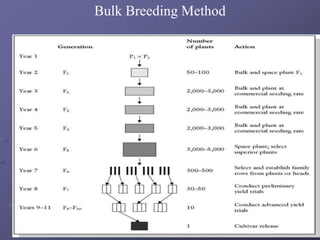
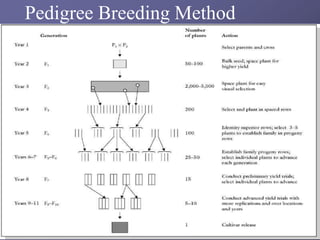
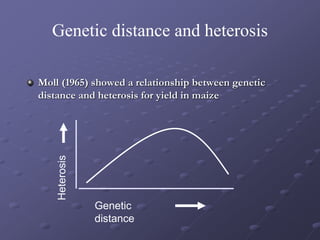
This document discusses different methods of fish breeding, including selective breeding, recombination breeding, and hybrid breeding. Selective breeding involves choosing individuals with desired traits to breed, and can result in reduced genetic variability over time. Recombination breeding combines traits from unrelated strains through techniques like crossbreeding and hybridization. Hybrid breeding aims to produce offspring that exhibit hybrid vigor or heterosis for increased performance. The genetic basis of heterosis includes dominance, overdominance, and epistasis effects between loci. Proper selection of parental lines and understanding of genetic processes is important for effective recombination and hybrid breeding in fish.