Embed presentation
Download to read offline

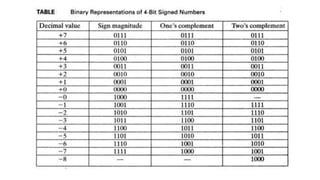
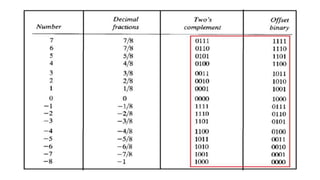






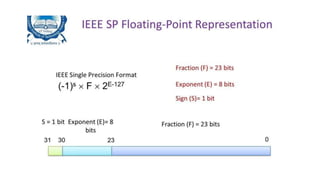
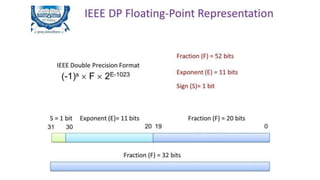

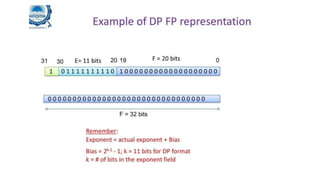

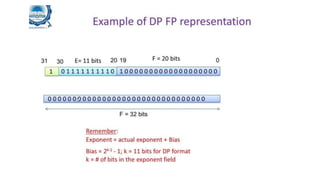







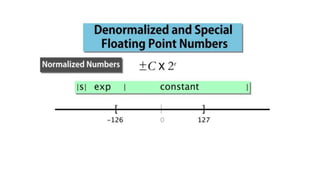
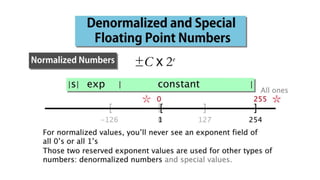
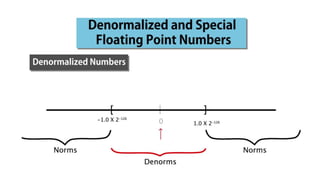
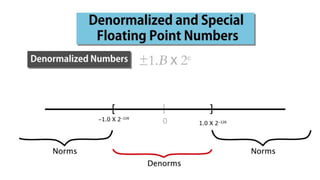
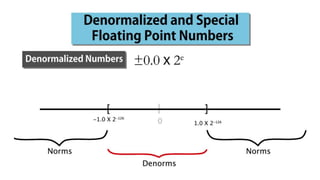
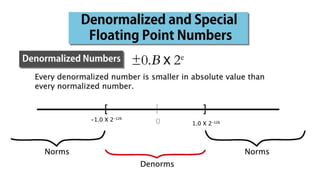
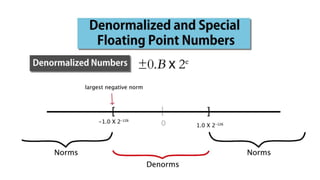
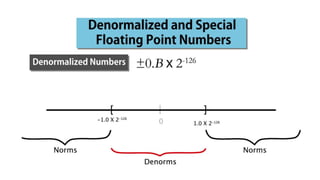
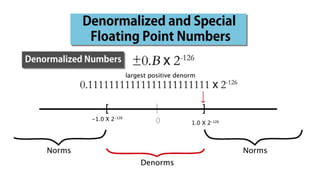
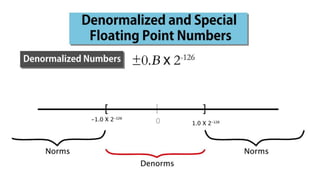

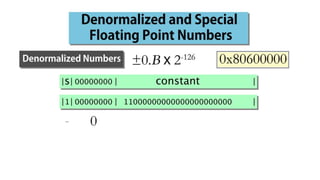
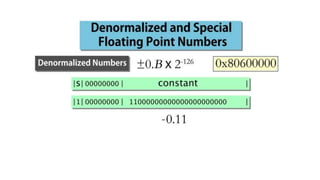
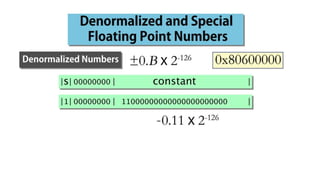
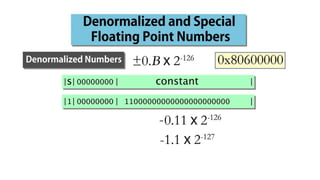








Fixed point representation uses a fixed number of bits to represent a number, with a fixed point separating the integer and fractional parts. Floating point representation uses a fixed number of bits to represent a number in three fields - sign, exponent, and significand (mantissa) - allowing a wider range of values to be represented but with less precision. Both fixed point and floating point representation are common ways for computers to represent real numbers.












































