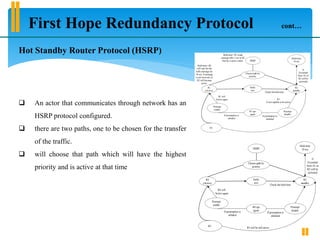
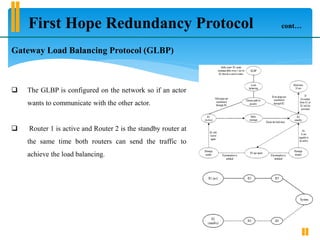
This document analyzes and compares first hop redundancy protocols (FHRPs) including HSRP, VRRP, and GLBP, focusing on their effectiveness in reducing packet loss and enhancing network availability. The study evaluates each protocol based on parameters such as packet size, CPU utilization, convergence duration, and bandwidth usage, concluding that GLBP outperforms both HSRP and VRRP. Recommendations for selecting the most suitable redundancy protocol based on network stability and load balancing are also provided.









![RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS
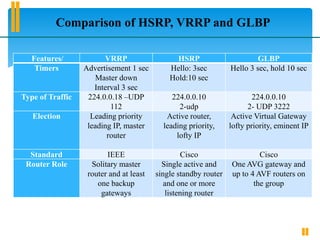
Protocols Packet
Size
CPU
utilization
(%)
Convergence
duration
[second]
Bandwidth
Utilization
[Kbps]
HSRP 100 0.69 8.056 0-1
VRRP 68 1.06 9.934 0-1
GLBP 108 0.54 7.344 0-1
Comparison of HSRP, VRRP and GLBP by using default values of hold
time, priority, preempt and ‘Hello’ time.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/usmanpresentation1-240622034512-f608cf57/85/first-hope-redundancy-protocol-in-networks-pptx-15-320.jpg)
![COMPARISION RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS
Protocols Packet
Size
CPU
utilization
(%)
Convergenc
e duration
[Sec.]
Bandwidth
Utilization
[Kbps]
HSRP 100 1.78 3.564 0-3
VRRP 68 2.15 7.935 0-3
GLBP 108 1.62 2.983 0-3
Test was performed by setting priority value 215, hold time to 6
seconds and rest to be the same.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/usmanpresentation1-240622034512-f608cf57/85/first-hope-redundancy-protocol-in-networks-pptx-16-320.jpg)