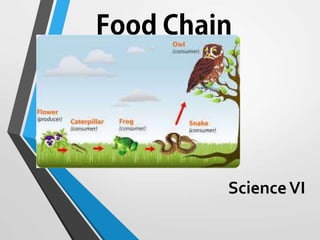
The document discusses food chains and food webs. It explains that a food chain involves producers, consumers, and decomposers. Producers such as plants make their own food through photosynthesis. Consumers, which are divided into herbivores, carnivores, and omnivores, obtain food by eating other organisms and cannot produce their own. Decomposers break down dead organisms and cycle nutrients. The document also describes food webs as interconnected food chains that more accurately represent feeding relationships in an ecosystem.