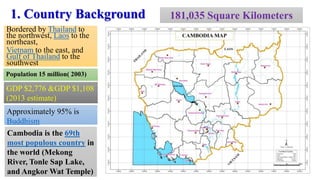
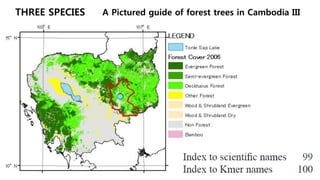
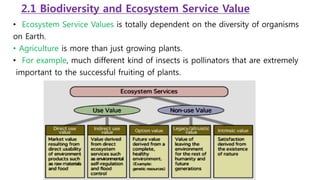
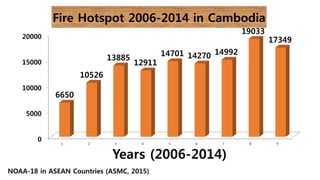
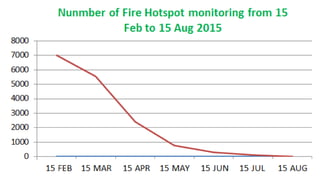
Cambodia has a high level of biodiversity but also faces significant threats to it from habitat loss and overexploitation. The country has over 1,600 species of plants and animals but deforestation is reducing habitats. Key conservation efforts include establishing protected areas as well as enforcing laws against illegal wildlife trafficking. However, continued monitoring and prevention of threats is still needed to fully preserve Cambodia's biodiversity for future generations.





















![Final cambodian biodiversity.pptx [autosaved]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalcambodianbiodiversity-151109035310-lva1-app6891/85/Final-cambodian-biodiversity-pptx-autosaved-33-320.jpg)