This document provides an overview of student development theory, including its history and key frameworks. It discusses four main theories: psychosocial, cognitive-structural, typology, and person-environment. As examples, it outlines Chickering's seven vectors of identity development, Perry's stages of intellectual development, Myers-Briggs typology indicators, and Astin's theory of student involvement. The presentation aims to give a brief definition and background of student development theory.






![References
Astin, A. W. (1999). Student Involvement: A Developmental
Theory for Higher Education. Retrieved from
https://www.middlesex.mass.edu/ace/downloads/astininv.pdf
Duboc, J. (2012). Brain and gears. [Digital Image].
Retrieved from
https://www.flickr.com/photos/duboc/7896404652/ through
Creative Commons
Karpilo, L. N. (n.d. ). Working with College Students:
Applying Student Development Theories to Practice.
Retrieved from
http://www.uaa.alaska.edu/studentaffairs/upload/Student-
Development-Theory-final-version.pdf
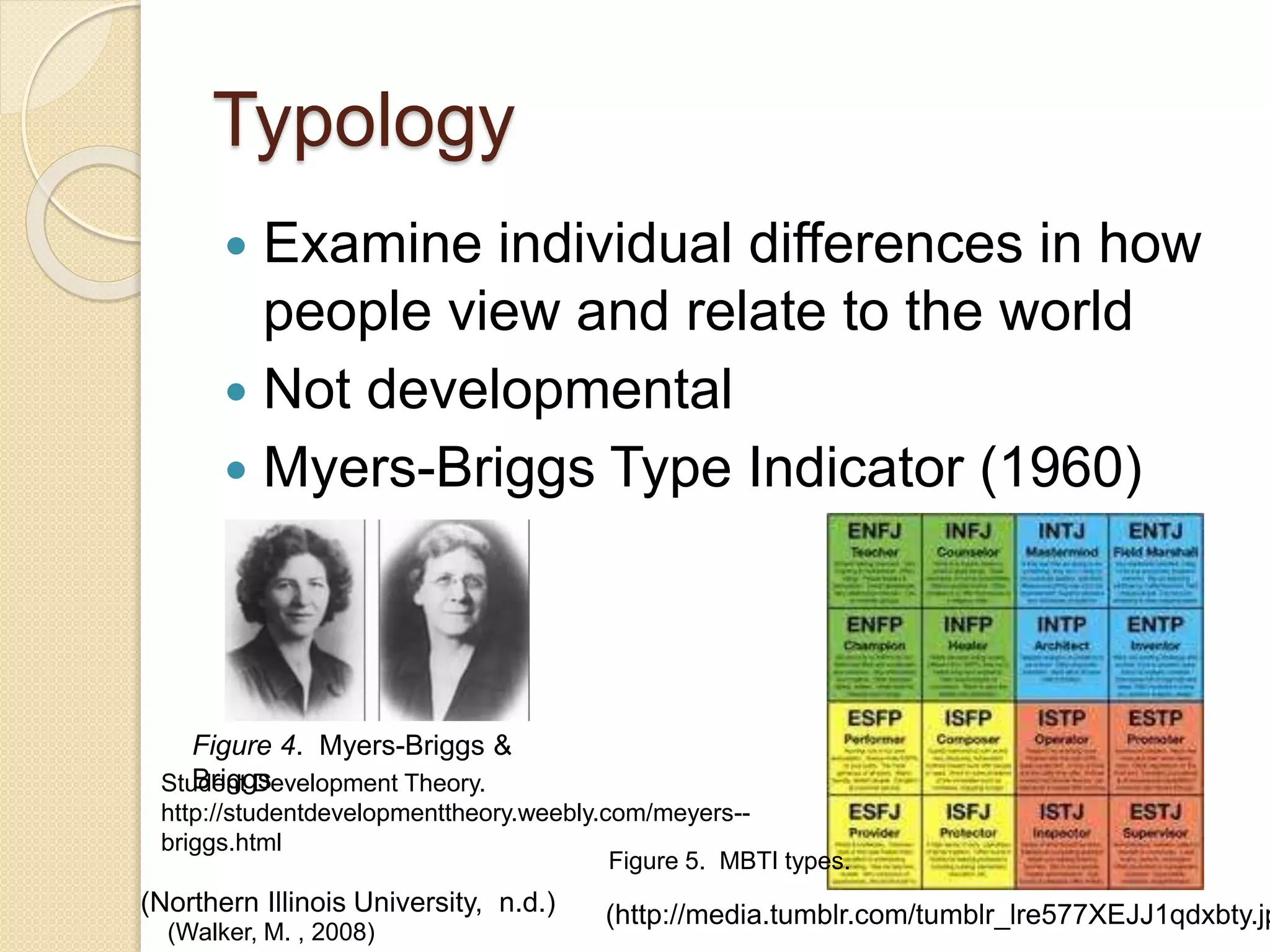
MBTI Types. (n.d.). MBTI Types [Digital Image]. Retrieved
from http://media.tumblr.com/tumblr_lre577XEJJ1qdxbty.jpg
Northern Illinois University. (n.d.). A Brief Introduction to
Student Development Theory. Retrieved from
http://www.niu.edu/engagedlearning/themed_learning/A%20B
rief%20Introduction%20to%20Student%20Development%20
Theory.pdf](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3714f6c1-ac4d-44c6-834b-62c3127c163c-160211055250/75/Fox_EDU644_Student-Development-Theory-12-2048.jpg)

