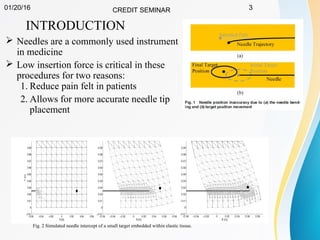
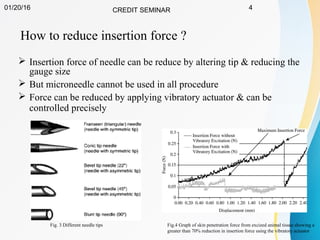
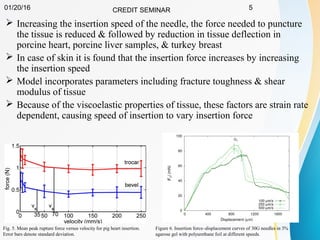
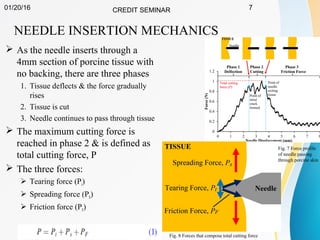
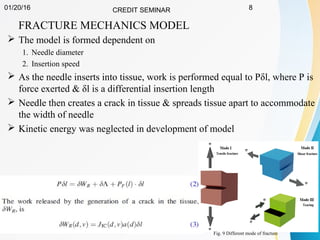
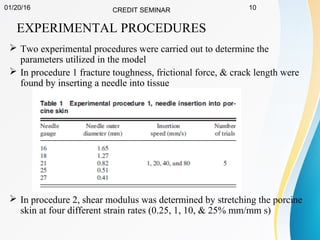
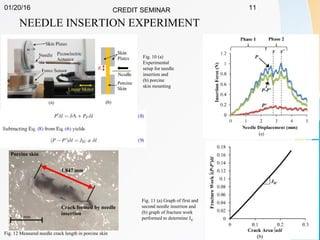
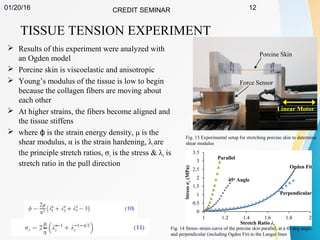
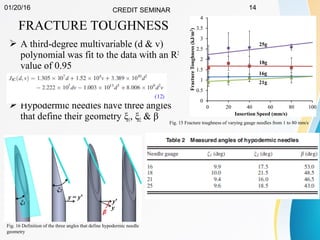
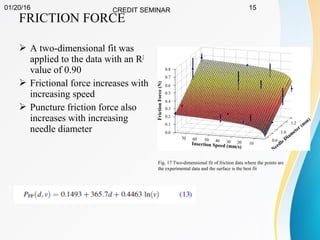
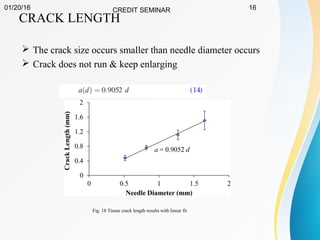
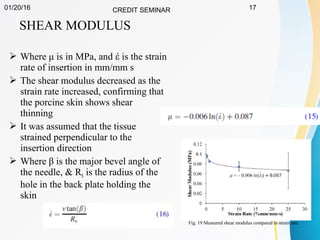
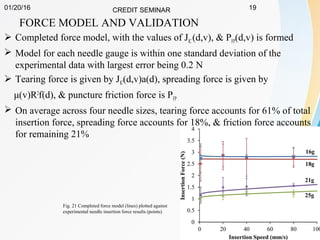
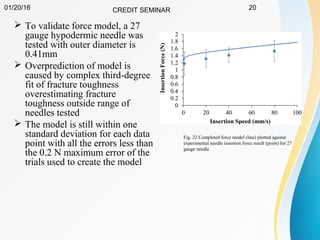
This document summarizes a study on developing a fracture mechanics model to predict the insertion force of needles cutting through tissue. Experimental tests were conducted to determine the fracture toughness, shear modulus, frictional force, and crack length for different size needles inserted at various speeds into porcine skin. A force model was developed incorporating these parameters and validated against experimental force measurements, with errors less than 0.2 N. The model accurately predicts insertion forces and shows that 61% of the force comes from creating a crack in the tissue, while 21% is from friction and 18% from spreading the tissue. Increasing insertion speed was found to not reduce force for porcine skin.