The document summarizes recent research on using machine learning to improve the accuracy of static code analysis tools in identifying actionable warnings. It discusses challenges with high false positive rates in static analysis tools and describes several studies that aimed to address this. The key points are:
1) Multiple studies have worked to reduce false positives by extracting features from code and using machine learning to classify warnings as actionable or not.
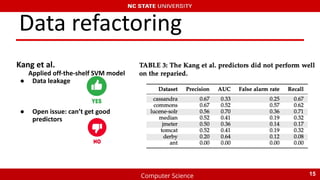
2) However, issues with data leakage across features and instances limited the effectiveness of early models.
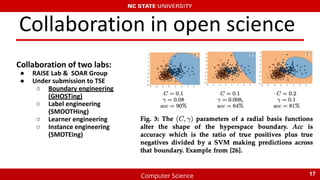
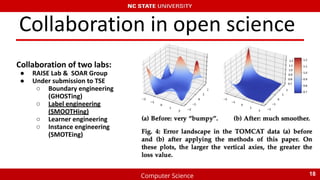
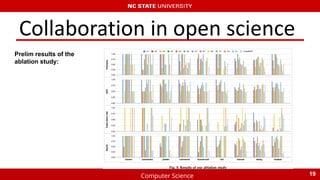
3) More recent collaboration between research groups applied techniques like boundary, label, learner, and instance engineering to refine the data and achieved preliminary improved results.
4) Open science and collaboration helped integrate findings



![Computer Science
Challenges
• High false positive rate
Why high false positive rate?
- SA tools are over-cautious
- 35% - 91% of warnings generated
can not be acted on [Heckman’
2011]
4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalicse22presentaionsherry-220421002339/85/final_ICSE-22-Presentaion_Sherry-pdf-4-320.jpg)


![Computer Science
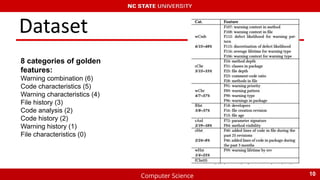
Dataset
- Label: actionable &
unactionable [Liang’ 2010]
- Version control system &
issue tracking system
8
Grand truth:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalicse22presentaionsherry-220421002339/85/final_ICSE-22-Presentaion_Sherry-pdf-8-320.jpg)
![Computer Science
Dataset
Feature extraction [Wang’
2018]:
- Slicing features from 9 SE
projects with a Java tool
- Feature name, category,
meaning, method
9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalicse22presentaionsherry-220421002339/85/final_ICSE-22-Presentaion_Sherry-pdf-9-320.jpg)





![Computer Science
Reference
[Kang’ 2022] Kang, Hong Jin, Khai Loong Aw, and David Lo. "Detecting False Alarms from Automatic Static Analysis Tools: How Far are
We?." arXiv preprint arXiv:2202.05982 (2022).
[Yang’ 2021] Yang, Xueqi, et al. "Learning to recognize actionable static code warnings (is intrinsically easy)." Empirical Software
Engineering 26.3 (2021): 1-24.
[Yang’ 2021] Yang, Xueqi, et al. "Understanding static code warnings: An incremental AI approach." Expert Systems with Applications
167 (2021): 114134.
[Wang’ 2018] Wang, Junjie, Song Wang, and Qing Wang. "Is there a" golden" feature set for static warning identification? an
experimental evaluation." Proceedings of the 12th ACM/IEEE international symposium on empirical software engineering and
measurement. 2018.
[Heckman’ 2011] Heckman, Sarah, and Laurie Williams. "A systematic literature review of actionable alert identification techniques for
automated static code analysis." Information and Software Technology 53.4 (2011): 363-387.
[Levina’ 2004] Levina, Elizaveta, and Peter Bickel. "Maximum likelihood estimation of intrinsic dimension." Advances in neural
information processing systems 17 (2004).
20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalicse22presentaionsherry-220421002339/85/final_ICSE-22-Presentaion_Sherry-pdf-20-320.jpg)
