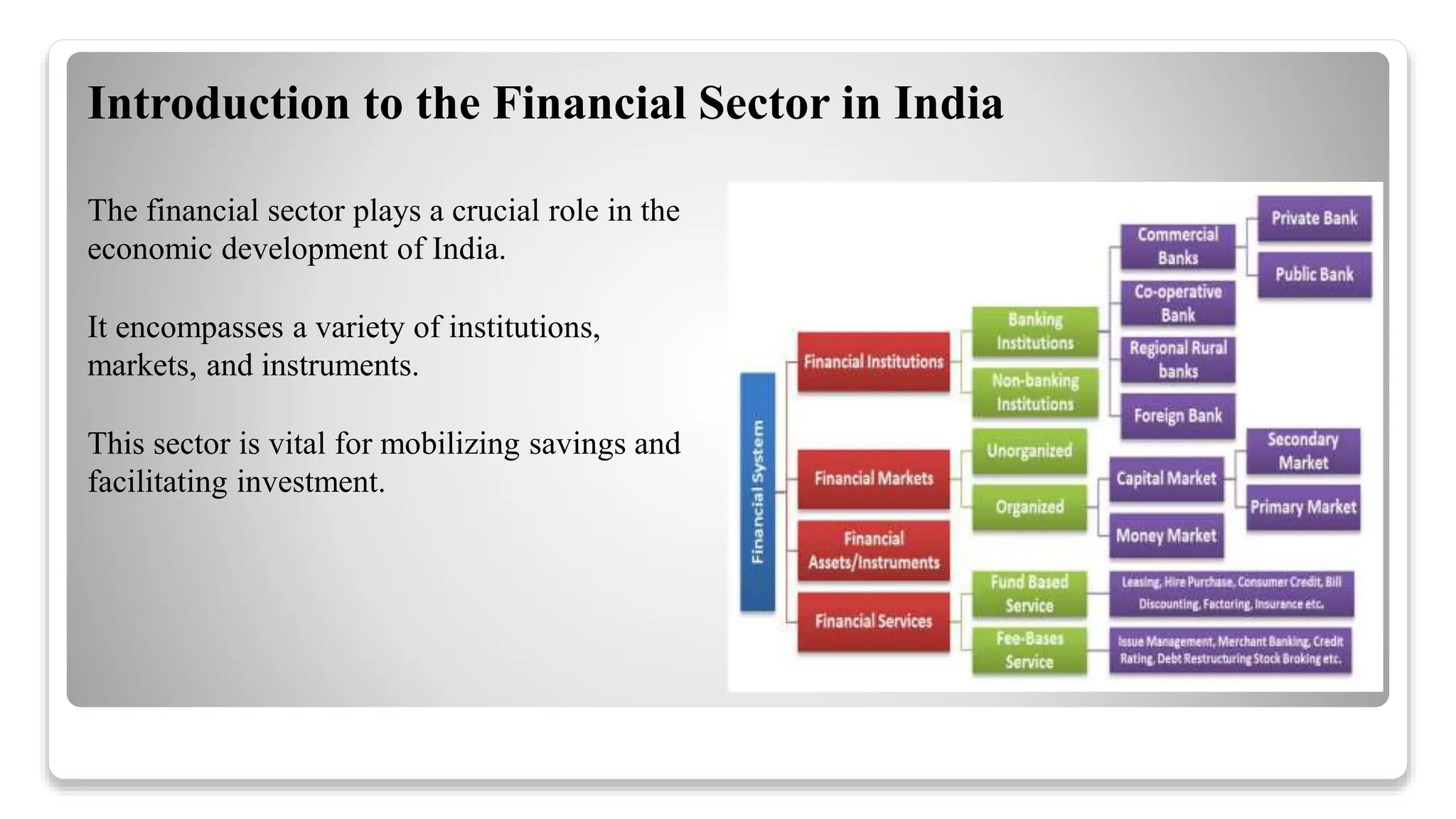
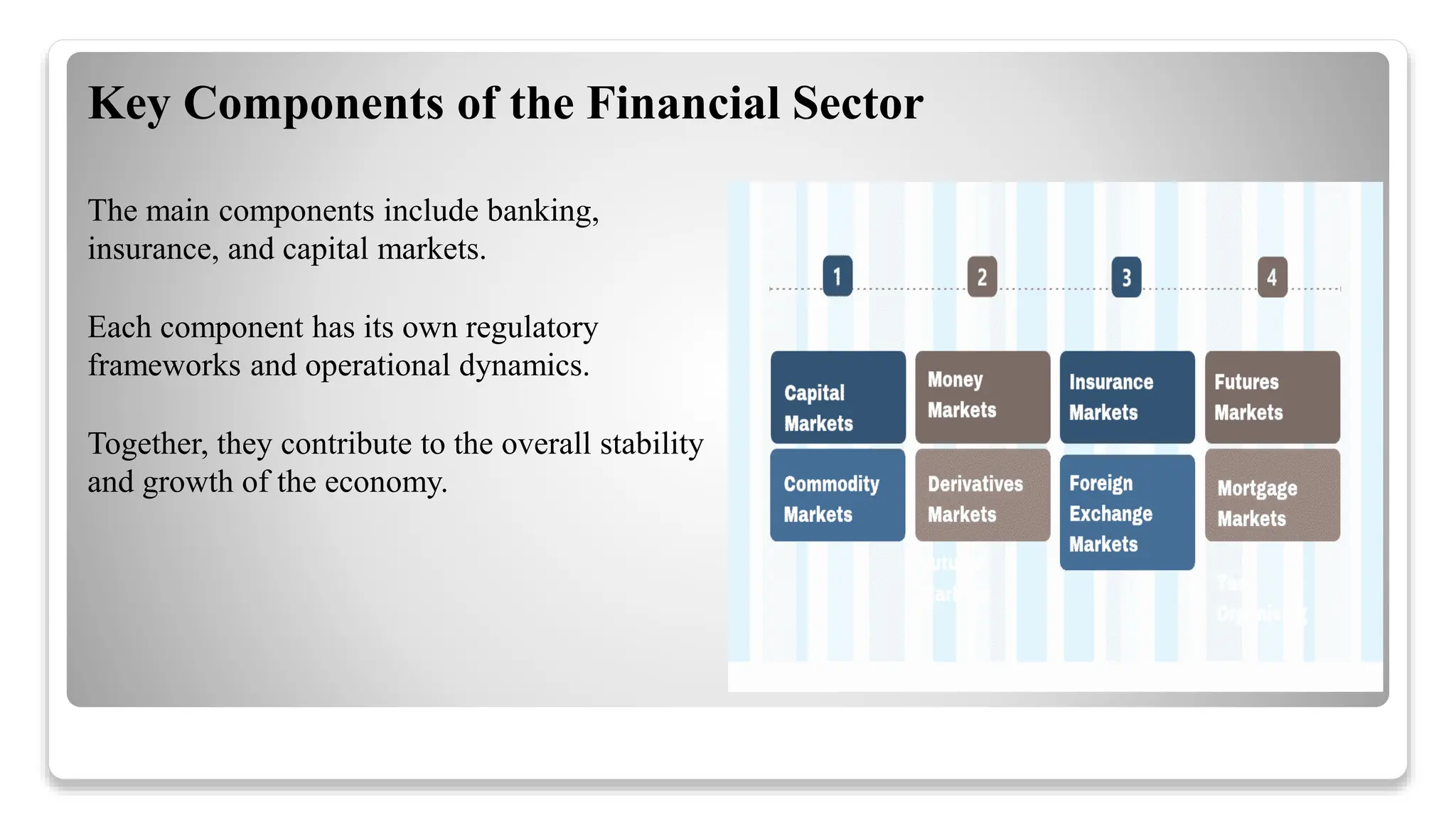
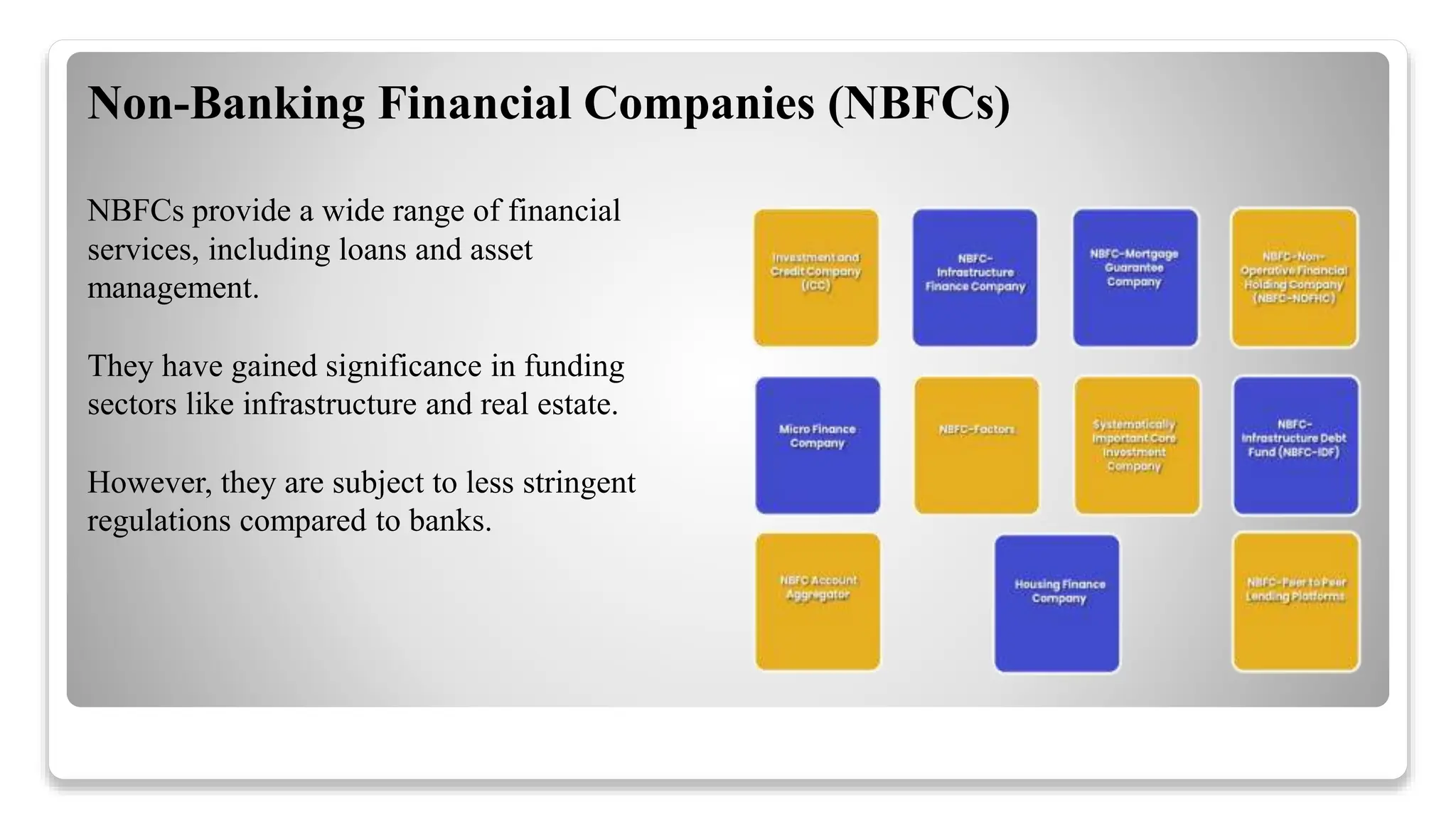
The financial sector in India is vital for economic development, comprising banking, insurance, and capital markets regulated by various authorities such as the RBI and SEBI. It plays a key role in mobilizing savings, facilitating investments, and enhancing financial inclusion, while facing challenges like non-performing assets and regulatory compliance. Future trends indicate a shift towards technology adoption, sustainable finance, and a focus on customer-centric services.