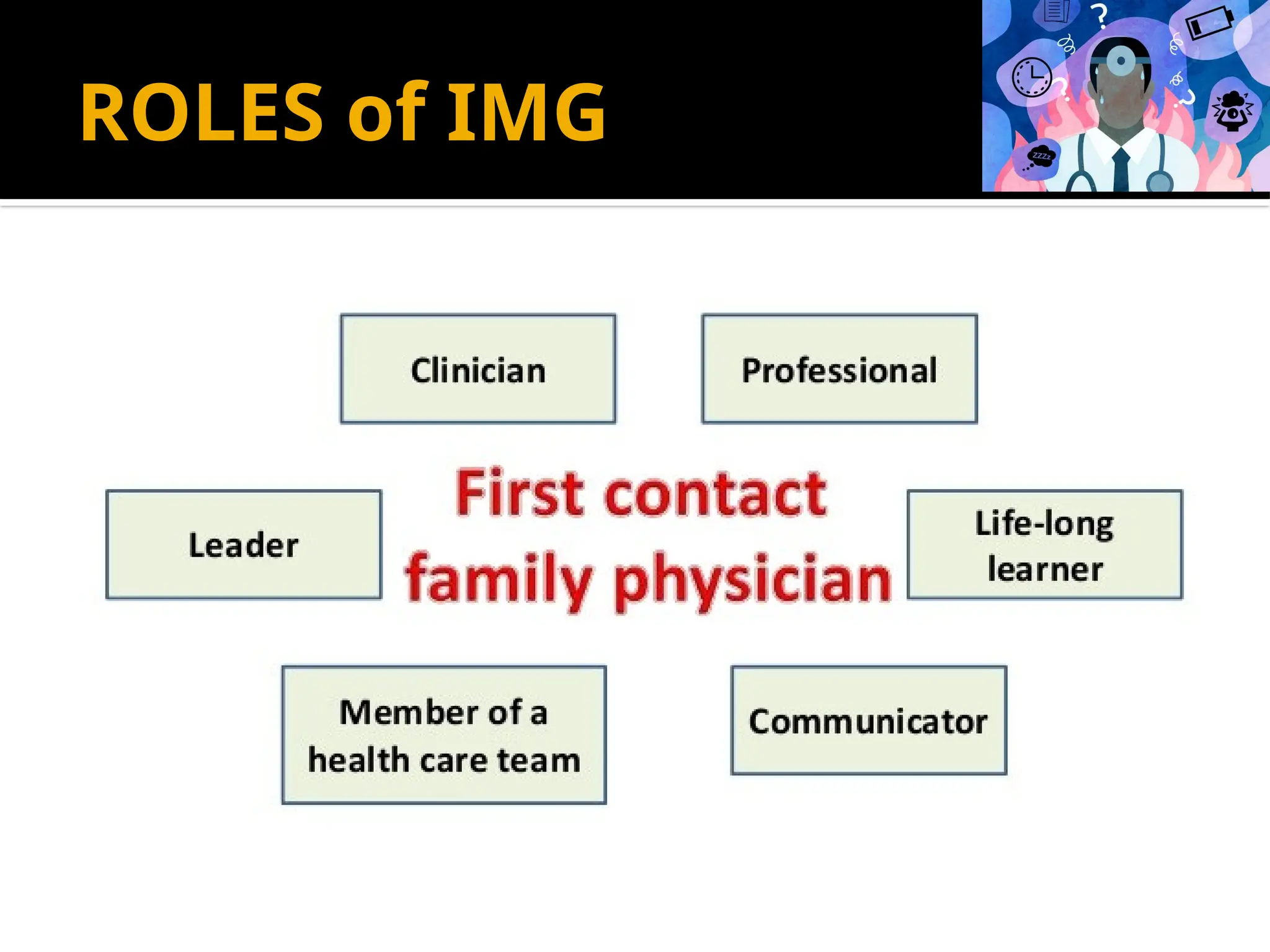
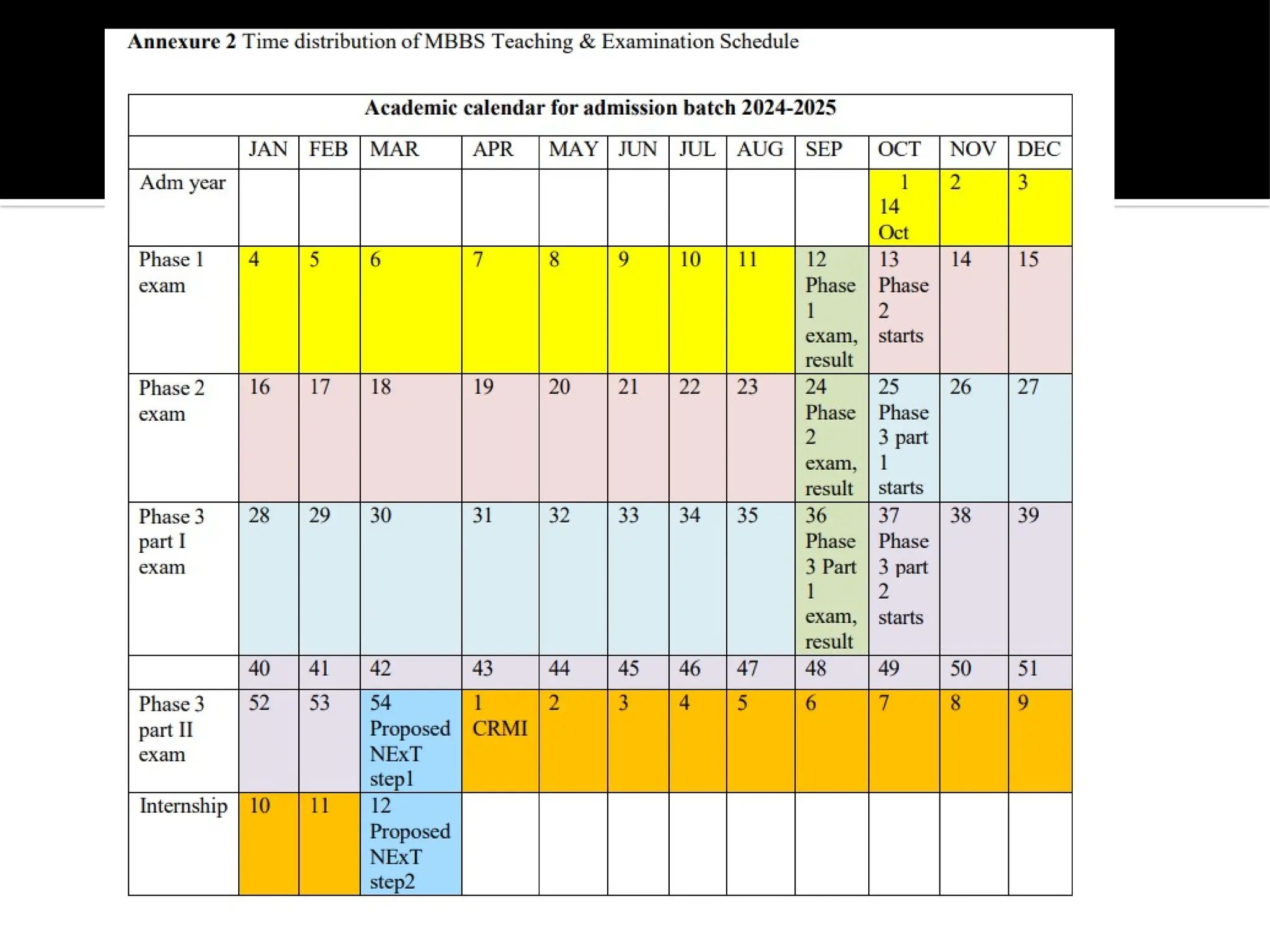
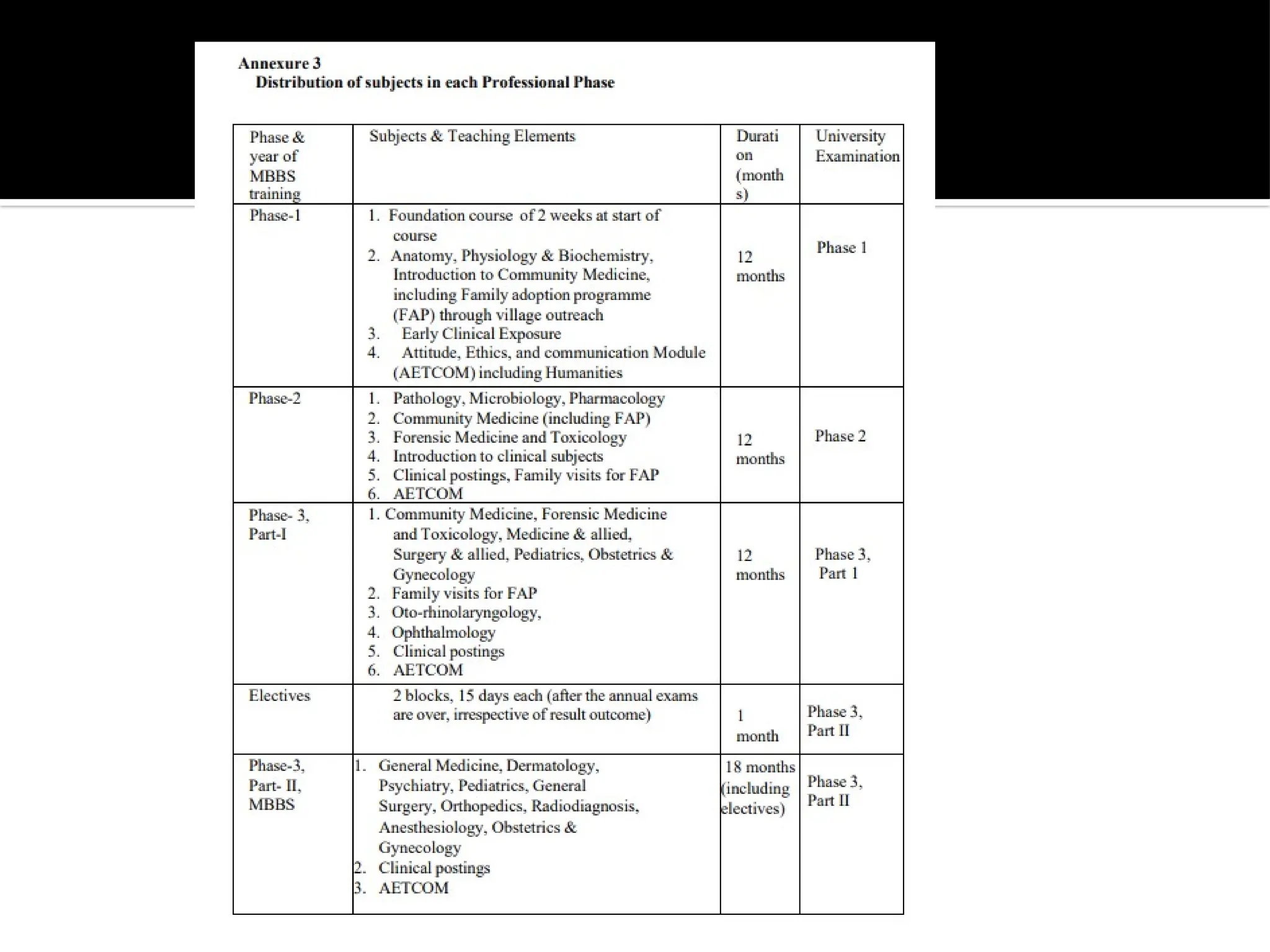
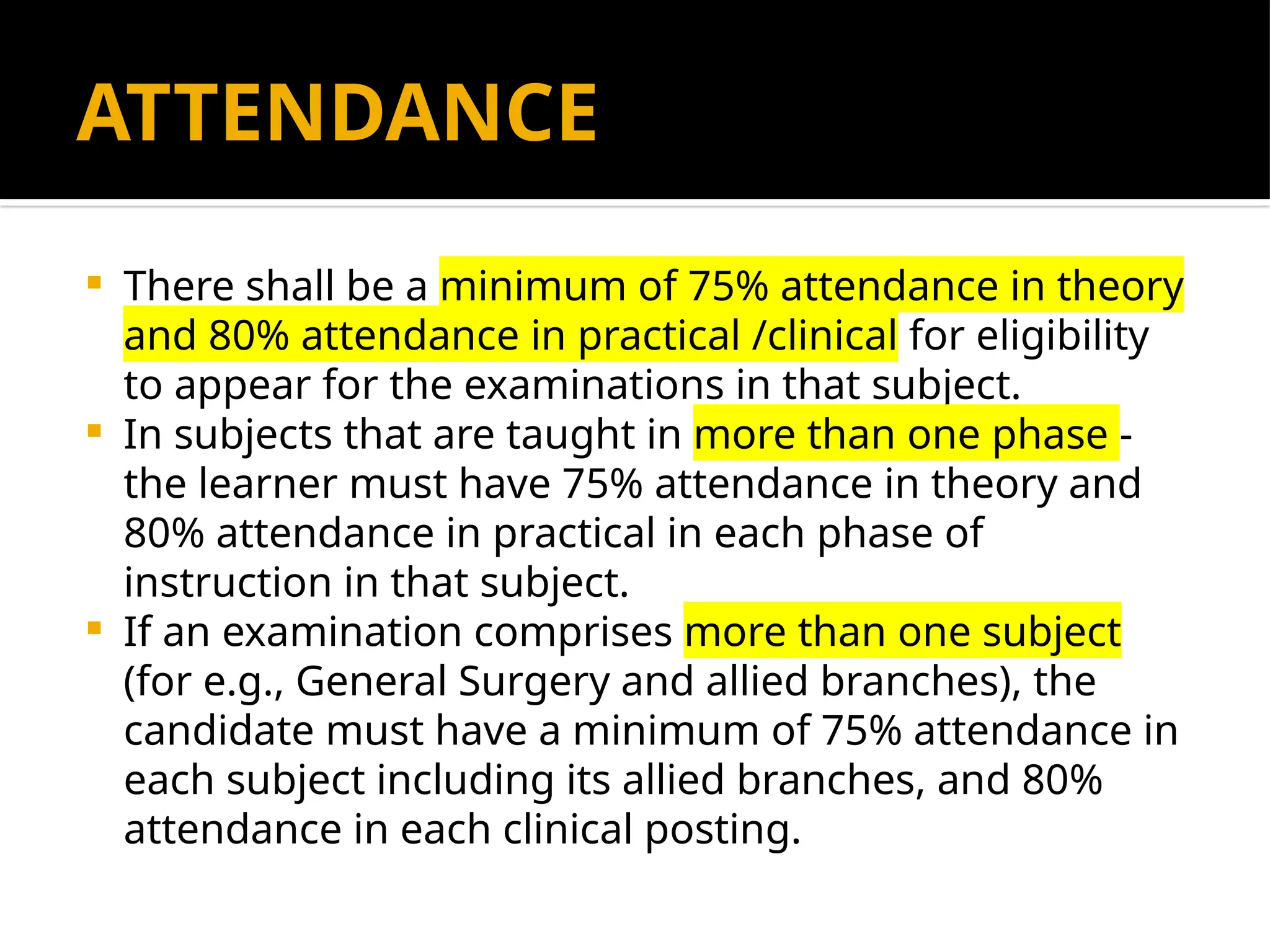
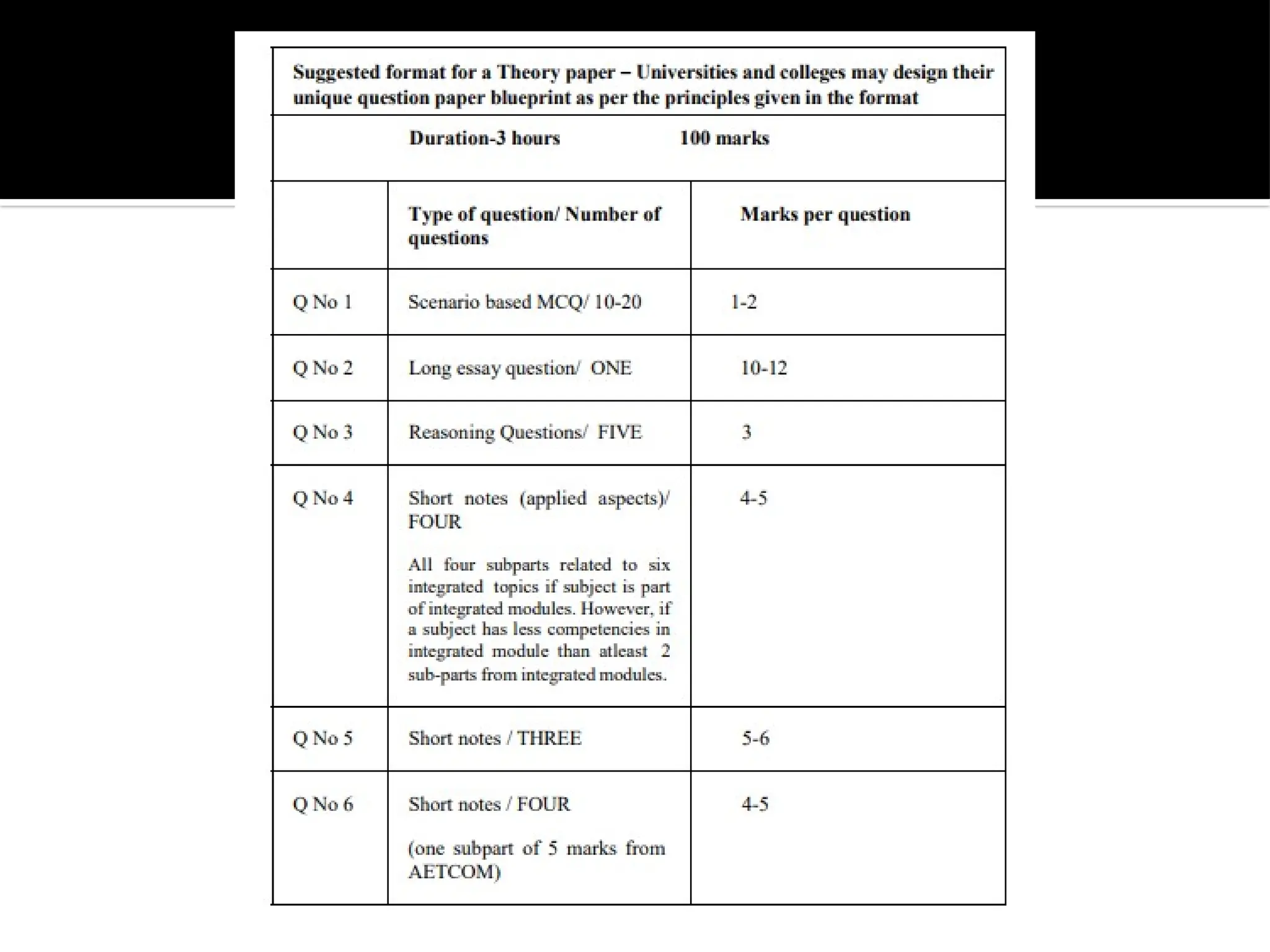
The document outlines the structure and requirements of the MBBS curriculum for Indian Medical Graduates (IMGs), detailing competencies, training phases, assessment criteria, and internship requirements. It emphasizes attendance, certifiable competencies, and the progression criteria necessary for graduation, including internal assessments and examinations. Additionally, the document mentions post-graduation opportunities across various specialties and the pathway for clinical practice after obtaining the degree.