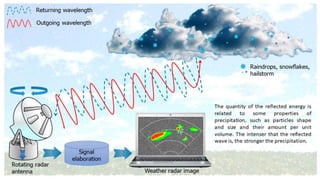
This document discusses forensic meteorology and how weather conditions can be analyzed and used as evidence in legal cases. It provides background on the history of meteorology and defines forensic meteorology as applying meteorological analysis to reconstruct past weather events. It then outlines different types of weather like sunshine, clouds, rain, snow, fog, thunder/lightning and wind. It also discusses how the National Weather Service forecasts weather and how temperature and rainfall can impact criminal activity levels. Finally it lists examples of types of legal cases where forensic meteorology could provide evidence like insurance claims, accidents, agriculture disputes and murders.