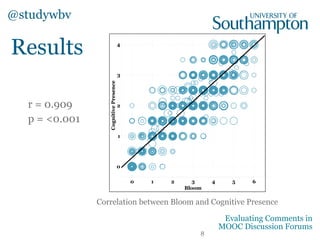
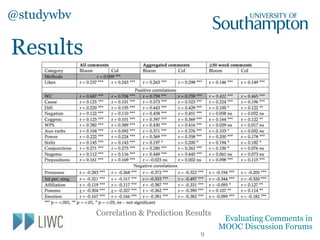
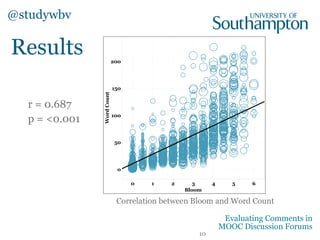
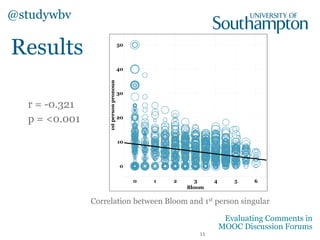
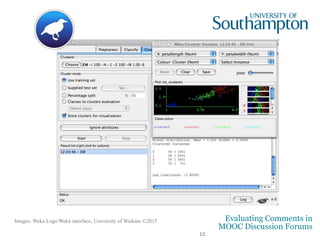
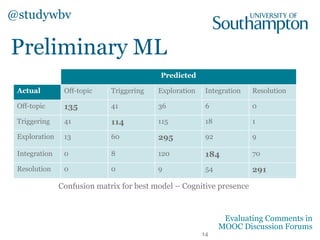
The document discusses a study evaluating comments in MOOCs using two frameworks: Bloom's Taxonomy and the Community of Inquiry model, analyzing 500 comments. It reveals significant correlations between levels of cognitive presence and learning outcomes, suggesting methods to categorize discourse in online learning. Preliminary machine learning approaches were employed to assess comment attributes, achieving moderate accuracy.