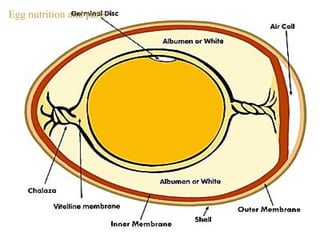
This document provides information about eggs and milk. It discusses egg nutrition, storage, and cooking methods. Key points about egg storage include storing them pointed end down in their original container away from heat and light. The document also discusses milk nutrition and dairy fat reduction techniques. It explains homogenization and pasteurization processes that are used for milk. Pasteurization involves heating milk to specific temperatures to destroy microorganisms. The recommended daily intake of milk is outlined.