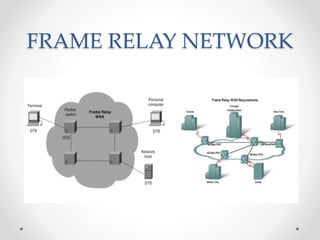
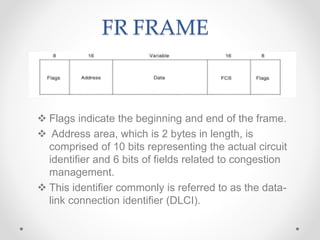
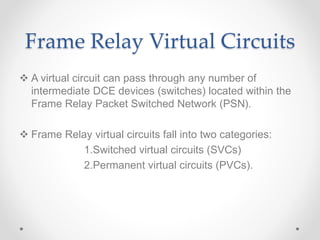
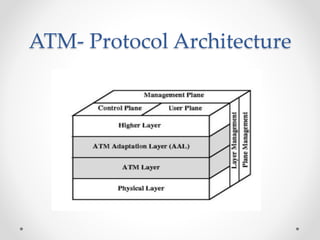
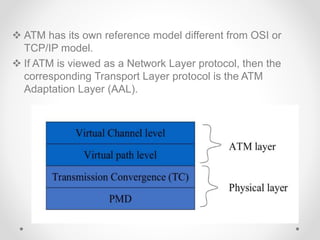
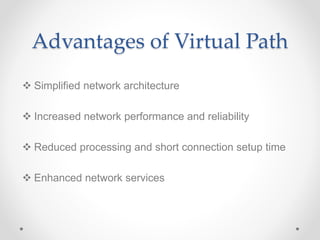
Frame relay is a high-performance WAN protocol that operates at the physical and data link layers of the OSI model, designed for connection-oriented communication across integrated services digital networks. It utilizes virtual circuits for data transmission, which can either be switched or permanent, allowing for flexible and efficient connection management. Additionally, ATM technology supports various data rates and includes a unique protocol architecture consisting of user, control, and management planes, aimed at improving network performance and reliability.