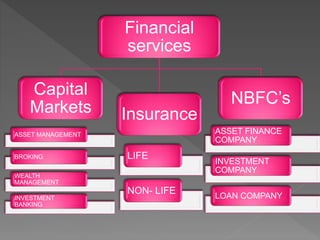
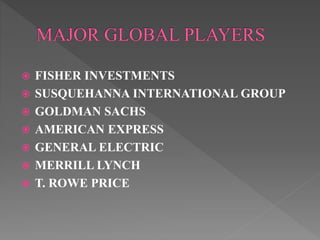
The document discusses the financial services sector in India, highlighting its various components such as banks, insurance companies, and non-banking financial companies (NBFCs), including their growth and challenges. It emphasizes the importance of financial inclusion, especially in rural areas, and the evolving regulatory environment for financial planning services. Additionally, it points out job creation in the sector, the rising demand from high-net-worth individuals, and the impact of technological advancements on widening access to financial services.