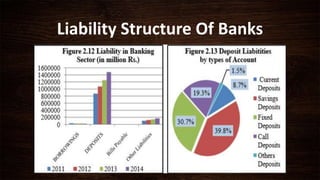
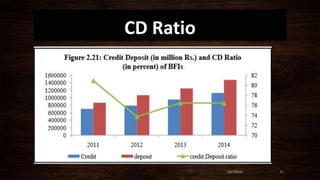
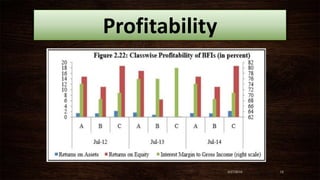
This document summarizes the Financial Stability Report for 2014 published by Nepal Rastra Bank. It discusses the macroeconomic environment and performance of the financial system in Nepal. The banking sector is well-capitalized and profitable. Non-performing loans remain low although they increased slightly. The central bank is taking measures to ensure financial stability in line with Basel III standards and has developed frameworks for problem bank resolution and liquidity monitoring. Overall, the financial system remains stable but continued consolidation in the banking sector is needed to improve stability, intermediation, and access to finance.