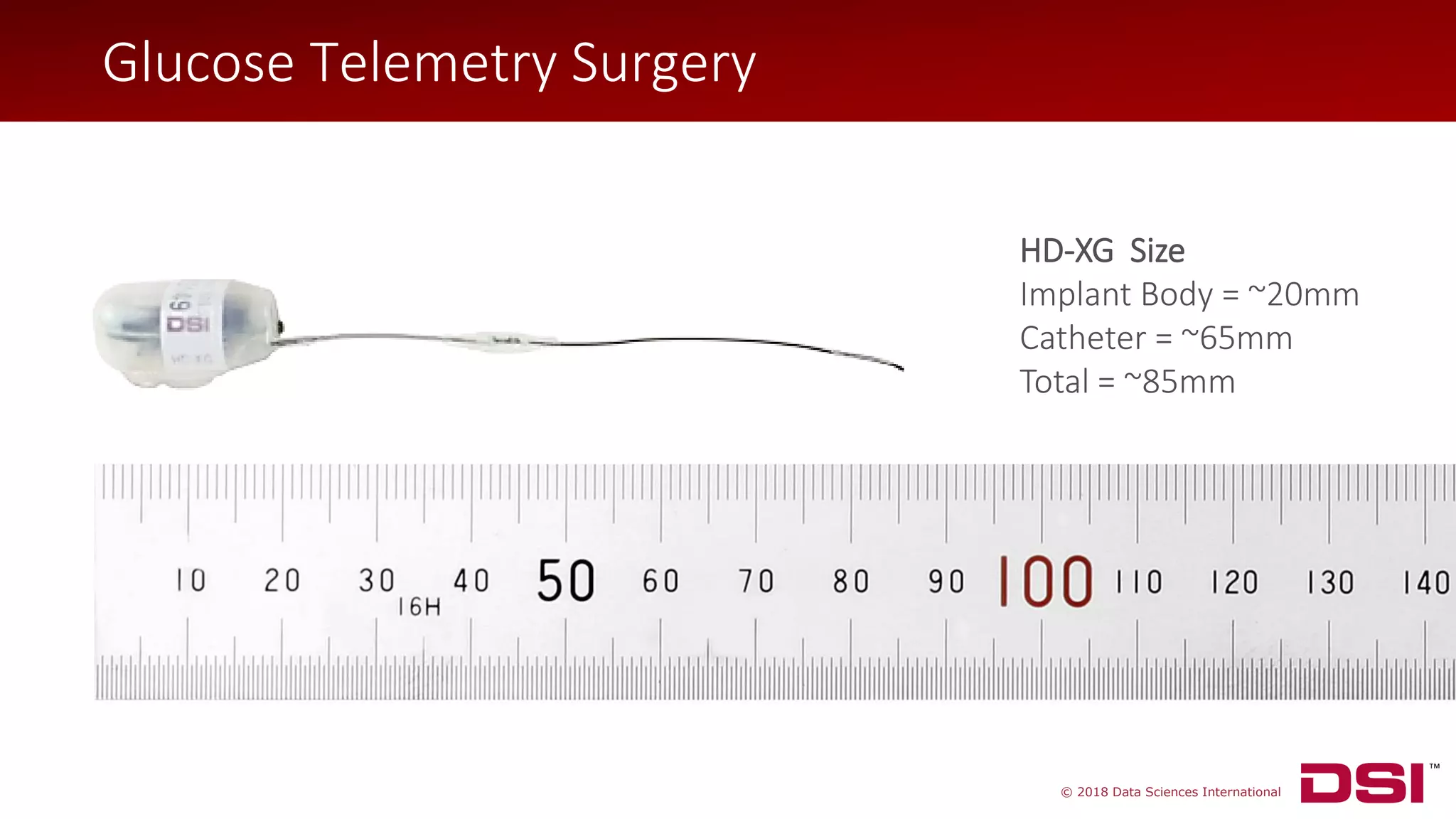
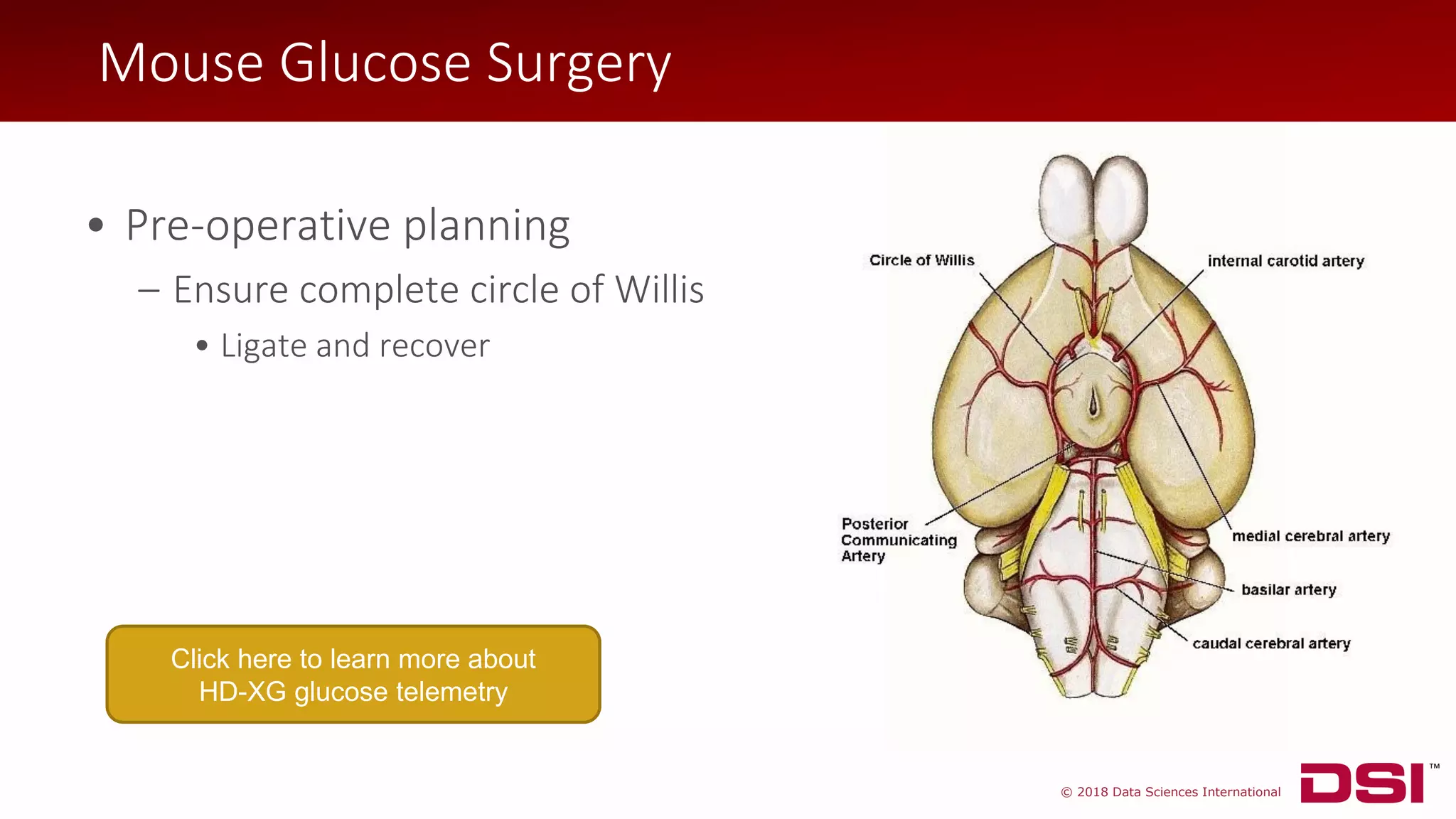
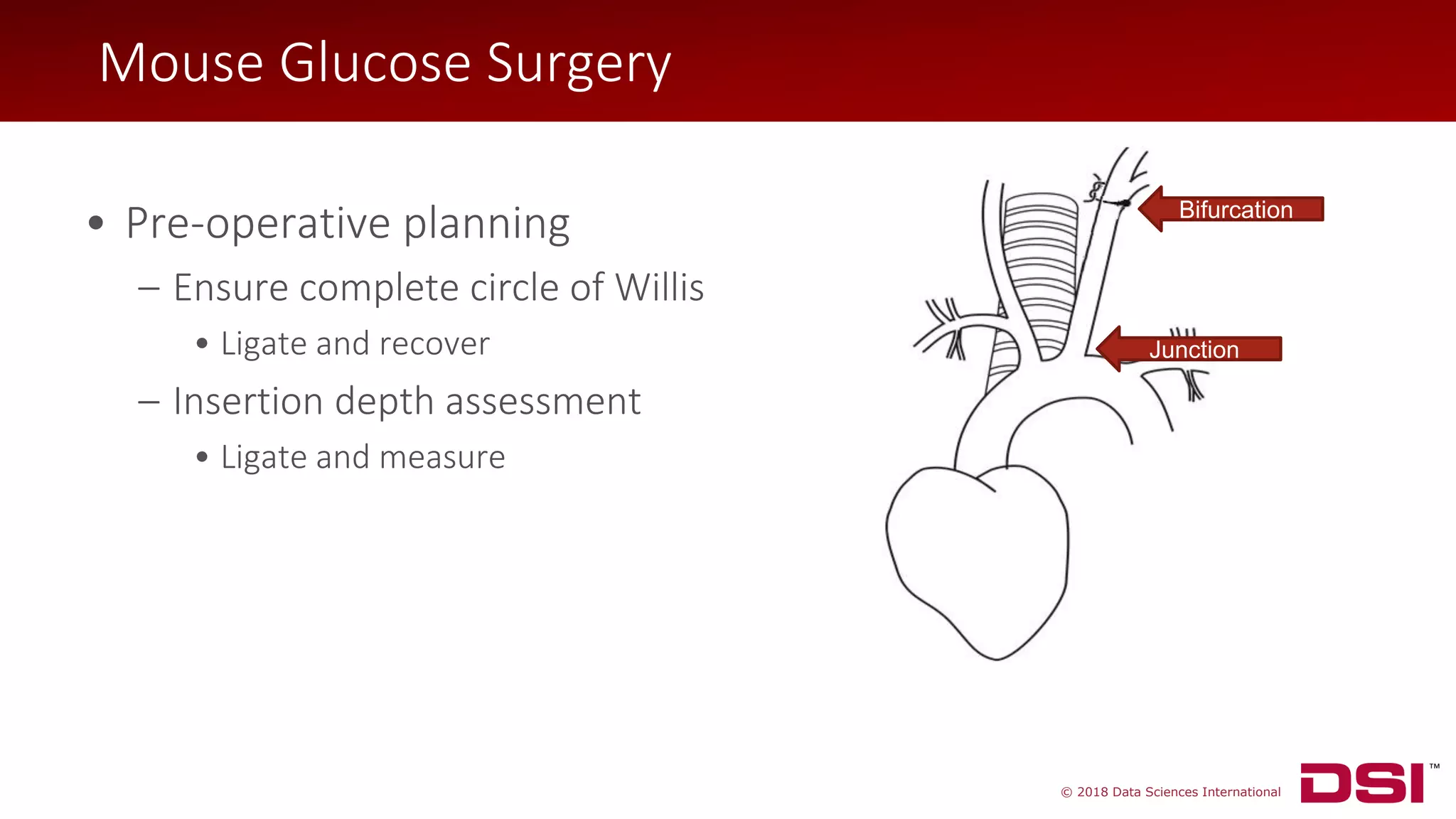

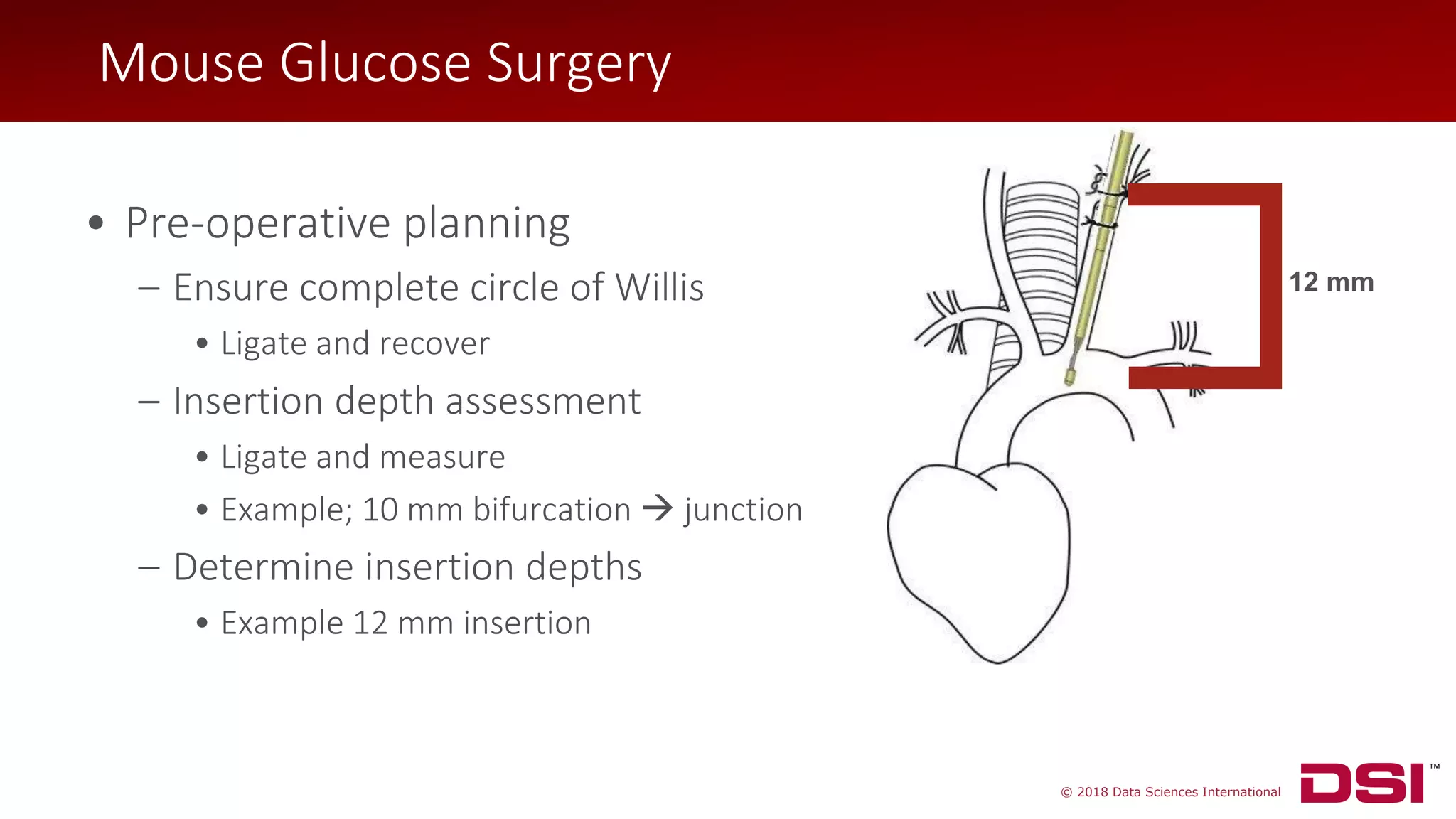
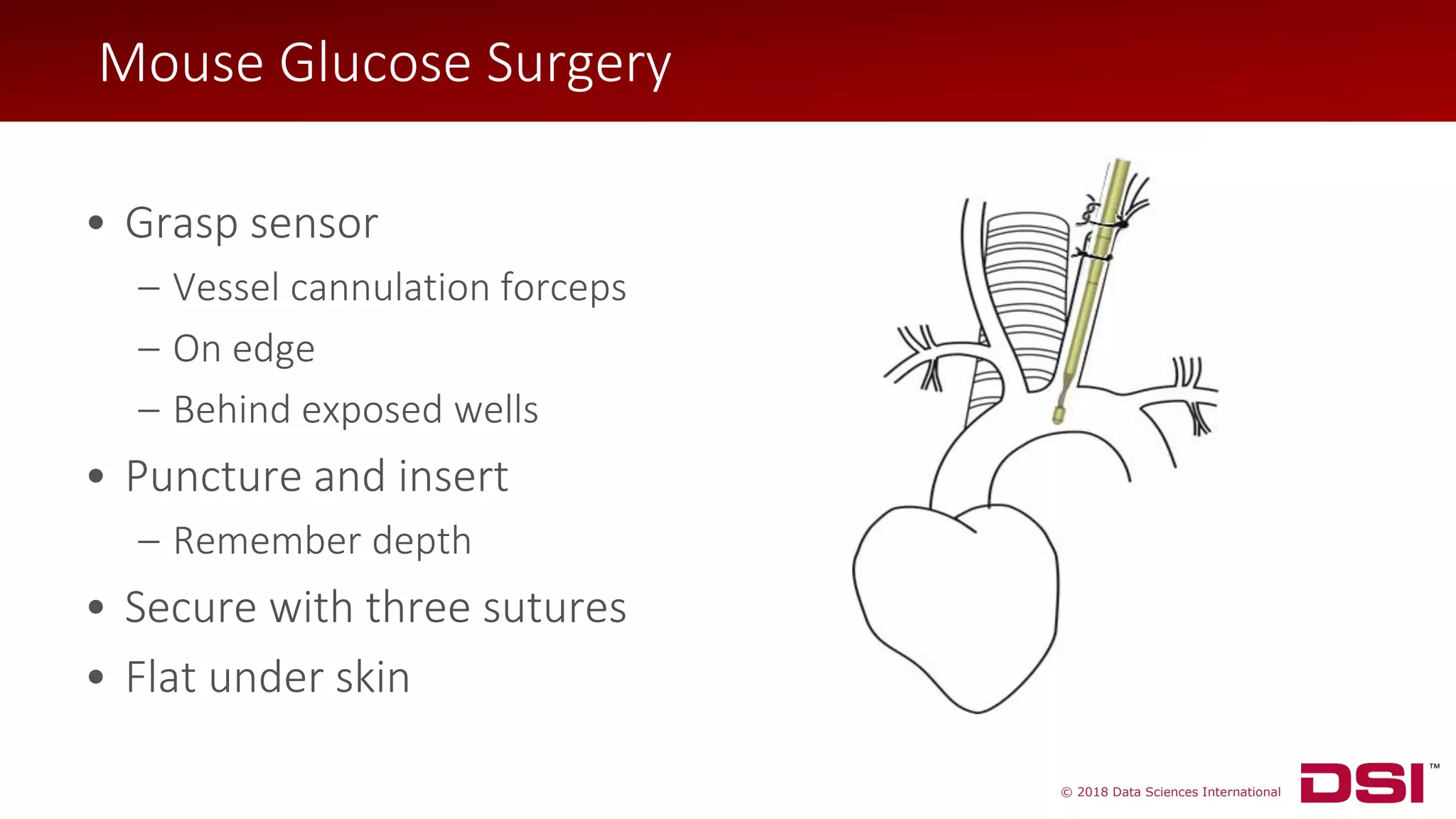
![© 2018 Data Sciences International
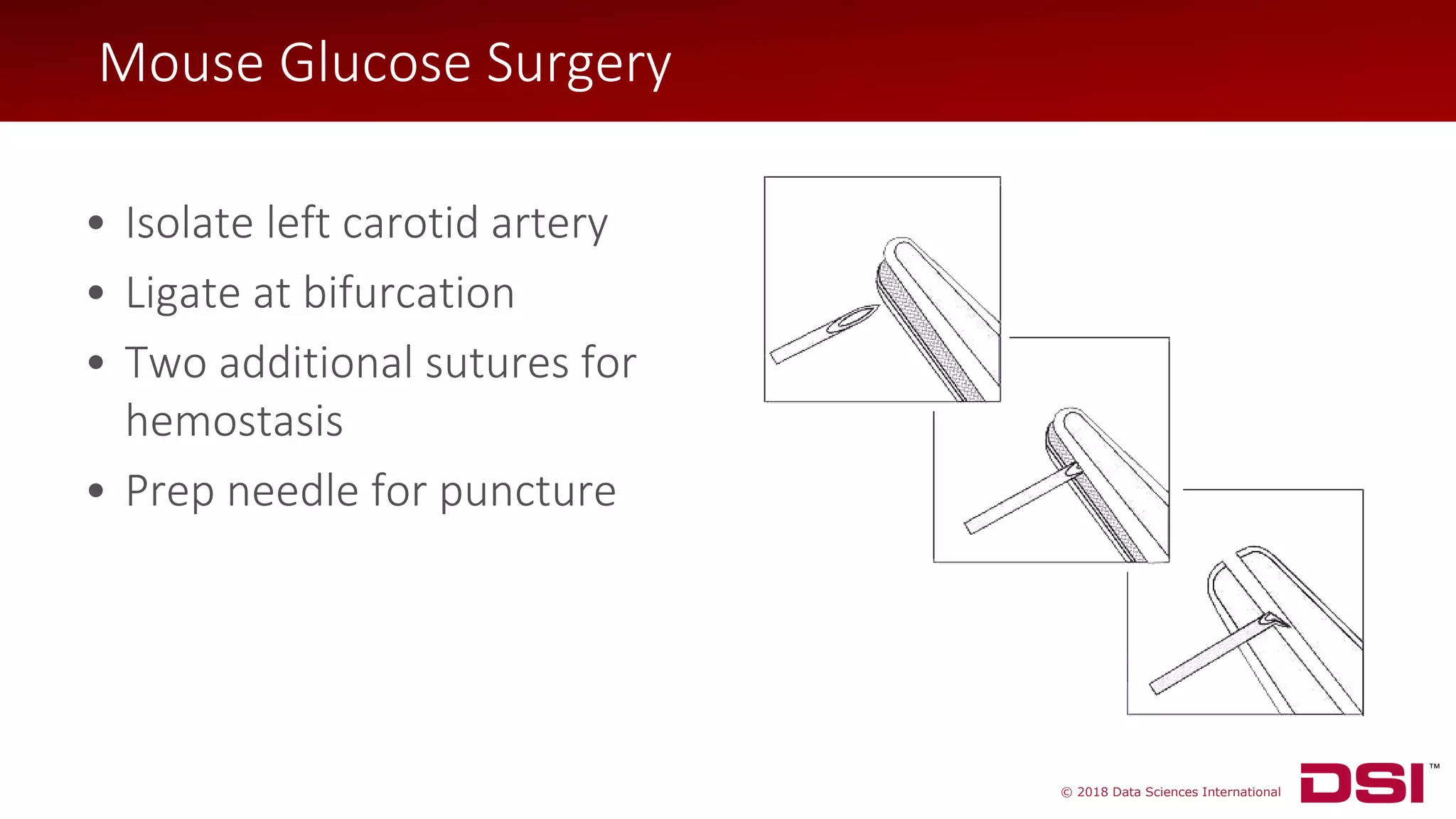
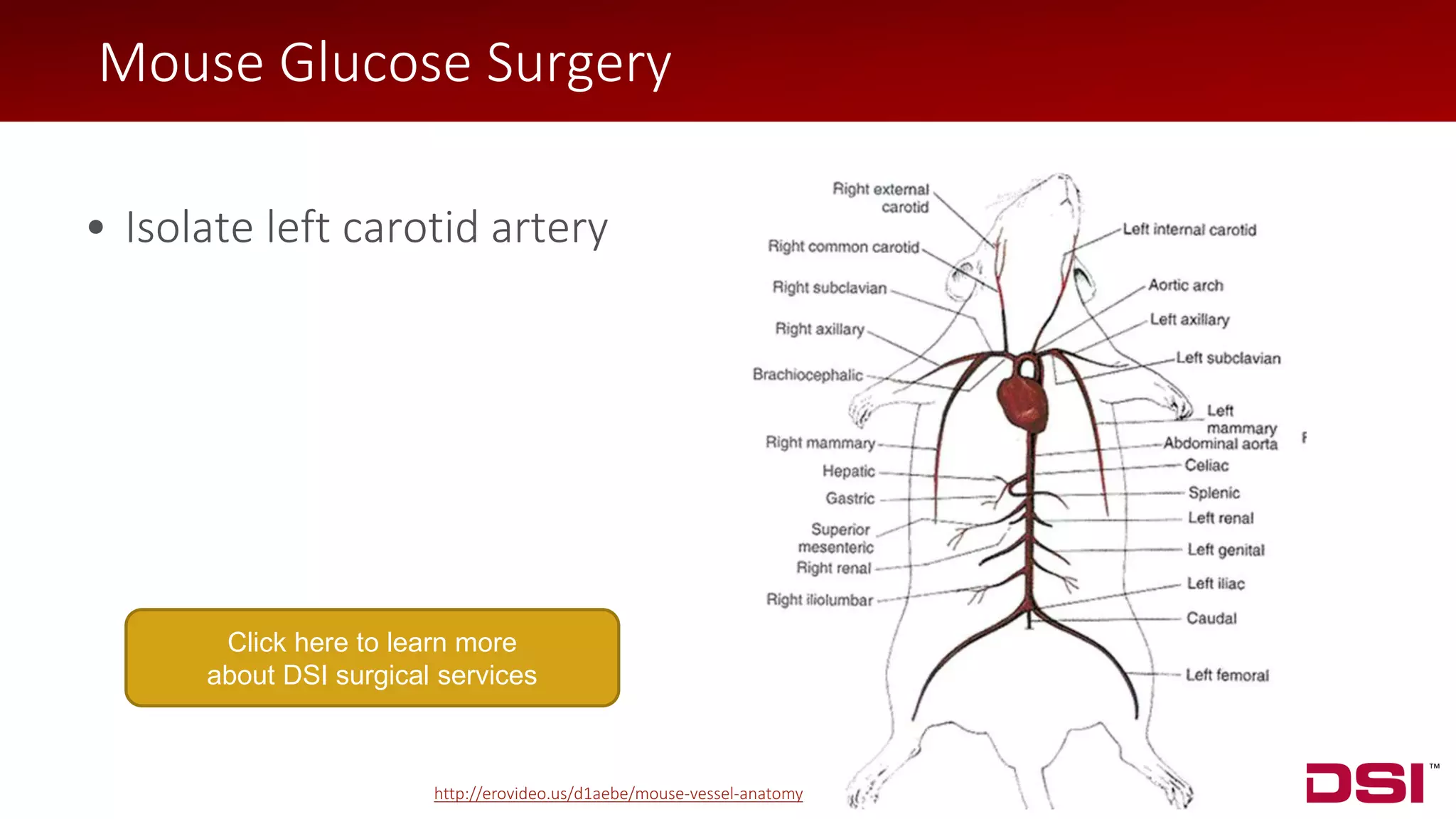
• Isolate left carotid artery
• Ligate at bifurcation
• Two additional sutures for
hemostasis
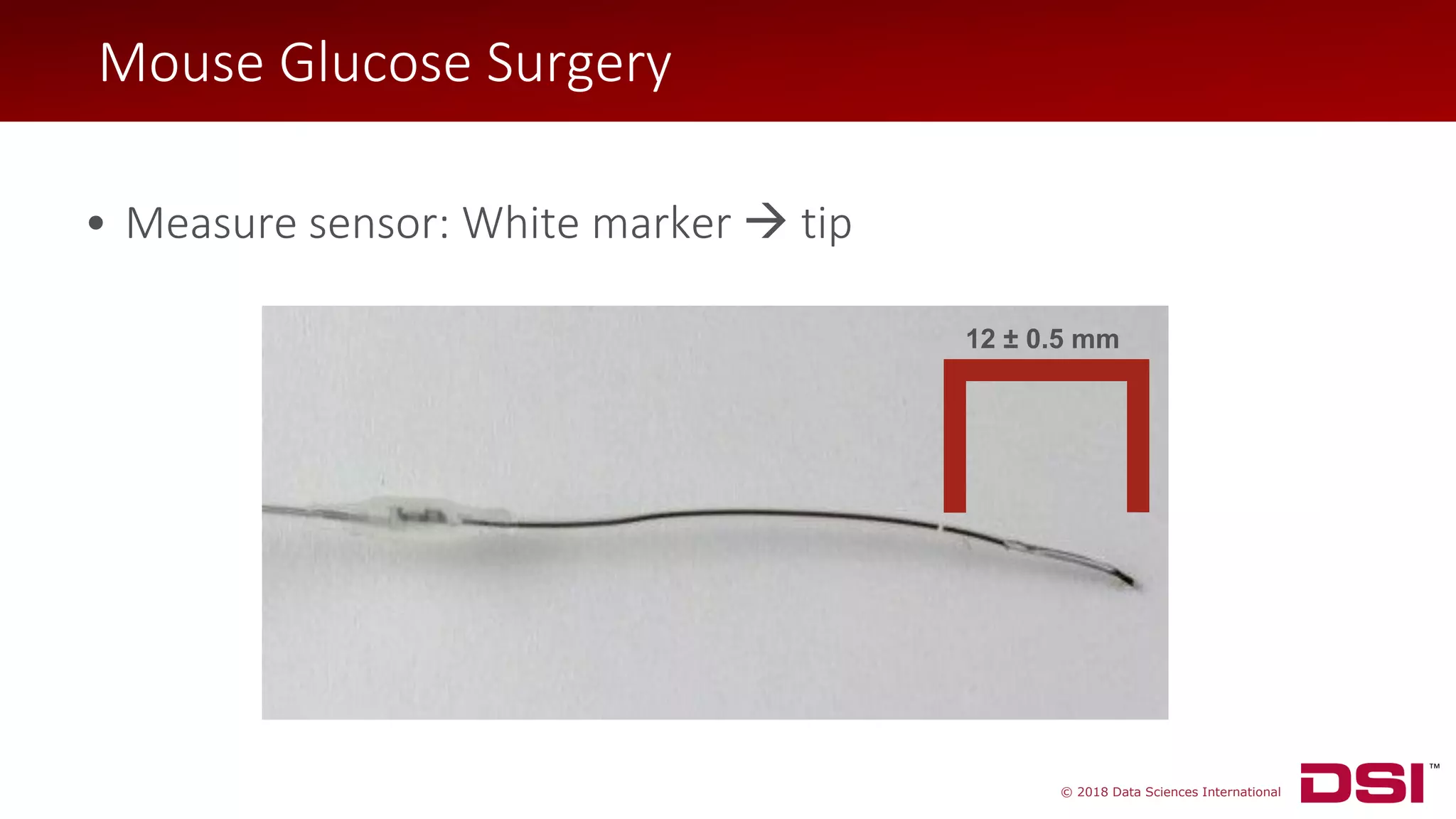
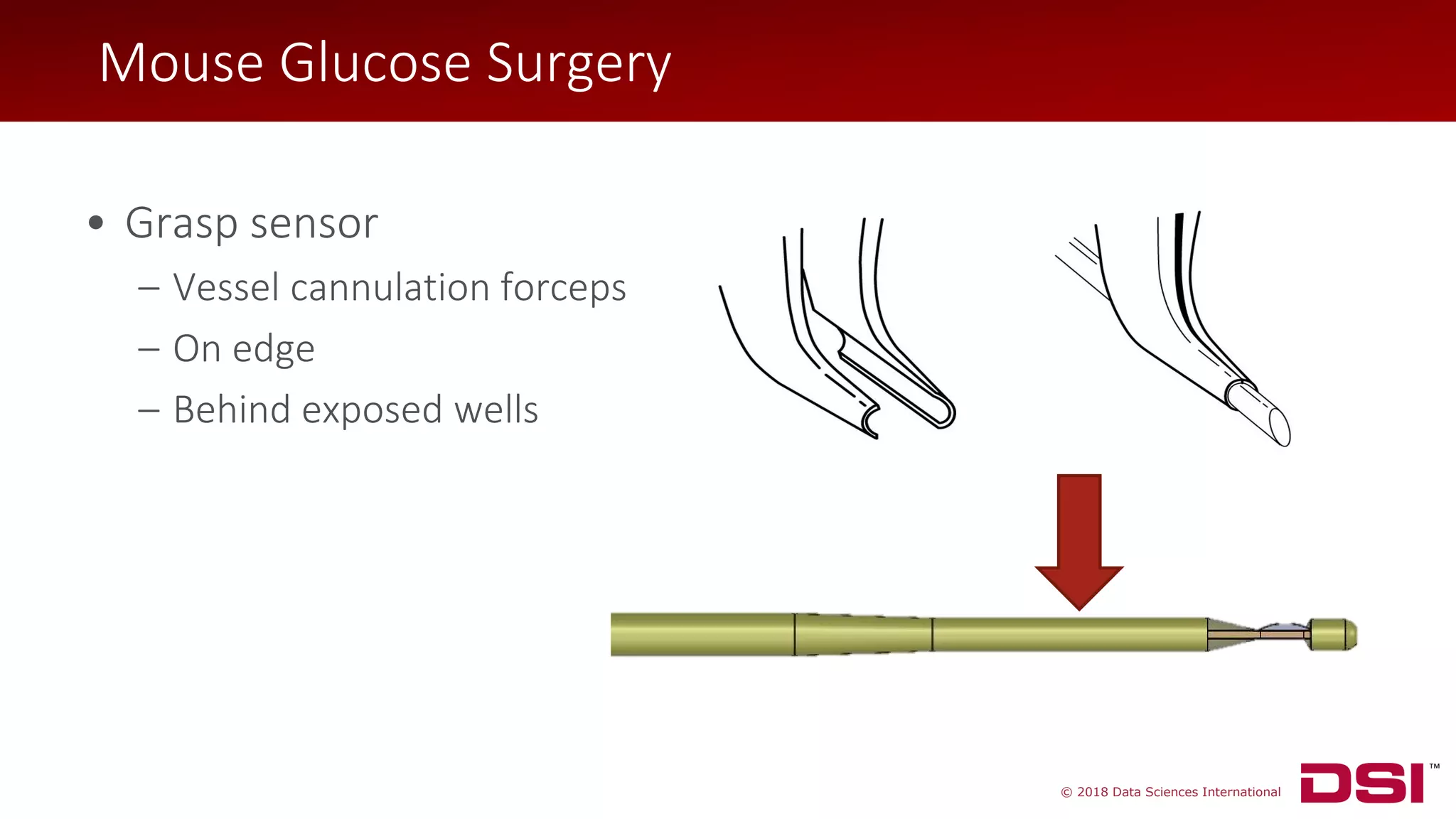
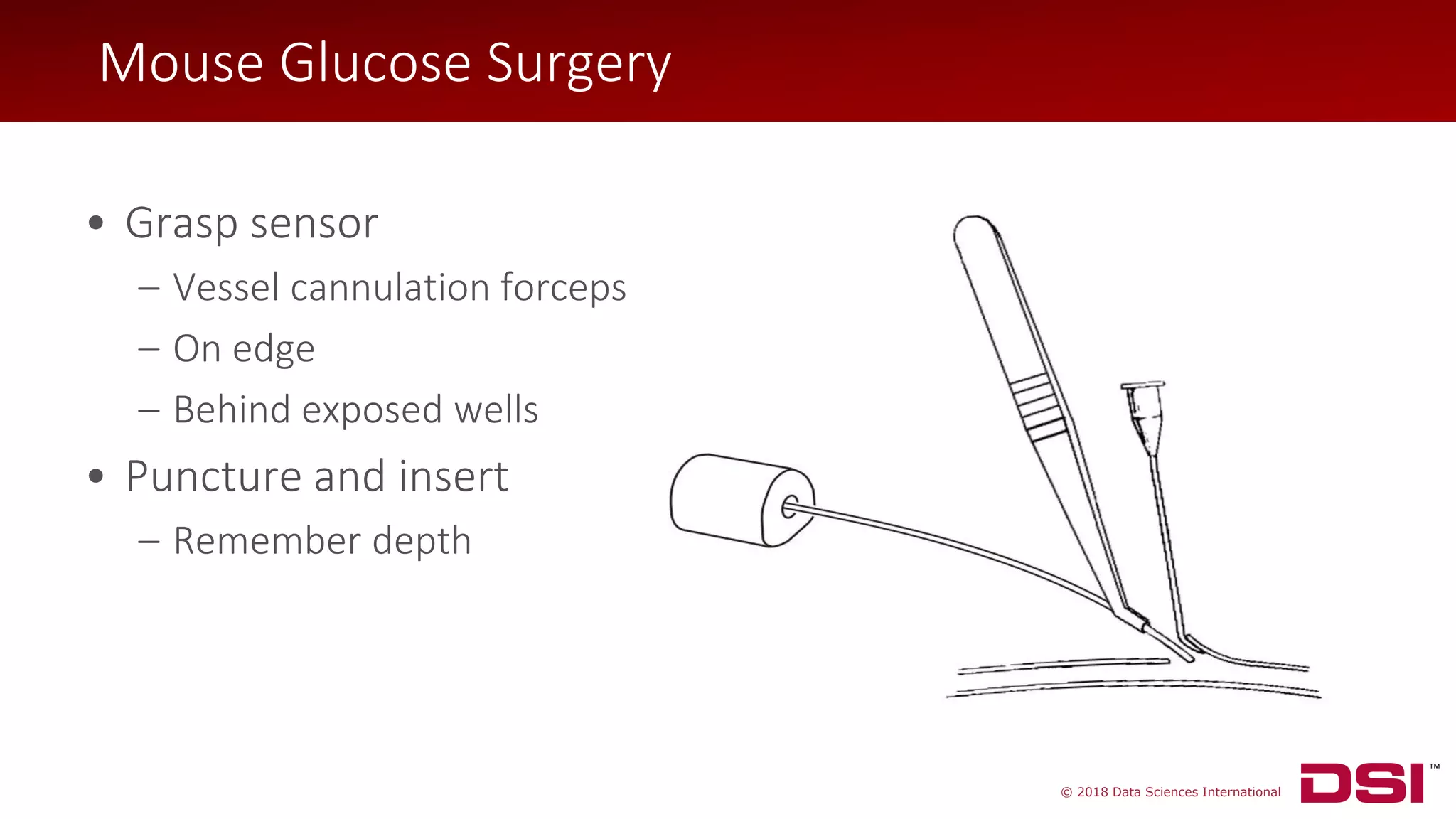
Mouse Glucose Surgery
[superior - cranial]
[inferior - caudal]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dsiglucose-2018masterslidesharefinal-180712135928/75/From-Mouse-to-Monkey-Revolutionizing-Research-via-Preclinical-Continuous-Glucose-Telemetry-40-2048.jpg)